 “The aberrant accumulation of disease-specific protein aggregates accompanying cognitive decline is a pathological hallmark of age-associated neurological disorders, also termed as proteinopathies, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and multiple sclerosis.
“The aberrant accumulation of disease-specific protein aggregates accompanying cognitive decline is a pathological hallmark of age-associated neurological disorders, also termed as proteinopathies, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and multiple sclerosis.
Along with oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, disruption in protein homeostasis (proteostasis), a network that constitutes protein surveillance system, plays a pivotal role in the pathobiology of these dementia disorders.
Cannabidiol, a non-psychotropic phytocannabinoid of Cannabis sativa, is known for its pleiotropic neuropharmacological effects on the central nervous system, including the ability to abate oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and protein misfolding. Over the past years, compelling evidence has documented disease-modifying role of cannabidiol in various preclinical and clinical models of neurological disorders, suggesting the potential therapeutic implications of cannabidiol in these disorders.
Because of its putative role in the proteostasis network in particular, cannabidiol could be a potent modulator for reversing not only age-associated neurodegeneration but also other protein misfolding disorders. However, the current understanding is insufficient to underpin this proposition. In this review, we discuss the potentiality of cannabidiol as a pharmacological modulator of the proteostasis network, highlighting its neuroprotective and aggregates clearing roles in the neurodegenerative disorders.
We anticipate that the current effort will advance our knowledge on the implication of CBD in proteostasis network, opening up a new therapeutic window for ageing proteinopathies.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33181336/
“Cannabidiol reduces oxidative stress and neuroinflammation of brain.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1568163720303445?via%3Dihub

 “Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive phytocannabinoid known for its beneficial effects including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Moreover, CBD is a compound with antidepressant, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and antipsychotic effects. Thanks to all these properties, the interest of the scientific community for it has grown.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive phytocannabinoid known for its beneficial effects including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Moreover, CBD is a compound with antidepressant, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and antipsychotic effects. Thanks to all these properties, the interest of the scientific community for it has grown.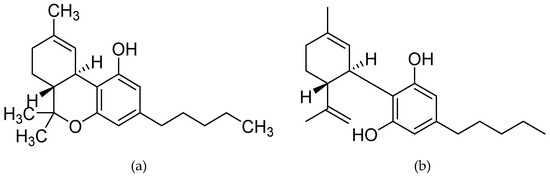
 “Δ9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the main bioactive compound found in the plant Cannabis sativa, exerts its effects by activating cannabinoid receptors present in many neural cells.
“Δ9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the main bioactive compound found in the plant Cannabis sativa, exerts its effects by activating cannabinoid receptors present in many neural cells. “Objectives
“Objectives “Neurological disorders such as neurodegenerative diseases or traumatic brain injury are associated with cognitive, motor and behavioural changes that influence the quality of life of the patients. Although different therapeutic strategies have been developed and tried until now to decrease the neurological decline, no treatment has been found to cure these pathologies.
“Neurological disorders such as neurodegenerative diseases or traumatic brain injury are associated with cognitive, motor and behavioural changes that influence the quality of life of the patients. Although different therapeutic strategies have been developed and tried until now to decrease the neurological decline, no treatment has been found to cure these pathologies.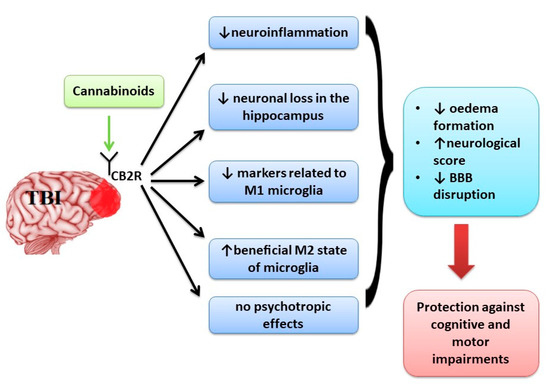
 “Objectives: To investigate the action of cannabinoids on spasticity and pain in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis, by means of neurophysiological indexes.
“Objectives: To investigate the action of cannabinoids on spasticity and pain in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis, by means of neurophysiological indexes. “Painful tonic spasm (PTS) is a common yet debilitating symptom in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), especially those with longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis. Although carbamazepine is an effective treatment, it poses the risk of severe adverse reactions, such as Steven-Johnson syndrome (SJS).
“Painful tonic spasm (PTS) is a common yet debilitating symptom in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), especially those with longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis. Although carbamazepine is an effective treatment, it poses the risk of severe adverse reactions, such as Steven-Johnson syndrome (SJS). “Cannabidiol (
“Cannabidiol ( “Moderate to severe spasticity is commonly reported in Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and its management is still a challenge. Cannabinoids were recently suggested as add-on therapy for the treatment of spasticity and chronic pain in MS but there is no conclusive scientific evidence on their safety, especially on cognition and over long periods.
“Moderate to severe spasticity is commonly reported in Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and its management is still a challenge. Cannabinoids were recently suggested as add-on therapy for the treatment of spasticity and chronic pain in MS but there is no conclusive scientific evidence on their safety, especially on cognition and over long periods.