 “Cannabidiol (CBD), a non-intoxicating component of cannabis, or the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabiol (THC), shows anti-hyperalgesia and anti-inflammatory properties.
“Cannabidiol (CBD), a non-intoxicating component of cannabis, or the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabiol (THC), shows anti-hyperalgesia and anti-inflammatory properties.

 “Cannabidiol (CBD), a non-intoxicating component of cannabis, or the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabiol (THC), shows anti-hyperalgesia and anti-inflammatory properties.
“Cannabidiol (CBD), a non-intoxicating component of cannabis, or the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabiol (THC), shows anti-hyperalgesia and anti-inflammatory properties.
“In summary, these results suggest that psychoactive cannabinoid exposure during adolescence is unlikely to have a major effect on the escalation of cocaine intake or the development of compulsive-like responding per se in adulthood in a rat model of cocaine self-administration.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30224774 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-31921-5]]>
“The Cannabis genus originated in Central Asia and is probably one of the most ancient nonfood crops to be cultivated by humans. Its medicinal properties have been recognized for centuries. Isolation of the psychoactive compound, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, followed by the identification of cannabidiol, led to increased focus on the therapeutic potential of the plant. One of the prominent species, Cannabis sativa, may produce more than 100 different cannabinoids.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30224192 https://www.clinicaltherapeutics.com/article/S0149-2918(18)30331-X/fulltext]]>
 “Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) is a promising therapeutic target for a variety of disorders. Distinct efficacy profiles showed different therapeutic effects on CB1 dependent on three classes of ligands: agonists, antagonists, and inverse agonists. To discriminate the distinct efficacy profiles of the ligands, we carried out molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to identify the dynamic behaviors of inactive and active conformations of CB1 structures with the ligands. In addition, the molecular mechanics Poisson-Boltzmann surface area (MM-PBSA) method was applied to analyze the binding free energy decompositions of the CB1-ligand complexes. With these two methods, we found the possibility that the three classes of ligands can be discriminated. Our findings shed light on the understanding of different efficacy profiles of ligands by analyzing the structural behaviors of intact CB1 structures and the binding energies of ligands, thereby yielding insights that are useful for the design of new potent CB1 drugs.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30213978
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-31749-z
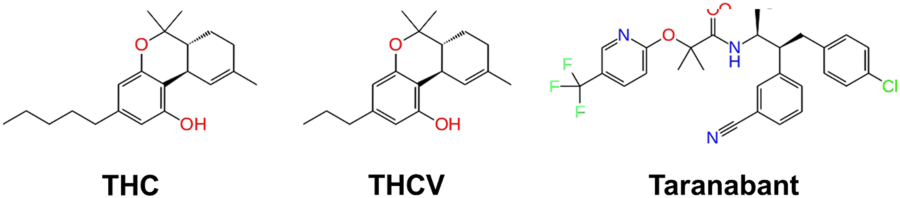
“Chemical structure of the partial agonist THC, antagonist THCV, and inverse agonist Taranabant.”
“Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) is a promising therapeutic target for a variety of disorders. Distinct efficacy profiles showed different therapeutic effects on CB1 dependent on three classes of ligands: agonists, antagonists, and inverse agonists. To discriminate the distinct efficacy profiles of the ligands, we carried out molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to identify the dynamic behaviors of inactive and active conformations of CB1 structures with the ligands. In addition, the molecular mechanics Poisson-Boltzmann surface area (MM-PBSA) method was applied to analyze the binding free energy decompositions of the CB1-ligand complexes. With these two methods, we found the possibility that the three classes of ligands can be discriminated. Our findings shed light on the understanding of different efficacy profiles of ligands by analyzing the structural behaviors of intact CB1 structures and the binding energies of ligands, thereby yielding insights that are useful for the design of new potent CB1 drugs.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30213978
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-31749-z
“Chemical structure of the partial agonist THC, antagonist THCV, and inverse agonist Taranabant.”
 “Drug addiction is a chronic relapsing disorder that produces a dramaticglobal health burden worldwide. Not effective treatment of drug addiction is currently available probably due to the difficulties to find an appropriate target to manage this complex disease raising the needs for further identification of novel therapeutic approaches.
The endocannabinoid system has been found to play a crucial role in the neurobiological substrate underlying drug addiction.
Endocannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors are widely expressed in the main areas of the mesocorticolimbic system that participate in the initiation and maintenance of drug consumption and in the development of compulsion and loss of behavioral control occurring during drug addiction.
The identification of the important role played by CB1 cannabinoid receptors in drug addiction encouraged the possible used of an early commercialized CB1 receptor antagonist for treating drug addiction.
However, the incidence of serious psychiatric adverse events leaded to the sudden withdrawal from the market of this CB1 antagonist and all the research programs developed by pharmaceutical companies to obtain new CB1 antagonists were stopped.
Currently, new research strategies are under development to target the endocannabinoid system for drug addiction avoiding these side effects, which include allosteric negative modulators of CB1 receptors and compounds targeting CB2 receptors.
Recent studies showing the potential role of CB2 receptors in the addictive properties of different drugs of abuse have open a promising research opportunity to develop novel possible therapeutic approaches.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30217570
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0006295218303952
“Drug addiction is a chronic relapsing disorder that produces a dramaticglobal health burden worldwide. Not effective treatment of drug addiction is currently available probably due to the difficulties to find an appropriate target to manage this complex disease raising the needs for further identification of novel therapeutic approaches.
The endocannabinoid system has been found to play a crucial role in the neurobiological substrate underlying drug addiction.
Endocannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors are widely expressed in the main areas of the mesocorticolimbic system that participate in the initiation and maintenance of drug consumption and in the development of compulsion and loss of behavioral control occurring during drug addiction.
The identification of the important role played by CB1 cannabinoid receptors in drug addiction encouraged the possible used of an early commercialized CB1 receptor antagonist for treating drug addiction.
However, the incidence of serious psychiatric adverse events leaded to the sudden withdrawal from the market of this CB1 antagonist and all the research programs developed by pharmaceutical companies to obtain new CB1 antagonists were stopped.
Currently, new research strategies are under development to target the endocannabinoid system for drug addiction avoiding these side effects, which include allosteric negative modulators of CB1 receptors and compounds targeting CB2 receptors.
Recent studies showing the potential role of CB2 receptors in the addictive properties of different drugs of abuse have open a promising research opportunity to develop novel possible therapeutic approaches.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30217570
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0006295218303952
“Cystic fibrosis (CF) is caused by gene mutations resulting in defective cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein activity. CFTR modulators have been developed to improve CFTR protein function. The combination of ivacaftor (IVA) and lumacaftor (LUM) partially restores CFTR protein function of F508del, the most common CF mutation.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30217546
“Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) remains an important issue for patients receiving chemotherapy despite guideline-consistent antiemetic therapy. Trials using delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol-rich (THC) products demonstrate limited antiemetic effect, significant adverse events and flawed study design. Trials using cannabidiol-rich (CBD) products demonstrate improved efficacy and psychological adverse event profile. No definitive trials have been conducted to support the use of cannabinoids for this indication, nor has the potential economic impact of incorporating such regimens into the Australian healthcare system been established. CannabisCINV aims to assess the efficacy, safety and cost-effectiveness of adding TN-TC11M, an oral THC/CBD extract to guideline-consistent antiemetics in the secondary prevention of CINV.
“Cannabis sativa L. (C. sativa) is an annual dioecious plant, which shares its origins with the inception of the first agricultural human societies in Asia. Over the course of time different parts of the plant have been utilized for therapeutic and recreational purposes, for instance, extraction of healing oils from seed, or the use of inflorescences for their psychoactive effects. The key psychoactive constituent in C. sativa is called Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (D9-THC). The endocannabinoid system seems to be phylogenetically ancient, as it was present in the most primitive vertebrates with a neuronal network. N-arachidonoylethanolamine (AEA) and 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) are the main endocannabinoids ligands present in the animal kingdom, and the main endocannabinoid receptors are cannabinoid type-1 (CB1) receptor and cannabinoid type-2 (CB2) receptor.
 “We recently reported that a CB2R agonist, GW405833 (GW), reduced both the ACh-induced Ca2+ oscillations and the L-arginine-induced Ca2+ signal enhancement in mouse pancreatic acinar cells, suggesting that GW-induced inhibition may prevent the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis.
In this study, we aim to evaluate the effects of other cannabinoid ligands on Ca2+ signaling in acinar cells.
In conclusion, CB2R agonists play critical roles in modulating Ca2+ signals in mouse pancreatic acinar cells, while other cannabinoid ligands modulate Ca2+ oscillations in a heterogeneous manner through a CB receptor or non-CB-receptor mechanism.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30202013
“We recently reported that a CB2R agonist, GW405833 (GW), reduced both the ACh-induced Ca2+ oscillations and the L-arginine-induced Ca2+ signal enhancement in mouse pancreatic acinar cells, suggesting that GW-induced inhibition may prevent the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis.
In this study, we aim to evaluate the effects of other cannabinoid ligands on Ca2+ signaling in acinar cells.
In conclusion, CB2R agonists play critical roles in modulating Ca2+ signals in mouse pancreatic acinar cells, while other cannabinoid ligands modulate Ca2+ oscillations in a heterogeneous manner through a CB receptor or non-CB-receptor mechanism.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30202013