
 “The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis, a balance in internal environment (temperature, mood, and immune system) and energy input and output in living, biological systems.
“The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis, a balance in internal environment (temperature, mood, and immune system) and energy input and output in living, biological systems.
In addition to regulating physiological processes, the ECS directly influences anxiety, feeding behaviour/appetite, emotional behaviour, depression, nervous functions, neurogenesis, neuroprotection, reward, cognition, learning, memory, pain sensation, fertility, pregnancy, and pre-and post-natal development.
The ECS is also involved in several pathophysiological diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases. In recent years, genetic and pharmacological manipulation of the ECS has gained significant interest in medicine, research, and drug discovery and development.
The distribution of the components of the ECS system throughout the body, and the physiological/pathophysiological role of the ECS-signalling pathways in many diseases, all offer promising opportunities for the development of novel cannabinergic, cannabimimetic, and cannabinoid-based therapeutic drugs that genetically or pharmacologically modulate the ECS via inhibition of metabolic pathways and/or agonism or antagonism of the receptors of the ECS. This modulation results in the differential expression/activity of the components of the ECS that may be beneficial in the treatment of a number of diseases.
This manuscript in-depth review will investigate the potential of the ECS in the treatment of various diseases, and to put forth the suggestion that many of these secondary metabolites of Cannabis sativa L. (hereafter referred to as “C. sativa L.” or “medical cannabis”), may also have potential as lead compounds in the development of cannabinoid-based pharmaceuticals for a variety of diseases.”
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/22/17/9472

 “Background:
“Background:  “Cannabidiol is increasingly considered for treatment of a wide range of medical conditions.
“Cannabidiol is increasingly considered for treatment of a wide range of medical conditions.  “Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by structural damage, death, and functional disruption of cholinergic neurons (ChNs) as a result of intracellular amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregation, extracellular neuritic plaques, and hyperphosphorylation of protein tau (p-Tau) overtime.
“Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by structural damage, death, and functional disruption of cholinergic neurons (ChNs) as a result of intracellular amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregation, extracellular neuritic plaques, and hyperphosphorylation of protein tau (p-Tau) overtime. “Cannabis is an annual plant with a long history of use as food, feed, fiber, oil, medicine, and narcotics. Despite realizing its true value, it has not yet found its true place. Cannabis has had a long history with many ups and downs, and now it is our turn to promote it.
“Cannabis is an annual plant with a long history of use as food, feed, fiber, oil, medicine, and narcotics. Despite realizing its true value, it has not yet found its true place. Cannabis has had a long history with many ups and downs, and now it is our turn to promote it.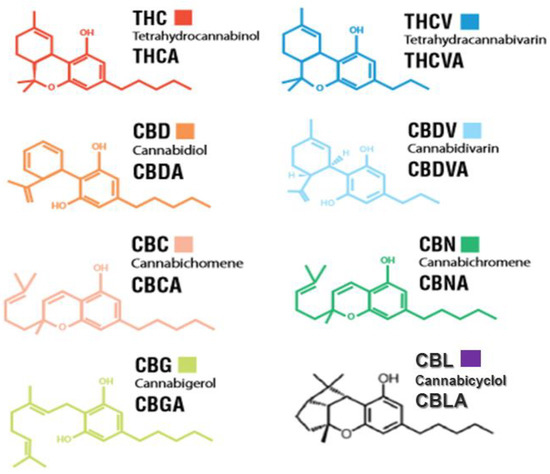
 “The immune-suppressive effects of cannabidiol (CBD) are attributed to the modulation of essential immunological signaling pathways and receptors. Mechanistic understanding of the pharmacological effects of CBD emphasizes the therapeutic potential of CBD as a novel immune modulator.
“The immune-suppressive effects of cannabidiol (CBD) are attributed to the modulation of essential immunological signaling pathways and receptors. Mechanistic understanding of the pharmacological effects of CBD emphasizes the therapeutic potential of CBD as a novel immune modulator. “Diabetes is a chronic disease associated with a high number of complications such as peripheral neuropathy, which causes sensorial disturbances and may lead to the development of diabetic neuropathic pain (DNP). The current treatment for DNP is just palliative and the drugs may cause severe adverse effects, leading to discontinuation of treatment. Thus, new therapeutic targets need to be urgently investigated.
“Diabetes is a chronic disease associated with a high number of complications such as peripheral neuropathy, which causes sensorial disturbances and may lead to the development of diabetic neuropathic pain (DNP). The current treatment for DNP is just palliative and the drugs may cause severe adverse effects, leading to discontinuation of treatment. Thus, new therapeutic targets need to be urgently investigated. “In recent years, the role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in various cardiovascular conditions has been a subject of great interest. The ECS is composed of cannabinoid receptors, their endogenous ligands, also known as endocannabinoids, and enzymes responsible for the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids.
“In recent years, the role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in various cardiovascular conditions has been a subject of great interest. The ECS is composed of cannabinoid receptors, their endogenous ligands, also known as endocannabinoids, and enzymes responsible for the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids. “Alcohol use disorders affect millions of people worldwide and there is growing evidence that excessive alcohol intake causes severe damage to the brain of both humans and animals.
“Alcohol use disorders affect millions of people worldwide and there is growing evidence that excessive alcohol intake causes severe damage to the brain of both humans and animals. “Obesity rates are increasing worldwide and there is a need for novel therapeutic treatment options.
“Obesity rates are increasing worldwide and there is a need for novel therapeutic treatment options.