 “Cannabis was extensively utilized for its medicinal properties till the 19th century. A steep decline in its medicinal usage was observed later due to its emergence as an illegal recreational drug. Advances in technology and scientific findings led to the discovery of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound of cannabis, that further led to the discovery of endogenous cannabinoids system consisting of G-protein-coupled receptors – cannabinoid receptor 1 and cannabinoid receptor 2 along with their ligands, mainly anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Endocannabinoid (EC) is shown to be a modulator not only for physiological functions but also for the immune system, endocrine network, and central nervous system. Medicinal research and meta-data analysis over the last few decades have shown a significant potential for both THC and cannabidiol (CBD) to exert palliative effects. People suffering from many forms of advanced stages of cancers undergo chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting followed by severe and chronic neuropathic pain and weight loss. THC and CBD exhibit effective analgesic, anxiolytic, and appetite-stimulating effect on patients suffering from cancer. Drugs currently available in the market to treat such chemotherapy-induced cancer-related ailments are Sativex (GW Pharmaceutical), Dronabinol (Unimed Pharmaceuticals), and Nabilone (Valeant Pharmaceuticals). Apart from exerting palliative effects, THC also shows promising role in the treatment of cancer growth, neurodegenerative diseases (multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease), and alcohol addiction and hence should be exploited for potential benefits. The current review discusses the nature and role of CB receptors, specific applications of cannabinoids, and major studies that have assessed the role of cannabinoids in cancer management.”
“Cannabis was extensively utilized for its medicinal properties till the 19th century. A steep decline in its medicinal usage was observed later due to its emergence as an illegal recreational drug. Advances in technology and scientific findings led to the discovery of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound of cannabis, that further led to the discovery of endogenous cannabinoids system consisting of G-protein-coupled receptors – cannabinoid receptor 1 and cannabinoid receptor 2 along with their ligands, mainly anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Endocannabinoid (EC) is shown to be a modulator not only for physiological functions but also for the immune system, endocrine network, and central nervous system. Medicinal research and meta-data analysis over the last few decades have shown a significant potential for both THC and cannabidiol (CBD) to exert palliative effects. People suffering from many forms of advanced stages of cancers undergo chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting followed by severe and chronic neuropathic pain and weight loss. THC and CBD exhibit effective analgesic, anxiolytic, and appetite-stimulating effect on patients suffering from cancer. Drugs currently available in the market to treat such chemotherapy-induced cancer-related ailments are Sativex (GW Pharmaceutical), Dronabinol (Unimed Pharmaceuticals), and Nabilone (Valeant Pharmaceuticals). Apart from exerting palliative effects, THC also shows promising role in the treatment of cancer growth, neurodegenerative diseases (multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease), and alcohol addiction and hence should be exploited for potential benefits. The current review discusses the nature and role of CB receptors, specific applications of cannabinoids, and major studies that have assessed the role of cannabinoids in cancer management.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33723124/
“Specific targeting of cannabinoid receptors can be used to manage severe side effects during chemotherapy, palliative care, and overall cancer management. Furthermore, research evidences on cannabinoids have suggested tumor inhibiting and suppressing properties which warrant reconsidering legality of the substance. Studies on CB1 and CB2 receptors, in case of cancers, have demonstrated the psychoactive constituents of cannabinoids to be potent against tumor growth. Interestingly, studies have also shown that activation of CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors by their respective synthetic agonists tends to limit human cancer cell growth, suggesting the role of the endocannabinoid system as a novel target for treatment of cancers.”

 “Glioblastomas (GBMs) are aggressive brain tumors with frequent genetic alterations in TP53 and PTEN tumor suppressor genes rendering resistance to standard chemotherapeutics. Cannabinoid type 1 and 2 (CB1/CB2) receptor expression in GBMs and antitumor activity of cannabinoids in glioma cells and animal models, raised promises for a targeted treatment of these tumors. The susceptibility of human glioma cells to CB2-agonists and their mechanism of action are not fully elucidated. We determined CB1 and CB2 expression in 14 low-grade and 21 high-grade tumor biopsies, GBM-derived primary cultures and established cell lines. The non-selective CB receptor agonist WIN55,212-2 (but not its inactive enantiomer) or the CB2-selective agonist JWH133 induced apoptosis in patient-derived glioma cultures and five established glioma cell lines despite p53 and/or PTEN deficiency. Growth inhibitory efficacy of cannabinoids correlated with CB1/CB2 expression (EC50 WIN55,212-2: 7.36-15.70 µM, JWH133: 12.15-143.20 µM). Treatment with WIN55,212-2 or JWH133 led to activation of the apoptotic mitochondrial pathway and DNA fragmentation. Synthetic cannabinoid action was associated with the induction of autophagy and knockdown of autophagy genes augmented cannabinoid-induced apoptotic cell death. The high susceptibility of human glioblastoma cells to synthetic cannabinoids, despite genetic defects contributing to apoptosis resistance, makes cannabinoids promising anti-glioma therapeutics.”
“Glioblastomas (GBMs) are aggressive brain tumors with frequent genetic alterations in TP53 and PTEN tumor suppressor genes rendering resistance to standard chemotherapeutics. Cannabinoid type 1 and 2 (CB1/CB2) receptor expression in GBMs and antitumor activity of cannabinoids in glioma cells and animal models, raised promises for a targeted treatment of these tumors. The susceptibility of human glioma cells to CB2-agonists and their mechanism of action are not fully elucidated. We determined CB1 and CB2 expression in 14 low-grade and 21 high-grade tumor biopsies, GBM-derived primary cultures and established cell lines. The non-selective CB receptor agonist WIN55,212-2 (but not its inactive enantiomer) or the CB2-selective agonist JWH133 induced apoptosis in patient-derived glioma cultures and five established glioma cell lines despite p53 and/or PTEN deficiency. Growth inhibitory efficacy of cannabinoids correlated with CB1/CB2 expression (EC50 WIN55,212-2: 7.36-15.70 µM, JWH133: 12.15-143.20 µM). Treatment with WIN55,212-2 or JWH133 led to activation of the apoptotic mitochondrial pathway and DNA fragmentation. Synthetic cannabinoid action was associated with the induction of autophagy and knockdown of autophagy genes augmented cannabinoid-induced apoptotic cell death. The high susceptibility of human glioblastoma cells to synthetic cannabinoids, despite genetic defects contributing to apoptosis resistance, makes cannabinoids promising anti-glioma therapeutics.”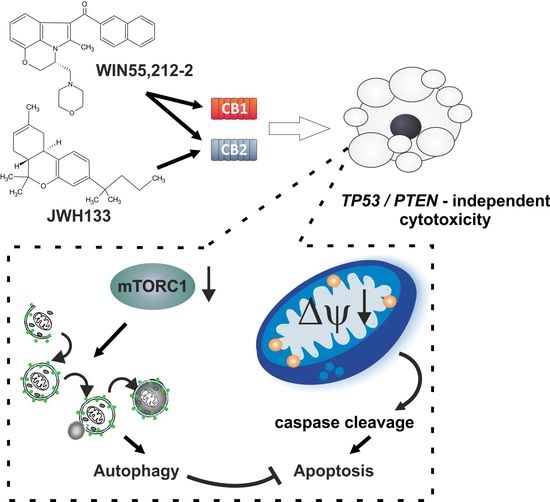
 “Cannabis sativa contains more than 500 constituents, yet the anticancer properties of the vast majority of cannabis compounds remains unknown. We aimed to identify cannabis compounds and their combinations presenting cytotoxicity against bladder urothelial carcinoma (UC), the most common urinary system cancer.
“Cannabis sativa contains more than 500 constituents, yet the anticancer properties of the vast majority of cannabis compounds remains unknown. We aimed to identify cannabis compounds and their combinations presenting cytotoxicity against bladder urothelial carcinoma (UC), the most common urinary system cancer. “Plant-based therapies date back centuries. Cannabis sativa is one such plant that was used medicinally up until the early part of the 20th century.
“Plant-based therapies date back centuries. Cannabis sativa is one such plant that was used medicinally up until the early part of the 20th century.
 “Bisphenol A (BPA) is an endocrine disruptor that negatively affects spermatogenesis, a process where Sertoli cells play a central role. Thus, in the present study we sought to ascertain whether BPA could modulate the endocannabinoid (eCB) system in exposed mouse primary Sertoli cells.
“Bisphenol A (BPA) is an endocrine disruptor that negatively affects spermatogenesis, a process where Sertoli cells play a central role. Thus, in the present study we sought to ascertain whether BPA could modulate the endocannabinoid (eCB) system in exposed mouse primary Sertoli cells. “Cannabis has long been used for healing and recreation in several regions of the world. Over 400 bioactive constituents, including more than 100 phytocannabinoids, have been isolated from this plant. The non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) and the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) are the major and widely studied constituents from this plant.
“Cannabis has long been used for healing and recreation in several regions of the world. Over 400 bioactive constituents, including more than 100 phytocannabinoids, have been isolated from this plant. The non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) and the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) are the major and widely studied constituents from this plant. “Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a highly infectious respiratory disease caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. A significant proportion of COVID-19 patients develop Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) resulting from hyperactivation of the immune system and cytokine storm, which leads to respiratory and multi-organ failure, and death. Currently, there are no effective treatments against hyperimmune syndrome and ARDS.
“Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a highly infectious respiratory disease caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. A significant proportion of COVID-19 patients develop Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) resulting from hyperactivation of the immune system and cytokine storm, which leads to respiratory and multi-organ failure, and death. Currently, there are no effective treatments against hyperimmune syndrome and ARDS.