“The global incidence of respiratory diseases and complications is increasing. Therefore, new methods of treatment, as well as prevention, need to be investigated.
“The global incidence of respiratory diseases and complications is increasing. Therefore, new methods of treatment, as well as prevention, need to be investigated.
A group of compounds that should be considered for use in respiratory diseases is cannabinoids. There are three groups of cannabinoids – plant-derived phytocannabinoids, synthetic cannabinoids, and endogenous endocannabinoids including the enzymes responsible for their synthesis and degradation.
All cannabinoids exert their biological effects through either type 1 cannabinoid receptors (CB1) and/or type 2 cannabinoid receptors (CB2). In numerous studies (in vitro and in vivo), cannabinoids and inhibitors of endocannabinoid degradation have shown beneficial anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-cancer, and anti-fibrotic properties.
Although in the respiratory system, most of the studies have focused on the positive properties of cannabinoids and inhibitors of endocannabinoid degradation. There are few research reports discussing the negative impact of these compounds. This review summarizes the properties and mechanisms of action of cannabinoids and inhibitors of endocannabinoid degradation in various models of respiratory diseases.
A short description of the effects selected cannabinoids have on the human respiratory system and their possible use in the fight against COVID-19 is also presented. Additionally, a brief summary is provided of cannabinoid receptors properties and their expression in the respiratory system and cells of the immune system.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34648805/
“Phytocannabinoids are terpenophenolic compounds produced by specialized parts of the Cannabis sativa plant and are found in high concentrations in marijuana and hashish. In most of models, these compounds have shown positive biological properties. Anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-cancer and anti-fibrotic actions are especially emphasized.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0014299921007160?via%3Dihub

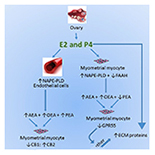
 “In humans, various sites like cannabinoid receptors (CBR) having a binding affinity with cannabinoids are distributed on the surface of different cell types, where endocannabinoids (ECs) and derivatives of fatty acid can bind. The binding of these substance(s) triggers the activation of specific receptors required for various physiological functions, including pain sensation, memory, and appetite.
“In humans, various sites like cannabinoid receptors (CBR) having a binding affinity with cannabinoids are distributed on the surface of different cell types, where endocannabinoids (ECs) and derivatives of fatty acid can bind. The binding of these substance(s) triggers the activation of specific receptors required for various physiological functions, including pain sensation, memory, and appetite. 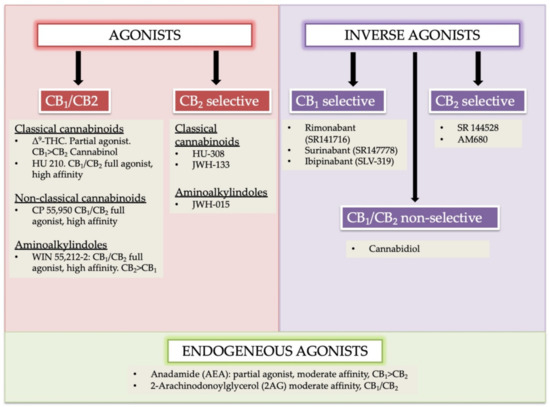
 “This article provides a concise overview of how cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system (ECS) have significant implications for the prevention and treatment of metabolic syndrome (MetS) and for the treatment of cardiovascular disorders, including cardiac fibrosis.
“This article provides a concise overview of how cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system (ECS) have significant implications for the prevention and treatment of metabolic syndrome (MetS) and for the treatment of cardiovascular disorders, including cardiac fibrosis. “Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a life-threatening complication of end-stage liver disease characterized by the rapid decline of kidney function. Herein, we explored the therapeutic potential of targeting the
“Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a life-threatening complication of end-stage liver disease characterized by the rapid decline of kidney function. Herein, we explored the therapeutic potential of targeting the 
 “Hepatic fibrosis is the consequence of an unresolved wound healing process in response to chronic liver injury and involves multiple cell types and molecular mechanisms. The hepatic endocannabinoid and apelin systems are two signalling pathways with a substantial role in the liver fibrosis pathophysiology-both are upregulated in patients with advanced liver disease. Endogenous
“Hepatic fibrosis is the consequence of an unresolved wound healing process in response to chronic liver injury and involves multiple cell types and molecular mechanisms. The hepatic endocannabinoid and apelin systems are two signalling pathways with a substantial role in the liver fibrosis pathophysiology-both are upregulated in patients with advanced liver disease. Endogenous 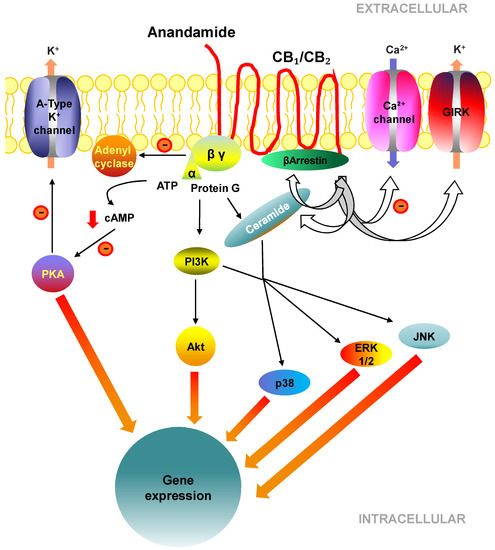
 “Chronic allograft dysfunction (CAD), defined as the replacement of functional renal tissue by extracellular matrix proteins, remains the first cause of graft loss.
“Chronic allograft dysfunction (CAD), defined as the replacement of functional renal tissue by extracellular matrix proteins, remains the first cause of graft loss. “Formation of schistosomal granulomata surrounding the ova can result in schistosomiasis-associated liver fibrosis (SSLF). The current standard of treatment is praziquantel (PZQ), which cannot effectively reverse SSLF.
“Formation of schistosomal granulomata surrounding the ova can result in schistosomiasis-associated liver fibrosis (SSLF). The current standard of treatment is praziquantel (PZQ), which cannot effectively reverse SSLF. “The
“The