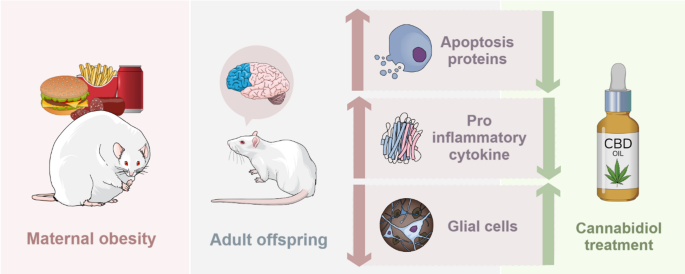
“Maternal obesity during pregnancy poses significant health risks for both mother and progeny, including long-term impacts on brain function. In previous studies, we demonstrated that cafeteria diet (CAF) consumption during gestation induces neuroinflammation and behavioral deficits in the offspring, which are reversed by cannabidiol (CBD) treatment. However, the effects of CBD on apoptosis-related pathways in this context remain unclear.
Here, we investigated whether CBD treatment can modulate pro-apoptotic signaling and glial cells morphology in adult offspring of obese mothers.
Wistar rats were fed a CAF for 12 weeks before mating, during pregnancy, and lactation. Offspring received oral CBD (50 mg/kg) for 3 weeks starting at postnatal day 70. In the prefrontal cortex, we assessed apoptosis-related proteins, TNFα gene expression, and astrocytes and microglia morphology.
Male and female offspring of CAF-fed dams showed increased levels of BAD, which were mitigated by CBD treatment. JNK was also elevated in female offspring of obese mothers, and CBD reduced this increase. In females, CBD treatment led to a decrease in AKT concentrations. TNFα expression was elevated in the prefrontal cortex of male offspring of obese mothers. Additionally, a reduction in GFAP- and IBA-1-positive cells in the prefrontal cortex was observed in male offspring of obese dams, which was reversed by CBD.
These findings suggest that maternal obesity promotes a pro-apoptotic and inflammatory brain environment, and CBD may counteract these effects via modulation of glial activity and apoptotic pathways.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40892197/
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11011-025-01687-7