 “This article provides a concise overview of how cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system (ECS) have significant implications for the prevention and treatment of metabolic syndrome (MetS) and for the treatment of cardiovascular disorders, including cardiac fibrosis.
“This article provides a concise overview of how cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system (ECS) have significant implications for the prevention and treatment of metabolic syndrome (MetS) and for the treatment of cardiovascular disorders, including cardiac fibrosis.
Recent findings: Over the past few years, the ECS has emerged as a pivotal component of the homeostatic mechanisms for the regulation of many bodily functions, including inflammation, digestion, and energy metabolism. Therefore, the pharmacological modulation of the ECS by cannabinoids represents a novel strategy for the management of many diseases. Specifically, increasing evidence from preclinical research studies has opened new avenues for the development of cannabinoid-based therapies for the management and potential treatment of MetS and cardiovascular diseases. Current information indicates that modulation of the ECS can help maintain overall health and well-being due to its homeostatic function. From a therapeutic perspective, cannabinoids and the ECS have also been shown to play a key role in modulating pathophysiological states such as inflammatory, neurodegenerative, gastrointestinal, metabolic, and cardiovascular diseases, as well as cancer and pain. Thus, targeting and modulating the ECS with cannabinoids or cannabinoid derivatives may represent a major disease-modifying medical advancement to achieve successful treatment for MetS and certain cardiovascular diseases.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33089434/
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11906-020-01112-7

 “Cannabidiol (CBD) is known for its vasorelaxant (including in the human pulmonary artery), anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory properties. The aim of our study was to examine the potential preventive effect of chronic CBD administration (10 mg/kg/day for three weeks) on monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary hypertension (PH) rats.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is known for its vasorelaxant (including in the human pulmonary artery), anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory properties. The aim of our study was to examine the potential preventive effect of chronic CBD administration (10 mg/kg/day for three weeks) on monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary hypertension (PH) rats.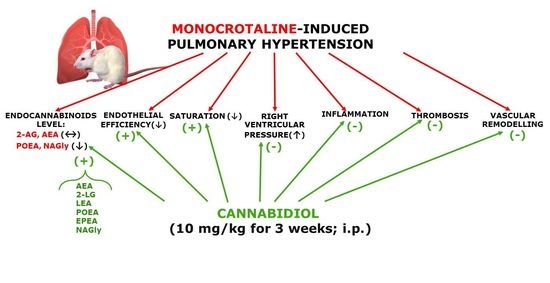
 “Chronic ethanol abuse can lead to harmful consequences for the heart, resulting in systolic dysfunction, variability in the heart rate, arrhythmia, and cardiac remodelling. However, the precise molecular mechanism responsible for ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy is poorly understood. In this regard, the present study aimed to describe the RIP1/RIP3/MLKL-mediated necroptotic cell death that may be involved in ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy and characterize CBR-mediated effects on the signalling pathway and myocardial injury.
“Chronic ethanol abuse can lead to harmful consequences for the heart, resulting in systolic dysfunction, variability in the heart rate, arrhythmia, and cardiac remodelling. However, the precise molecular mechanism responsible for ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy is poorly understood. In this regard, the present study aimed to describe the RIP1/RIP3/MLKL-mediated necroptotic cell death that may be involved in ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy and characterize CBR-mediated effects on the signalling pathway and myocardial injury. “In recent years, the role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in various cardiovascular conditions has been a subject of great interest. The ECS is composed of cannabinoid receptors, their endogenous ligands, also known as endocannabinoids, and enzymes responsible for the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids.
“In recent years, the role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in various cardiovascular conditions has been a subject of great interest. The ECS is composed of cannabinoid receptors, their endogenous ligands, also known as endocannabinoids, and enzymes responsible for the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids.
 “The study documented here was aimed to find the molecular interactions of some of the cannabinoid constituents of
“The study documented here was aimed to find the molecular interactions of some of the cannabinoid constituents of  “Increased levels of
“Increased levels of  “In vivo studies show that
“In vivo studies show that  “Cardiovascular complications are the major cause of mortality in diabetic patients. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying diabetes-associated arrhythmias are unclear.
“Cardiovascular complications are the major cause of mortality in diabetic patients. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying diabetes-associated arrhythmias are unclear.