 “The level of the major endocannabinoids anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) are altered in several types of carcinomas, and are known to regulate tumor growth. Thusly, this study hypothesized that the HEp-2 human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) cell line releases AEA and 2-AG, and aimed to determine if their exogenous supplementation has an anti-proliferative effect in vitro.
“The level of the major endocannabinoids anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) are altered in several types of carcinomas, and are known to regulate tumor growth. Thusly, this study hypothesized that the HEp-2 human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) cell line releases AEA and 2-AG, and aimed to determine if their exogenous supplementation has an anti-proliferative effect in vitro.
In this in vitro observational study a commercial human LSCC cell line (HEp-2) was used to test for endogenous AEA and 2-AG release via liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). The anti-proliferative effect of AEA and 2-AG supplementation was evaluated via WST-1 proliferation assay. It was observed that the HEp-2 LSCC cell line released AEA and 2-AG; the median quantity of AEA released was 15.69 ng mL-1 (range: 14.55-15.95 ng mL-1) and the median quantity of 2-AG released was 2.72 ng -1 (range: 2.67-2.74 ng mL-1). Additionally, both AEA and 2-AG exhibited an anti-proliferative effect. The anti-proliferative effect of 2-AG was stronger than that of AEA. These findings suggest that AEA might function via a CB1 receptor-independent pathway and that 2-AG might function via a CB2-dependent pathway.
The present findings show that the HEp-2 LSCC cell line releases the major endocannabinoids AEA and 2-AG, and that their supplementation inhibits tumor cell proliferation in vitro. Thus, cannabinoid ligands might represent novel drug candidates for laryngeal cancers, although functional in vivo studies are required in order to validate their potency.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33797678/
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10561-021-09917-9

 “Cannabis sativa
“Cannabis sativa “Autophagy is a “self-degradation” process whereby malfunctioned cytoplasmic constituents and protein aggregates are engulfed by a vesicle called the autophagosome, and subsequently degraded by the lysosome. Autophagy plays a crucial role in sustaining protein homeostasis and can be an alternative source of energy under detrimental circumstances. Studies have demonstrated a paradoxical function for autophagy in cancer, displaying both tumour suppressive and tumour promotive roles. In early phases of tumour development autophagy promotes cancer cell death. In later phases, autophagy enables cancer cells to survive and withstand therapy.
“Autophagy is a “self-degradation” process whereby malfunctioned cytoplasmic constituents and protein aggregates are engulfed by a vesicle called the autophagosome, and subsequently degraded by the lysosome. Autophagy plays a crucial role in sustaining protein homeostasis and can be an alternative source of energy under detrimental circumstances. Studies have demonstrated a paradoxical function for autophagy in cancer, displaying both tumour suppressive and tumour promotive roles. In early phases of tumour development autophagy promotes cancer cell death. In later phases, autophagy enables cancer cells to survive and withstand therapy. 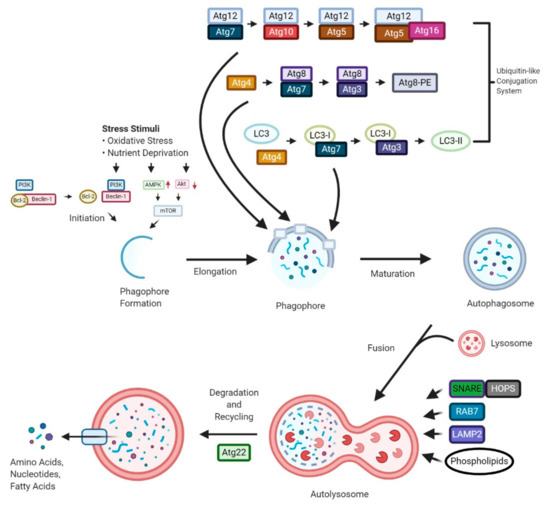

 “Purpose: Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is the fourth most frequent cancer diagnosis among pregnant females. A multidisciplinary team is mandatory to obtain the best treatment and prognosis for the mother and for the baby. Here, we present the case of a patient diagnosed with HL and its evolution during 2 pregnancies.
“Purpose: Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is the fourth most frequent cancer diagnosis among pregnant females. A multidisciplinary team is mandatory to obtain the best treatment and prognosis for the mother and for the baby. Here, we present the case of a patient diagnosed with HL and its evolution during 2 pregnancies. “Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death in women worldwide. In the last years, cannabinoids have gained attention in the clinical setting and clinical trials with cannabinoid-based preparations are underway. However, contradictory anti-tumour properties have also been reported. Thus, the elucidation of the molecular mechanisms behind their anti-tumour efficacy is crucial to better understand its therapeutic potential.
“Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death in women worldwide. In the last years, cannabinoids have gained attention in the clinical setting and clinical trials with cannabinoid-based preparations are underway. However, contradictory anti-tumour properties have also been reported. Thus, the elucidation of the molecular mechanisms behind their anti-tumour efficacy is crucial to better understand its therapeutic potential. “Cannabis was extensively utilized for its medicinal properties till the 19th century. A steep decline in its medicinal usage was observed later due to its emergence as an illegal recreational drug. Advances in technology and scientific findings led to the discovery of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound of cannabis, that further led to the discovery of endogenous cannabinoids system consisting of G-protein-coupled receptors – cannabinoid receptor 1 and cannabinoid receptor 2 along with their ligands, mainly anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Endocannabinoid (EC) is shown to be a modulator not only for physiological functions but also for the immune system, endocrine network, and central nervous system. Medicinal research and meta-data analysis over the last few decades have shown a significant potential for both THC and cannabidiol (CBD) to exert palliative effects. People suffering from many forms of advanced stages of cancers undergo chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting followed by severe and chronic neuropathic pain and weight loss. THC and CBD exhibit effective analgesic, anxiolytic, and appetite-stimulating effect on patients suffering from cancer. Drugs currently available in the market to treat such chemotherapy-induced cancer-related ailments are Sativex (GW Pharmaceutical), Dronabinol (Unimed Pharmaceuticals), and Nabilone (Valeant Pharmaceuticals). Apart from exerting palliative effects, THC also shows promising role in the treatment of cancer growth, neurodegenerative diseases (multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease), and alcohol addiction and hence should be exploited for potential benefits. The current review discusses the nature and role of CB receptors, specific applications of cannabinoids, and major studies that have assessed the role of cannabinoids in cancer management.”
“Cannabis was extensively utilized for its medicinal properties till the 19th century. A steep decline in its medicinal usage was observed later due to its emergence as an illegal recreational drug. Advances in technology and scientific findings led to the discovery of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound of cannabis, that further led to the discovery of endogenous cannabinoids system consisting of G-protein-coupled receptors – cannabinoid receptor 1 and cannabinoid receptor 2 along with their ligands, mainly anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Endocannabinoid (EC) is shown to be a modulator not only for physiological functions but also for the immune system, endocrine network, and central nervous system. Medicinal research and meta-data analysis over the last few decades have shown a significant potential for both THC and cannabidiol (CBD) to exert palliative effects. People suffering from many forms of advanced stages of cancers undergo chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting followed by severe and chronic neuropathic pain and weight loss. THC and CBD exhibit effective analgesic, anxiolytic, and appetite-stimulating effect on patients suffering from cancer. Drugs currently available in the market to treat such chemotherapy-induced cancer-related ailments are Sativex (GW Pharmaceutical), Dronabinol (Unimed Pharmaceuticals), and Nabilone (Valeant Pharmaceuticals). Apart from exerting palliative effects, THC also shows promising role in the treatment of cancer growth, neurodegenerative diseases (multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease), and alcohol addiction and hence should be exploited for potential benefits. The current review discusses the nature and role of CB receptors, specific applications of cannabinoids, and major studies that have assessed the role of cannabinoids in cancer management.” “Cannabidiol (CBD) has been shown to slow cancer cell growth and is toxic to human glioblastoma cell lines. Thus, CBD could be an effective therapeutic for glioblastoma.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) has been shown to slow cancer cell growth and is toxic to human glioblastoma cell lines. Thus, CBD could be an effective therapeutic for glioblastoma.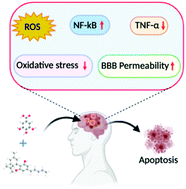
 “Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is an imbalance between the ER’s protein-folding load and capacity. It can be induced by various physiological conditions, activating the unfolded protein response to re-establish homeostasis, promoting cell survival. Under severe or chronic stress, apoptosis is induced. Normal cells generally do not experience continuous ER stress induction. The stressful conditions experienced in the tumour microenvironment facilitates chronic ER stress and UPR activation, which plays a pivotal role in tumour survival.
“Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is an imbalance between the ER’s protein-folding load and capacity. It can be induced by various physiological conditions, activating the unfolded protein response to re-establish homeostasis, promoting cell survival. Under severe or chronic stress, apoptosis is induced. Normal cells generally do not experience continuous ER stress induction. The stressful conditions experienced in the tumour microenvironment facilitates chronic ER stress and UPR activation, which plays a pivotal role in tumour survival.