“While natural Δ9-tetrahidrocannabinol (Δ9THC), cannabidiol (CBD), and their therapeutic potential have been extensively researched, some cannabinoids have not been widely investigated.
“While natural Δ9-tetrahidrocannabinol (Δ9THC), cannabidiol (CBD), and their therapeutic potential have been extensively researched, some cannabinoids have not been widely investigated.
The present article compiles data from the literature that highlights research on and the therapeutic possibilities of lesser known phytocannabinoids, which we have divided into varinic, acidic, and “minor” (i.e., cannabinoids that are not present in high quantities in common varieties of Cannabis sativa L).
A growing interest in these compounds, which are enriched in some cannabis varieties, has already resulted in enough preclinical information to show that they are promising therapeutic agents for a variety of diseases.
Each phytocannabinoid has a “preferential” mechanism of action, and often target the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and/or CB2. The recent resolution of the structure of cannabinoid receptors demonstrates the atypical nature of cannabinoid binding, and that different binding modes depend on the agonist or partial agonist/inverse agonist, which allows for differential signaling, even acting on the same cannabinoid receptor. In addition, other players and multiple signaling pathways may be targeted/engaged by phytocannabinoids, thereby expanding the mechanistic possibilities for therapeutic use.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32416215
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1043661820311099?via%3Dihub

 “The inhibitor of DNA binding (Id) proteins are regulators of cell cycle and cell differentiation. Of all Id family proteins, Id1 is mostly linked to tumorigenesis, cellular senescence as well as cell proliferation and survival.
“The inhibitor of DNA binding (Id) proteins are regulators of cell cycle and cell differentiation. Of all Id family proteins, Id1 is mostly linked to tumorigenesis, cellular senescence as well as cell proliferation and survival. “There is increasing interest in the use of purified
“There is increasing interest in the use of purified 
 “The intraperitoneal administration of chemotherapeutics has emerged as a potential route in ovarian cancer treatment. Nanoparticles as carriers for these agents could be interesting by increasing the retention of chemotherapeutics within the peritoneal cavity. Moreover, nanoparticles could be internalised by cancer cells and let the drug release near the biological target, which could increase the anticancer efficacy.
“The intraperitoneal administration of chemotherapeutics has emerged as a potential route in ovarian cancer treatment. Nanoparticles as carriers for these agents could be interesting by increasing the retention of chemotherapeutics within the peritoneal cavity. Moreover, nanoparticles could be internalised by cancer cells and let the drug release near the biological target, which could increase the anticancer efficacy.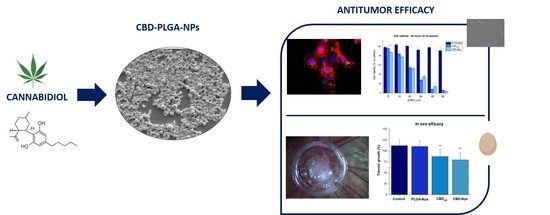
 “Cannabis sativa and its principal components, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and
“Cannabis sativa and its principal components, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and 

 “The prevalence rates of depression and anxiety are at least two times higher in diabetic patients, increasing morbidity and mortality.
“The prevalence rates of depression and anxiety are at least two times higher in diabetic patients, increasing morbidity and mortality. “Gestational methylazoxymethanol acetate (MAM) treatment produces offspring with adult phenotype relevant to schizophrenia, including positive- and negative-like symptoms, cognitive deficits, dopaminergic dysfunction, structural and functional abnormalities.
“Gestational methylazoxymethanol acetate (MAM) treatment produces offspring with adult phenotype relevant to schizophrenia, including positive- and negative-like symptoms, cognitive deficits, dopaminergic dysfunction, structural and functional abnormalities.
 “Cannabis sativa is an aromatic annual flowering plant with several botanical varieties, used for different purposes, like the production of fibers, the production of oil from the seeds, and especially for recreational or medical purposes.
“Cannabis sativa is an aromatic annual flowering plant with several botanical varieties, used for different purposes, like the production of fibers, the production of oil from the seeds, and especially for recreational or medical purposes.