
Methods: We conducted an online convenience sample survey of patients from three medical cannabis practice sites who had reported using opioids. A total of 1181 patients responded, 656 were excluded for not using medical cannabis in combination with opioid use or not meeting the definition of chronic pain, leaving 525 patients who had used prescription opioid medications continuously for at least three months to treat chronic pain and were using medical cannabis in combination with their prescribed opioid use.
Results: Overall, 40.4% (n=204) reported that they stopped all opioids, 45.2% (n=228) reported some decrease in their opioid usage, 13.3% (n=67) reported no change in opioid usage, and 1.1% (n=6) reported an increase in opioid usage. The majority (65.3%, n=299) reported that they sustained the opioid change for over a year. Almost half (48.2%, n=241) reported a 40-100% decrease in pain while 8.6% (n=43) had no change in pain and 2.6% (n=13) had worsening pain. The majority reported improved ability to function (80.0%, n=420) and improved quality of life (87.0%, n=457) with medical cannabis. The majority (62.8%, n=323) did not want to take opioids in the future. While the change in pain level was not affected by age and gender, the younger age group had improved ability to function compared with the middle and older age groups.
Conclusions: Patients in this study reported that cannabis was a useful adjunct and substitute for prescription opioids in treating their chronic pain and had the added benefit of improving the ability to function and quality of life.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33409086/
“Our results show a remarkable percentage of patients both reporting complete cessation of opioids and decreasing opioid usage by the addition of medical cannabis, with results lasting for over a year for the majority. Additional benefits of medical cannabis included improved ability to function and improved quality of life, especially for the younger age group. We believe our results lend further support that medical cannabis provided in a standardized protocol can lead to decreased pain and opioid usage, improved function, and quality of life measures, and even complete cessation of opioids in patients with chronic pain treated by opioids.”

 “Background: The ongoing opioid overdose crisis is driven largely by exposure to illicitly-manufactured fentanyl. Preliminary observational and experimental research suggests that cannabis could potentially play a role in reducing use of prescription opioids among individuals with chronic pain. However, there is limited data on the effects of cannabis on illicit opioid consumption, particularly fentanyl, especially among individuals on opioid agonist therapy (OAT). We sought to assess the longitudinal association between cannabis use and exposure to fentanyl among people on OAT.
“Background: The ongoing opioid overdose crisis is driven largely by exposure to illicitly-manufactured fentanyl. Preliminary observational and experimental research suggests that cannabis could potentially play a role in reducing use of prescription opioids among individuals with chronic pain. However, there is limited data on the effects of cannabis on illicit opioid consumption, particularly fentanyl, especially among individuals on opioid agonist therapy (OAT). We sought to assess the longitudinal association between cannabis use and exposure to fentanyl among people on OAT.
 “Recently, there has been a growing interest in the medical applications of Cannabis plants. They owe their unique properties to a group of secondary metabolites known as phytocannabinoids, which are specific for this genus. Phytocannabinoids, and cannabinoids generally, can interact with cannabinoid receptors being part of the endocannabinoid system present in animals. Over the years a growing body of scientific evidence has been gathered, suggesting that these compounds have therapeutic potential.
“Recently, there has been a growing interest in the medical applications of Cannabis plants. They owe their unique properties to a group of secondary metabolites known as phytocannabinoids, which are specific for this genus. Phytocannabinoids, and cannabinoids generally, can interact with cannabinoid receptors being part of the endocannabinoid system present in animals. Over the years a growing body of scientific evidence has been gathered, suggesting that these compounds have therapeutic potential.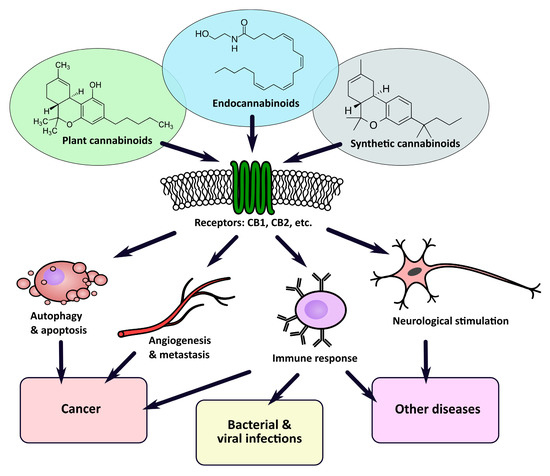
 “Gynaecological cancers can be primary neoplasms, originating either from the reproductive tract or the products of conception, or secondary neoplasms, representative of metastatic disease. For some of these cancers, the exact causes are unknown; however, it is recognised that the precise aetiopathogeneses for most are multifactorial and include exogenous (such as diet) and endogenous factors (such as genetic predisposition), which mutually interact in a complex manner.
“Gynaecological cancers can be primary neoplasms, originating either from the reproductive tract or the products of conception, or secondary neoplasms, representative of metastatic disease. For some of these cancers, the exact causes are unknown; however, it is recognised that the precise aetiopathogeneses for most are multifactorial and include exogenous (such as diet) and endogenous factors (such as genetic predisposition), which mutually interact in a complex manner.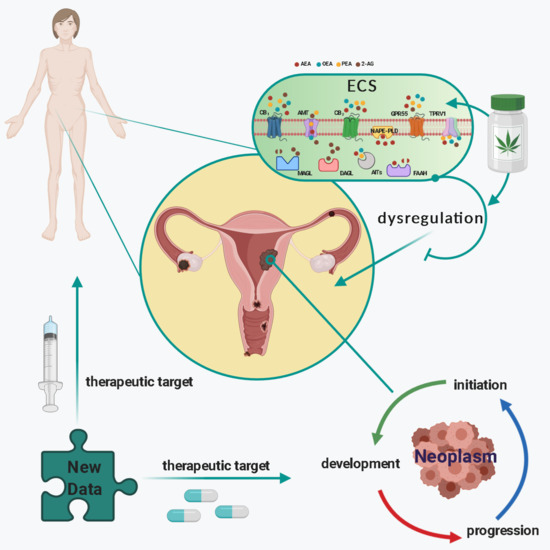
 “Plant-based therapies date back centuries. Cannabis sativa is one such plant that was used medicinally up until the early part of the 20th century.
“Plant-based therapies date back centuries. Cannabis sativa is one such plant that was used medicinally up until the early part of the 20th century.
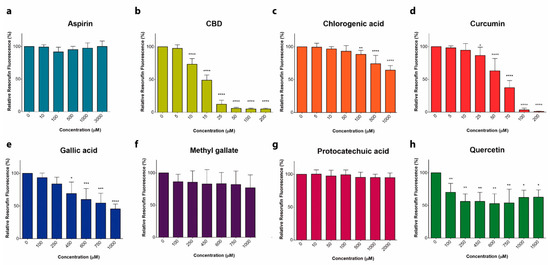
 “Objectives: This article presents findings from a large prospective examination of Canadian medical cannabis patients, with a focus on the impacts of cannabis on prescription opioid use and quality of life over a 6-month period.
“Objectives: This article presents findings from a large prospective examination of Canadian medical cannabis patients, with a focus on the impacts of cannabis on prescription opioid use and quality of life over a 6-month period.
 “Cannabis sativa L. is an aromatic annual herb belonging to the family Cannabaceae and it is widely distributed worldwide. Cultivation, selling, and consumption of cannabis and cannabis related products, regardless of its use, was prohibited in Lebanon until April 22, 2020. Nevertheless, cannabis oil has been traditionally used unlawfully for many years in Lebanon to treat diseases such as arthritis, diabetes, cancer and few neurological disorders.
“Cannabis sativa L. is an aromatic annual herb belonging to the family Cannabaceae and it is widely distributed worldwide. Cultivation, selling, and consumption of cannabis and cannabis related products, regardless of its use, was prohibited in Lebanon until April 22, 2020. Nevertheless, cannabis oil has been traditionally used unlawfully for many years in Lebanon to treat diseases such as arthritis, diabetes, cancer and few neurological disorders.