 “The burden of chronic pain has affected many individuals leading to distress and discomfort, alongside numerous side effects with conventional therapeutic approaches.
“The burden of chronic pain has affected many individuals leading to distress and discomfort, alongside numerous side effects with conventional therapeutic approaches.
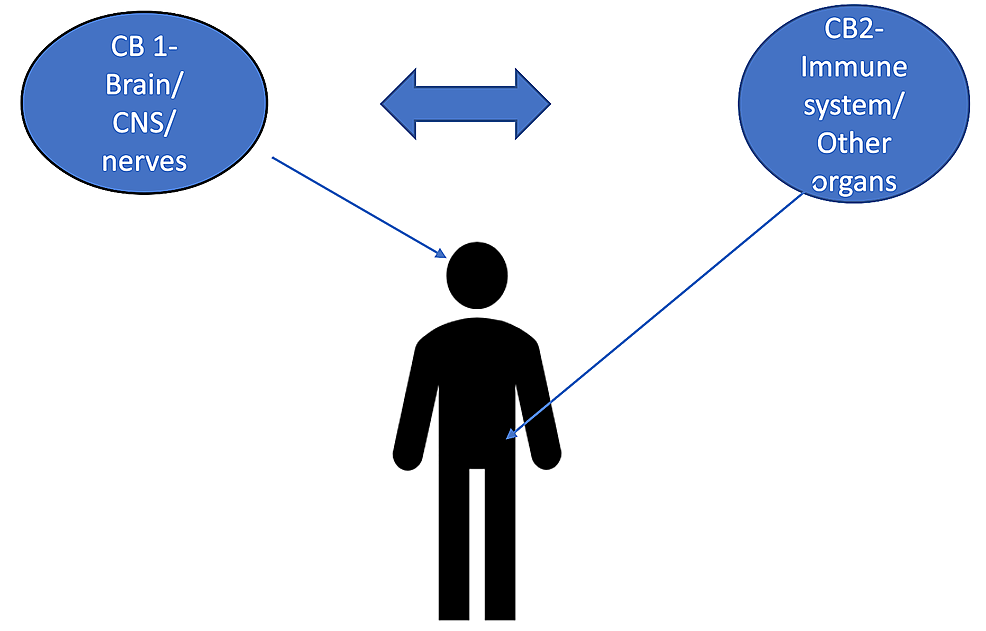
Cannabinoid receptors are naturally found in the human body and have long been an interest in antinociception. These include CB1 and CB2 receptors, which are promising candidates for the treatment of chronic inflammatory pain.
The mechanism of action of the receptors and how they approach pain control in inflammatory conditions show that it can be an adjunctive approach towards controlling these symptoms. Numerous studies have shown how the targeted approach towards these receptors has activated them promoting a release in cytokines, all leading to anti-inflammatory effects and immune system regulation.
Cannabinoid activation of glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) models also showed efficacy in pain management. Chronic conditions such as osteoarthritis were shown to also benefit from this considerable treatment. However, it is unclear how the cannabinoid system works in relation with the pain pathway. Therefore, in this review we aim to analyse the role of the cannabinoid system in chronic inflammatory pain.”

 “The identification of the human cannabinoid receptors and their roles in health and disease, has been one of the most significant biochemical and pharmacological advancements to have occurred in the past few decades. In spite of the major strides made in furthering endocannabinoid research, therapeutic exploitation of the endocannabinoid system has often been a challenging task.
“The identification of the human cannabinoid receptors and their roles in health and disease, has been one of the most significant biochemical and pharmacological advancements to have occurred in the past few decades. In spite of the major strides made in furthering endocannabinoid research, therapeutic exploitation of the endocannabinoid system has often been a challenging task. “The inflammatory sequence is the first phase of wound healing. Macrophages (MPhs) and mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) respond to an inflammatory microenvironment by adapting their functional activity, which polarizes them into the pro-inflammatory phenotypes M1 and MSC1. Prolongation of the inflammatory phase results in the formation of chronic wounds. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) possesses immunomodulatory properties that may impede this cellular phenotypic switch.
“The inflammatory sequence is the first phase of wound healing. Macrophages (MPhs) and mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) respond to an inflammatory microenvironment by adapting their functional activity, which polarizes them into the pro-inflammatory phenotypes M1 and MSC1. Prolongation of the inflammatory phase results in the formation of chronic wounds. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) possesses immunomodulatory properties that may impede this cellular phenotypic switch. “Graft versus host disease (GVHD) pathophysiology is a complex interplay between cells that comprise the adaptive and innate arms of the immune system. Effective prophylactic strategies are therefore contingent upon approaches that address contributions from both immune cell compartments.
“Graft versus host disease (GVHD) pathophysiology is a complex interplay between cells that comprise the adaptive and innate arms of the immune system. Effective prophylactic strategies are therefore contingent upon approaches that address contributions from both immune cell compartments. “Cannabinoids have long been used for their psychotropic and possible medical properties of symptom relief. In the past few years, a vast literature shows that cannabinoids are neuroprotective under different pathological situations.
“Cannabinoids have long been used for their psychotropic and possible medical properties of symptom relief. In the past few years, a vast literature shows that cannabinoids are neuroprotective under different pathological situations.

 “∆ 9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (∆9 -THC), the active phytocannabinoid in cannabis, is virtually an adjunct to the endogenous endocannabinoid signaling system.
“∆ 9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (∆9 -THC), the active phytocannabinoid in cannabis, is virtually an adjunct to the endogenous endocannabinoid signaling system. “While activation of cannabinoid (CB2) receptors has been shown to be neuroprotective, no studies have examined whether this neuroprotection is directed at cerebral arterioles and no studies have examined whether activation of CB2 receptors can rescue cerebrovascular dysfunction during a chronic disease state such as type 1 diabetes (T1D).
“While activation of cannabinoid (CB2) receptors has been shown to be neuroprotective, no studies have examined whether this neuroprotection is directed at cerebral arterioles and no studies have examined whether activation of CB2 receptors can rescue cerebrovascular dysfunction during a chronic disease state such as type 1 diabetes (T1D). “Non-Uremic Calciphylaxis (NUC) is a rare condition that often manifests as intractable and painful integumentary wounds, afflicting patients with a high burden of co-morbidity.
“Non-Uremic Calciphylaxis (NUC) is a rare condition that often manifests as intractable and painful integumentary wounds, afflicting patients with a high burden of co-morbidity.
