“Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignancies worldwide and the fourth leading cause of cancer deaths in the world. The association between HCC and cannabis has been identified in mice; however, to our knowledge has not been identified in humans. Therefore, we aim to investigate the relation between HCC and cannabis use in humans.
Methods: Using data from the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database between 2002 and 2014, we identified the patients with HCC and cannabis use diagnosis using the International Classification of Disease 9th version codes (ICD-9). Then, we identified patients without cannabis use as the control group. We adjusted for multiple potential confounders and performed multivariable logistic regression analysis to determine the association between cannabis abuse and HCC.
Results: A total of 101,231,036 patients were included in the study. Out of the total, 996,290 patients (1%) had the diagnosis of cannabis abuse versus 100,234,746 patients (99%) in the control group without cannabis abuse. We noticed that patients with cannabis abuse were younger (34 vs 48 years), had more males (61.7% vs 41.4%) and more African Americans (29.9% vs 14.2%) compared with the control group (P<0.001 for all). Besides, patients with cannabis use had more hepatitis B, hepatitis C, liver cirrhosis, and smoking, but had less obesity and gallstones, (P<0.001 for all). Using multivariable logistic regression, and after adjusting for potential confounders, patients with cannabis abuse were 55% less likely to have HCC (adjusted Odds Ratio {aOR}, 0.45, 95% Confidence Interval {CI}, 0.42-0.49, P<0.001) compared with patients without cannabis abuse.
Conclusion: Based on our large database analysis, we found that cannabis use patients were 55% less likely to have HCC compared to patients without cannabis use. Further prospective studies are needed to assess the role of cannabis use on HCC.”
“Our analysis revealed that cannabis users were 55% less likely to have HCC compared to non-cannabis users.”

 “Purpose:
“Purpose: 
 “Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection may evolve into cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, and this progression may be accelerated by specific risk factors, including overweight and obesity. Although evidence for a protective effect of cannabis use on elevated body weight has been found for other populations, no data are available for HBV-infected patients.
“Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection may evolve into cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, and this progression may be accelerated by specific risk factors, including overweight and obesity. Although evidence for a protective effect of cannabis use on elevated body weight has been found for other populations, no data are available for HBV-infected patients.  “The liver is a key metabolic organ that is particularly sensitive to environmental factors, including UV radiation. As UV radiation induces oxidative stress and inflammation, natural compounds are under investigation as one method to counteract these consequences.
“The liver is a key metabolic organ that is particularly sensitive to environmental factors, including UV radiation. As UV radiation induces oxidative stress and inflammation, natural compounds are under investigation as one method to counteract these consequences.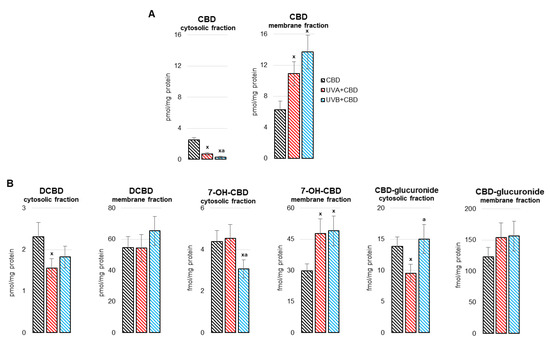
 “Introduction and objectives: Previous studies reveal conflicting data on the effect of cannabis use in patients with cirrhosis. This research evaluates the impact of cannabis on hepatic decompensation, health care utilization, and mortality in patients with cirrhosis.
“Introduction and objectives: Previous studies reveal conflicting data on the effect of cannabis use in patients with cirrhosis. This research evaluates the impact of cannabis on hepatic decompensation, health care utilization, and mortality in patients with cirrhosis. “(E)-β-caryophyllene (BCP) is a bicyclic sesquiterpene widely distributed in the plant kingdom, where it contributes a unique aroma to essential oils and has a pivotal role in the survival and evolution of higher plants.
“(E)-β-caryophyllene (BCP) is a bicyclic sesquiterpene widely distributed in the plant kingdom, where it contributes a unique aroma to essential oils and has a pivotal role in the survival and evolution of higher plants. “Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with metabolic syndrome, which often includes obesity, diabetes, and dyslipidemia. Several studies in mice and humans have implicated the involvement of the gut microbiome in NAFLD.
“Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with metabolic syndrome, which often includes obesity, diabetes, and dyslipidemia. Several studies in mice and humans have implicated the involvement of the gut microbiome in NAFLD. “Cannabidiol (CBD) is considered a non-psychoactive, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory compound derived from the Cannabis sativa plant.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is considered a non-psychoactive, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory compound derived from the Cannabis sativa plant. “Diet and lifestyle-induced dysregulated lipid metabolism have been implicated in fatty liver disease. Chronic redox modulation and hepatic inflammation are key pathological mediators and hallmarks of fatty liver disease associated liver steatosis and steatohepatitis.
“Diet and lifestyle-induced dysregulated lipid metabolism have been implicated in fatty liver disease. Chronic redox modulation and hepatic inflammation are key pathological mediators and hallmarks of fatty liver disease associated liver steatosis and steatohepatitis. “The synthetic atypical cannabinoid Abn-CBD, a
“The synthetic atypical cannabinoid Abn-CBD, a