 “Cannabinoids are the chemical compounds with a high affinity for cannabinoid receptors affecting the central nervous system through the release of neurotransmitters. However, the current knowledge related to the role of such compounds in the regulation of cellular aging is limited. This study aimed to investigate the effect of cannabidiol and tetrahydrocannabinol on the function of aged pancreatic islets.
“Cannabinoids are the chemical compounds with a high affinity for cannabinoid receptors affecting the central nervous system through the release of neurotransmitters. However, the current knowledge related to the role of such compounds in the regulation of cellular aging is limited. This study aimed to investigate the effect of cannabidiol and tetrahydrocannabinol on the function of aged pancreatic islets.
Main methods: The expression of p53, p38, p21, p16, and Glut2 genes and β-galactosidase activity were measured as hallmarks of cell aging applying real-time PCR, ELISA, and immunocytochemistry techniques. Pdx1 protein expression, insulin release, and oxidative stress markers were compared between young and aged rat pancreatic islet cells.
Key findings: Upon the treatment of aged pancreatic islets cells with cannabidiol and tetrahydrocannabinol, the expression of p53, p38, p21 and the activity of β-galactosidase were reduced. Cannabidiol and tetrahydrocannabinol increase insulin release, Pdx1, Glut2, and thiol molecules expression, while the oxidative stress parameters were decreased. The enhanced expression of Pdx1 and insulin release in aged pancreatic islet cells reflects the extension of cell healthy aging due to the significant reduction of ROS.
Significance: This study provides evidence for the involvement of cannabidiol and tetrahydrocannabinol in the oxidation process of cellular aging.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32553926/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0024320520307190?via%3Dihub
“Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are chemically reactive chemical species containing oxygen. ROS can damage lipid, DNA, RNA, and proteins, which, in theory, contributes to the physiology of aging.” https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reactive_oxygen_species

 “Despite widespread legalization, the impact of medicinal cannabis use on patient-level health and quality of life (QOL) has not been carefully evaluated.
“Despite widespread legalization, the impact of medicinal cannabis use on patient-level health and quality of life (QOL) has not been carefully evaluated. “The worldwide prevalence of neurological and neurodegenerative disorders, such as depression or Alzheimer’s disease, has spread extensively throughout the last decades, becoming an enormous health issue.
“The worldwide prevalence of neurological and neurodegenerative disorders, such as depression or Alzheimer’s disease, has spread extensively throughout the last decades, becoming an enormous health issue.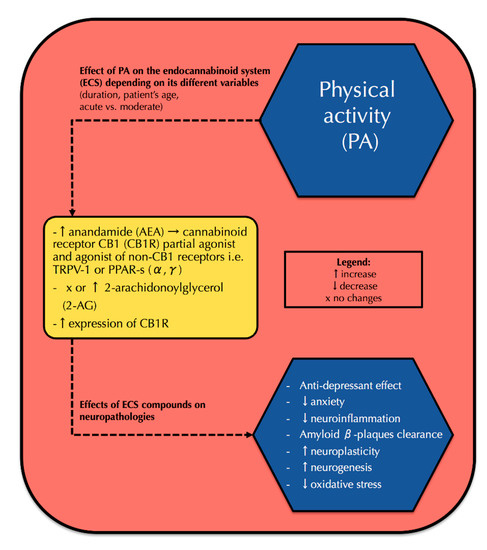
 “The emergence of multi-drug resistant bacteria such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) causes a major threat to public health due to its limited therapeutic options.
“The emergence of multi-drug resistant bacteria such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) causes a major threat to public health due to its limited therapeutic options.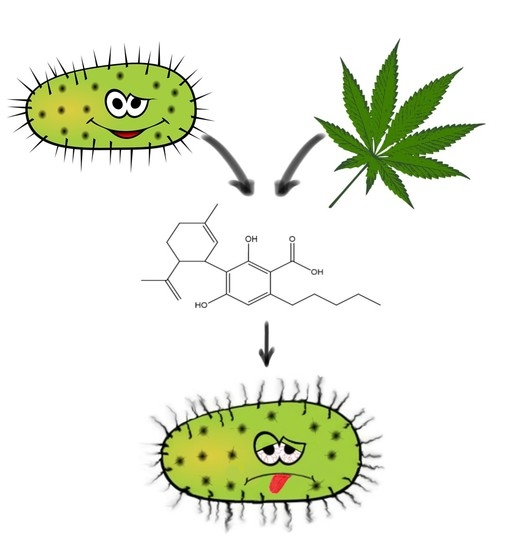
 “Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a frequent cause of abdominal pain and altered bowel habits, which is associated with significant healthcare utilization.
“Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a frequent cause of abdominal pain and altered bowel habits, which is associated with significant healthcare utilization. “Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) is the main phytocannabinoid in fiber and seed-oil hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) plants, but its potential health-related capabilities have been masked for years by a greater scientific interest towards its neutral derivative cannabidiol (CBD). This review aims to collect from the literature and critically discuss all the information about this molecule, starting from its biosynthesis, and focusing on its bioactivity, as an anti-inflammatory, anti-emetic, anti-convulsant, and anti-cancerogenic drug. Furthermore, in the awareness that, despite its multiple bioactive effects, currently poor efforts have been made to achieve its reliable purification, herein, we propose a relatively simple, fast, and inexpensive procedure for its recovery from pollen of industrial hemp cultivars. Spectroscopic and spectrometric techniques allowed us to unequivocally identify pure isolated CBDA and to distinguish it from the constitutional isomer tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA-A).”
“Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) is the main phytocannabinoid in fiber and seed-oil hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) plants, but its potential health-related capabilities have been masked for years by a greater scientific interest towards its neutral derivative cannabidiol (CBD). This review aims to collect from the literature and critically discuss all the information about this molecule, starting from its biosynthesis, and focusing on its bioactivity, as an anti-inflammatory, anti-emetic, anti-convulsant, and anti-cancerogenic drug. Furthermore, in the awareness that, despite its multiple bioactive effects, currently poor efforts have been made to achieve its reliable purification, herein, we propose a relatively simple, fast, and inexpensive procedure for its recovery from pollen of industrial hemp cultivars. Spectroscopic and spectrometric techniques allowed us to unequivocally identify pure isolated CBDA and to distinguish it from the constitutional isomer tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA-A).”
 “Identifying candidate drugs effective in the new coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) is crucial,
“Identifying candidate drugs effective in the new coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) is crucial,  “Cannabidiol (CBD) is a naturally occurring, non-psychotropic cannabinoid of the hemp plant Cannabis sativa L. and has been known to induce several physiological and pharmacological effects. While CBD is approved as a medicinal product subject to prescription, it is also widely sold over the counter (OTC) in the form of food supplements, cosmetics and electronic cigarette liquids. However, regulatory difficulties arise from its origin being a narcotic plant or its status as an unapproved novel food ingredient.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is a naturally occurring, non-psychotropic cannabinoid of the hemp plant Cannabis sativa L. and has been known to induce several physiological and pharmacological effects. While CBD is approved as a medicinal product subject to prescription, it is also widely sold over the counter (OTC) in the form of food supplements, cosmetics and electronic cigarette liquids. However, regulatory difficulties arise from its origin being a narcotic plant or its status as an unapproved novel food ingredient. “Introduction: Severe Behavioural Problems (SBP) are a major contributor to morbidity in children with Intellectual Disability (ID). Medications used to treat SBP in ID are associated with a high risk of side effects. Cannabidiol has potential therapeutic effects in SBP. This pilot study aimed to investigate the feasibility of conducting a randomized placebo-controlled trial of cannabidiol to reduce SBP in children with ID.
“Introduction: Severe Behavioural Problems (SBP) are a major contributor to morbidity in children with Intellectual Disability (ID). Medications used to treat SBP in ID are associated with a high risk of side effects. Cannabidiol has potential therapeutic effects in SBP. This pilot study aimed to investigate the feasibility of conducting a randomized placebo-controlled trial of cannabidiol to reduce SBP in children with ID. “Background: Recent approved medicines whose active principles are Δ9Tetrahidrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and/or cannabidiol (CBD) open novel perspectives for other phytocannabinoids also present in Cannabis sativa L. varieties. Furthermore, solid data on the potential benefits of acidic and varinic phytocannabinoids in a variety of diseases are already available. Mode of action of cannabigerol (CBG), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), cannabidivarin (CBDV) and cannabigerivarin (CBGV) is, to the very least, partial.
“Background: Recent approved medicines whose active principles are Δ9Tetrahidrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and/or cannabidiol (CBD) open novel perspectives for other phytocannabinoids also present in Cannabis sativa L. varieties. Furthermore, solid data on the potential benefits of acidic and varinic phytocannabinoids in a variety of diseases are already available. Mode of action of cannabigerol (CBG), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), cannabidivarin (CBDV) and cannabigerivarin (CBGV) is, to the very least, partial.