“Chronic ethanol abuse can lead to harmful consequences for the heart, resulting in systolic dysfunction, variability in the heart rate, arrhythmia, and cardiac remodelling. However, the precise molecular mechanism responsible for ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy is poorly understood. In this regard, the present study aimed to describe the RIP1/RIP3/MLKL-mediated necroptotic cell death that may be involved in ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy and characterize CBR-mediated effects on the signalling pathway and myocardial injury.
“Chronic ethanol abuse can lead to harmful consequences for the heart, resulting in systolic dysfunction, variability in the heart rate, arrhythmia, and cardiac remodelling. However, the precise molecular mechanism responsible for ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy is poorly understood. In this regard, the present study aimed to describe the RIP1/RIP3/MLKL-mediated necroptotic cell death that may be involved in ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy and characterize CBR-mediated effects on the signalling pathway and myocardial injury.
We performed an ethanol vapour administration experiment to analyse the effects of ethanol on cardiac structure and function in male C57BL/6J mice. Ethanol induced a significant decline in the cardiac structure and function, as evidenced by a decline in ejection fraction and fractional shortening, and an increase in serum Creatine Kinase levels, myocardial collagen content, and inflammatory reaction. Furthermore, ethanol also upregulated the expression levels of necroptosis-related markers such as p-RIP1, p-RIP3, and p-MLKL in the myocardium. Nec-1 treatment exerted significant cardioprotective effects by salvaging the heart tissue, improving the cardiac function, and mitigating inflammation and necroptosis.
In addition, ethanol abuse caused an imbalance in the endocannabinoid system and regulated two cannabinoid receptors (CB1R and CB2R) in the myocardium. Treatment with selective CB2R agonists, JWH-133 or AM1241, markedly improved the cardiac dysfunction and reduced the ethanol-induced necroptosis in the myocardium.
Altogether, our data provide evidence that ethanol abuse-induced cardiotoxicity can possibly be attributed to the RIP1/RIP3/MLKL-mediated necroptosis. Moreover, pharmacological activation of CB2R may represent a new cardioprotective strategy against ethanol-induced cardiotoxicity.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32681290/
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11010-020-03828-1

 “In recent years, the role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in various cardiovascular conditions has been a subject of great interest. The ECS is composed of cannabinoid receptors, their endogenous ligands, also known as endocannabinoids, and enzymes responsible for the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids.
“In recent years, the role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in various cardiovascular conditions has been a subject of great interest. The ECS is composed of cannabinoid receptors, their endogenous ligands, also known as endocannabinoids, and enzymes responsible for the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids. “Attenuating emesis elicited by both disease and medical treatments of disease remains a critical
“Attenuating emesis elicited by both disease and medical treatments of disease remains a critical  ‘T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is a highly heterogeneous malignant hematological disorder arising from T-cell progenitors.
‘T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is a highly heterogeneous malignant hematological disorder arising from T-cell progenitors. “Growing evidence recognises cannabinoid receptors as potential therapeutic targets for pain. Consequently, there is increasing interest in developing cannabinoid receptor agonists for treating pain.
“Growing evidence recognises cannabinoid receptors as potential therapeutic targets for pain. Consequently, there is increasing interest in developing cannabinoid receptor agonists for treating pain. “Alzheimer’s Dementia (AD) is a devastating neurodegenerative disease that affects approximately 17% of people aged 75-84. Neuropsychiatric symptoms (NPS) such as delusions, agitation, anxiety, and hallucinations are present in up to 95% of patients in all stages of dementia. To date, any approved and effective pharmacological interventions for the treatment of NPS are still not available.
“Alzheimer’s Dementia (AD) is a devastating neurodegenerative disease that affects approximately 17% of people aged 75-84. Neuropsychiatric symptoms (NPS) such as delusions, agitation, anxiety, and hallucinations are present in up to 95% of patients in all stages of dementia. To date, any approved and effective pharmacological interventions for the treatment of NPS are still not available. “Background: Recent approved medicines whose active principles are Δ9Tetrahidrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and/or cannabidiol (CBD) open novel perspectives for other phytocannabinoids also present in Cannabis sativa L. varieties. Furthermore, solid data on the potential benefits of acidic and varinic phytocannabinoids in a variety of diseases are already available. Mode of action of cannabigerol (CBG), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), cannabidivarin (CBDV) and cannabigerivarin (CBGV) is, to the very least, partial.
“Background: Recent approved medicines whose active principles are Δ9Tetrahidrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and/or cannabidiol (CBD) open novel perspectives for other phytocannabinoids also present in Cannabis sativa L. varieties. Furthermore, solid data on the potential benefits of acidic and varinic phytocannabinoids in a variety of diseases are already available. Mode of action of cannabigerol (CBG), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), cannabidivarin (CBDV) and cannabigerivarin (CBGV) is, to the very least, partial.
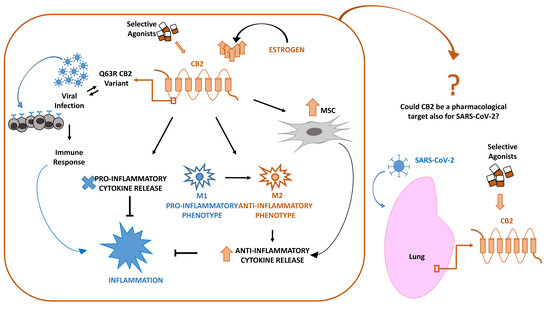
 “In late December 2019, a novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2 or CoV-19) appeared in Wuhan, China, causing a global pandemic. SARS-CoV-2 causes mild to severe respiratory tract inflammation, often developing into lung fibrosis with thrombosis in pulmonary small vessels and causing even death. COronaVIrus Disease (COVID-19) patients manifest exacerbated inflammatory and immune responses, cytokine storm, prevalence of pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages and increased levels of resident and circulating immune cells. Men show higher susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection than women, likely due to estrogens production. The protective role of estrogens, as well as an immune-suppressive activity that limits the excessive inflammation, can be mediated by cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2). The role of this receptor in modulating inflammation and immune response is well documented in fact in several settings. The stimulation of CB2 receptors is known to limit the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, shift the macrophage phenotype towards the anti-inflammatory M2 type and enhance the immune-modulating properties of mesenchymal stromal cells. For these reasons, we hypothesize that CB2 receptor can be a therapeutic
“In late December 2019, a novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2 or CoV-19) appeared in Wuhan, China, causing a global pandemic. SARS-CoV-2 causes mild to severe respiratory tract inflammation, often developing into lung fibrosis with thrombosis in pulmonary small vessels and causing even death. COronaVIrus Disease (COVID-19) patients manifest exacerbated inflammatory and immune responses, cytokine storm, prevalence of pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages and increased levels of resident and circulating immune cells. Men show higher susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection than women, likely due to estrogens production. The protective role of estrogens, as well as an immune-suppressive activity that limits the excessive inflammation, can be mediated by cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2). The role of this receptor in modulating inflammation and immune response is well documented in fact in several settings. The stimulation of CB2 receptors is known to limit the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, shift the macrophage phenotype towards the anti-inflammatory M2 type and enhance the immune-modulating properties of mesenchymal stromal cells. For these reasons, we hypothesize that CB2 receptor can be a therapeutic