 “Background and purpose: Cannabis has been used to treat epilepsy for millennia, with such use validated by regulatory approval of cannabidiol (CBD) for the treatment of Dravet syndrome. Unregulated artisanal cannabis-based products used to treat children with intractable epilepsies often contain relatively low doses of CBD but are enriched in other phytocannabinoids. This raises the possibility that other cannabis constituents might have anticonvulsant properties.
“Background and purpose: Cannabis has been used to treat epilepsy for millennia, with such use validated by regulatory approval of cannabidiol (CBD) for the treatment of Dravet syndrome. Unregulated artisanal cannabis-based products used to treat children with intractable epilepsies often contain relatively low doses of CBD but are enriched in other phytocannabinoids. This raises the possibility that other cannabis constituents might have anticonvulsant properties.
Experimental approach: We used the Scn1a+/- mouse model of Dravet syndrome to interrogate the cannabis plant for phytocannabinoids with anticonvulsant effects against hyperthermia-induced seizures. The most promising, cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), was further examined against spontaneous seizures and survival in Scn1a+/- mice. CBGA was also examined in conventional electroshock seizure models. In addition, we surveyed the pharmacological effects of CBGA across multiple drug targets.
Key results: The initial screen identified three phytocannabinoids with novel anticonvulsant properties: CBGA, cannabidivarinic acid (CBDVA) and cannabigerovarinic acid (CBGVA). CBGA was the most potent and potentiated the anticonvulsant effects of clobazam against hyperthermia-induced and spontaneous seizures, and was anticonvulsant in the MES threshold test. However, CBGA was proconvulsant in the 6-Hz threshold test and a high dose increased spontaneous seizure frequency in Scn1a+/- mice. CBGA was found to interact with numerous epilepsy-relevant targets including GPR55, TRPV1 channels and GABAA receptors.
Conclusion: These results suggest CBGA, CBDVA and CBGVA may contribute to the effects of cannabis-based products in childhood epilepsy. While these phytocannabinoids have anticonvulsant potential and could be lead compounds for drug development programs, several liabilities would need to be overcome before CBD is superseded by another in this class.”
https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.15661


 “Cannabis sativa
“Cannabis sativa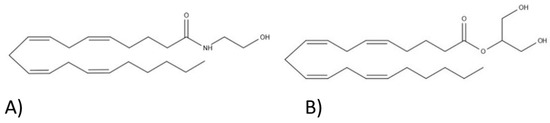
 “The Cannabis sativa plant has been used medicinally and recreationally for thousands of years, but recently only relatively some of its constituents have been identified.
“The Cannabis sativa plant has been used medicinally and recreationally for thousands of years, but recently only relatively some of its constituents have been identified.  “Evidence on the use and efficacy of medical cannabis for children is limited. We examined clinical and epidemiological characteristics of medical cannabis treatment and caregiver-reported effects in children and adolescents in Switzerland.
“Evidence on the use and efficacy of medical cannabis for children is limited. We examined clinical and epidemiological characteristics of medical cannabis treatment and caregiver-reported effects in children and adolescents in Switzerland.
 “Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive phytocannabinoid known for its beneficial effects including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Moreover, CBD is a compound with antidepressant, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and antipsychotic effects. Thanks to all these properties, the interest of the scientific community for it has grown.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive phytocannabinoid known for its beneficial effects including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Moreover, CBD is a compound with antidepressant, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and antipsychotic effects. Thanks to all these properties, the interest of the scientific community for it has grown. “Cannabinoids have been found to be effective in controlling seizures and the highly purified form of cannabinoid derived for Cannabis sativa . Cannabidiol (CBD) is now approved for Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) and Dravet syndrome. CBD was used in a 9-year-old boy with LGS (unknown etiology) with very good results. The electroencephalography (EEG) response was very dramatic with near normalization of EEG background and complete control of seizures. The effect of CBD on EEG with such an improvement has not been described previously. Also, this adds to evidence that early intervention in LGS with CBD might be more helpful and improve outcomes.”
“Cannabinoids have been found to be effective in controlling seizures and the highly purified form of cannabinoid derived for Cannabis sativa . Cannabidiol (CBD) is now approved for Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) and Dravet syndrome. CBD was used in a 9-year-old boy with LGS (unknown etiology) with very good results. The electroencephalography (EEG) response was very dramatic with near normalization of EEG background and complete control of seizures. The effect of CBD on EEG with such an improvement has not been described previously. Also, this adds to evidence that early intervention in LGS with CBD might be more helpful and improve outcomes.” “Voltage-gated sodium channels are targets for a range of pharmaceutical drugs developed for treatment of neurological diseases.
“Voltage-gated sodium channels are targets for a range of pharmaceutical drugs developed for treatment of neurological diseases.