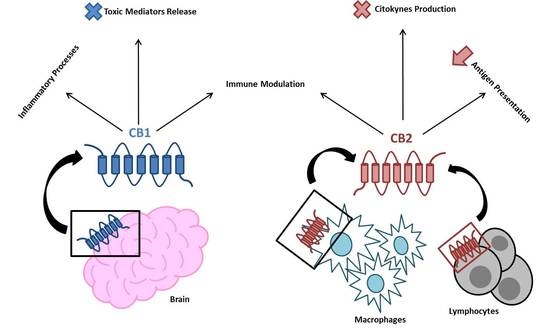
 “Endocannabinoid system consists of cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid type 2 (CB2) receptors, their endogenous ligands, and the enzymes responsible for their synthesis and degradation. CB2, to a great extent, and CB1, to a lesser extent, are involved in regulating the immune response. They also regulate the inflammatory processes by inhibiting pro-inflammatory mediator release and immune cell proliferation. This review provides an overview on the role of the endocannabinoid system with a major focus on cannabinoid receptors in the pathogenesis and onset of inflammatory and autoimmune pediatric diseases, such as immune thrombocytopenia, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, obesity, neuroinflammatory diseases, and type 1 diabetes mellitus. These disorders have a high social impact and represent a burden for the healthcare system, hence the importance of individuating more innovative and effective treatments. The endocannabinoid system could address this need, representing a possible new diagnostic marker and therapeutic target.”
“Endocannabinoid system consists of cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid type 2 (CB2) receptors, their endogenous ligands, and the enzymes responsible for their synthesis and degradation. CB2, to a great extent, and CB1, to a lesser extent, are involved in regulating the immune response. They also regulate the inflammatory processes by inhibiting pro-inflammatory mediator release and immune cell proliferation. This review provides an overview on the role of the endocannabinoid system with a major focus on cannabinoid receptors in the pathogenesis and onset of inflammatory and autoimmune pediatric diseases, such as immune thrombocytopenia, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, obesity, neuroinflammatory diseases, and type 1 diabetes mellitus. These disorders have a high social impact and represent a burden for the healthcare system, hence the importance of individuating more innovative and effective treatments. The endocannabinoid system could address this need, representing a possible new diagnostic marker and therapeutic target.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31771129
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/20/23/5875

 “As we learn more about the endocannabinoid system (ECS), our understanding and grasp of the system’s ubiquitous presence is expanding. In light of this, there is also a growing body of evidence for the therapeutic potential of ECS modulation in a range of clinical situations. Strategies include for example manipulation of the
“As we learn more about the endocannabinoid system (ECS), our understanding and grasp of the system’s ubiquitous presence is expanding. In light of this, there is also a growing body of evidence for the therapeutic potential of ECS modulation in a range of clinical situations. Strategies include for example manipulation of the  “The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is comprised of cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 (CB1R and CB2R), endogenous ligands, and regulatory enzymes, and serves to regulate several important physiological functions throughout the brain and body.
“The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is comprised of cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 (CB1R and CB2R), endogenous ligands, and regulatory enzymes, and serves to regulate several important physiological functions throughout the brain and body.



 “The anticancer effects of the omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPUFA), EPA and DHA may be due, at least in part, to conversion to their respective endocannabinoid derivatives, eicosapentaenoyl-ethanolamine (EPEA) and docosahexaenoyl-ethanolamine (DHEA).
“The anticancer effects of the omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPUFA), EPA and DHA may be due, at least in part, to conversion to their respective endocannabinoid derivatives, eicosapentaenoyl-ethanolamine (EPEA) and docosahexaenoyl-ethanolamine (DHEA). “L-dopa induced dyskinesia (LID) is a debilitating side-effect of the primary treatment used in Parkinson’s disease (PD), l-dopa. Here we investigate the effect of HU-308, a
“L-dopa induced dyskinesia (LID) is a debilitating side-effect of the primary treatment used in Parkinson’s disease (PD), l-dopa. Here we investigate the effect of HU-308, a  “Hepatic fibrosis is the consequence of an unresolved wound healing process in response to chronic liver injury and involves multiple cell types and molecular mechanisms. The hepatic endocannabinoid and apelin systems are two signalling pathways with a substantial role in the liver fibrosis pathophysiology-both are upregulated in patients with advanced liver disease. Endogenous
“Hepatic fibrosis is the consequence of an unresolved wound healing process in response to chronic liver injury and involves multiple cell types and molecular mechanisms. The hepatic endocannabinoid and apelin systems are two signalling pathways with a substantial role in the liver fibrosis pathophysiology-both are upregulated in patients with advanced liver disease. Endogenous 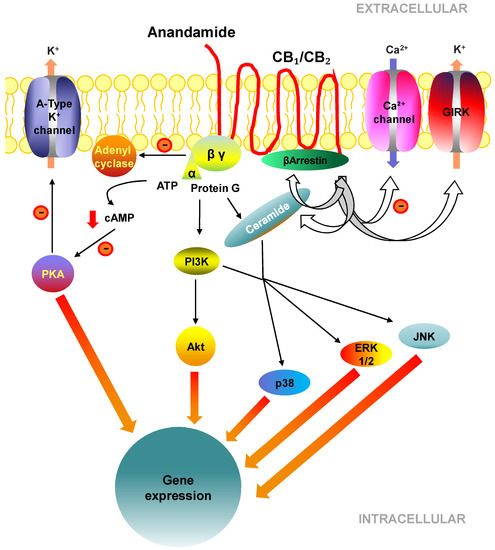
 “Preclinical studies have shown that cannabidiol (CBD) mitigates fear memories by facilitating their extinction or interfering with their generalization and reconsolidation. The brain regions and mechanisms underlying these effects, and their temporal window, are still poorly understood. The present paper aimed at investigating related questions in the dorsal hippocampus (DH) during contextual fear consolidation.
“Preclinical studies have shown that cannabidiol (CBD) mitigates fear memories by facilitating their extinction or interfering with their generalization and reconsolidation. The brain regions and mechanisms underlying these effects, and their temporal window, are still poorly understood. The present paper aimed at investigating related questions in the dorsal hippocampus (DH) during contextual fear consolidation.