“Cardiovascular complications are the major cause of mortality in diabetic patients. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying diabetes-associated arrhythmias are unclear.
“Cardiovascular complications are the major cause of mortality in diabetic patients. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying diabetes-associated arrhythmias are unclear.
We hypothesized that high glucose, could adversely affect Nav1.5, the major cardiac sodium channel isoform of the heart, at least partially via oxidative stress.
We further hypothesized that cannabidiol (CBD), one of the main constituents of Cannabis sativa, through its effects on Nav1.5, could protect against high glucose elicited oxidative stress and cytotoxicity.
KEY RESULTS:
High glucose evoked cell death associated with elevation in reactive oxygen species, right shifted the voltage dependence of conductance and steady state fast inactivation and increased persistent current leading to computational prolongation of action potential (hyperexcitability) which could result in long QT3 arrhythmia. CBD mitigated all the deleterious effects provoked by high glucose. Perfusion with Lidocaine (a well-known sodium channels inhibitor with anti-oxidant effects), or co-incubation of Tempol (a well-known anti-oxidant) elicited protection, comparable to CBD, against the deleterious effects of high glucose.
CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS:
These findings suggest that, through its favourable anti-oxidant and sodium channel inhibitory effects, CBD may protect against high-glucose induced arrhythmia and cytotoxicity.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32077098
https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/bph.15020

 “The most recent studies published or initiated in the last 18 months, investigating cannabidiol in the treatment of symptoms of schizophrenia and related conditions are summarized, including observed tolerability and reported side-effects.
“The most recent studies published or initiated in the last 18 months, investigating cannabidiol in the treatment of symptoms of schizophrenia and related conditions are summarized, including observed tolerability and reported side-effects. “To determine whether differences in disability status, spasticity severity, and spasticity duration at treatment start in patients with resistant multiple sclerosis (MS) spasticity might influence response to add-on tetrahydrocannabinol:
“To determine whether differences in disability status, spasticity severity, and spasticity duration at treatment start in patients with resistant multiple sclerosis (MS) spasticity might influence response to add-on tetrahydrocannabinol: “The cellular microenvironment plays a critical role in the maintenance of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) and their subsequent cell lineage differentiation. Recent studies suggested that individuals with adipocyte-related metabolic disorders have altered function and adipogenic potential of adipose stem cell subpopulations, primarily BM-MSCs, increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke or diabetes.
“The cellular microenvironment plays a critical role in the maintenance of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) and their subsequent cell lineage differentiation. Recent studies suggested that individuals with adipocyte-related metabolic disorders have altered function and adipogenic potential of adipose stem cell subpopulations, primarily BM-MSCs, increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke or diabetes.

 “Radiotherapy combined with chemotherapy is the major treatment modality for human glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). GBMs eventually relapse after treatment and the average survival of GBM patients is less than two years.
“Radiotherapy combined with chemotherapy is the major treatment modality for human glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). GBMs eventually relapse after treatment and the average survival of GBM patients is less than two years. “Highly purified
“Highly purified  “In this report, we present a case of a 16,9-year-old patient with multiple substance use disorder (
“In this report, we present a case of a 16,9-year-old patient with multiple substance use disorder ( “Patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) develop resistance to antitumor agents by mechanisms that involve the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This necessitates the development of new complementary drugs, e.g.,
“Patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) develop resistance to antitumor agents by mechanisms that involve the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This necessitates the development of new complementary drugs, e.g.,  “Plant phytochemicals have potential decontaminating properties, however, their role in the amelioration of hydrophobic water filtration membranes have not been elucidated yet.
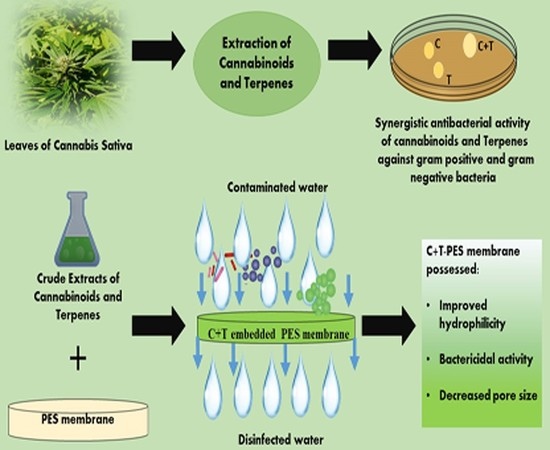
“Plant phytochemicals have potential decontaminating properties, however, their role in the amelioration of hydrophobic water filtration membranes have not been elucidated yet.