 “Pain prevalence among adults in the United States has increased 25% over the past two decades, resulting in high health-care costs and impacts to patient quality of life. In the last 30 years, our understanding of pain circuits and (intra)cellular mechanisms has grown exponentially, but this understanding has not yet resulted in improved therapies. Options for pain management are limited. Many analgesics have poor efficacy and are accompanied by severe side effects such as addiction, resulting in a devastating opioid abuse and overdose epidemic. These problems have encouraged scientists to identify novel molecular targets and develop alternative pain therapeutics.
“Pain prevalence among adults in the United States has increased 25% over the past two decades, resulting in high health-care costs and impacts to patient quality of life. In the last 30 years, our understanding of pain circuits and (intra)cellular mechanisms has grown exponentially, but this understanding has not yet resulted in improved therapies. Options for pain management are limited. Many analgesics have poor efficacy and are accompanied by severe side effects such as addiction, resulting in a devastating opioid abuse and overdose epidemic. These problems have encouraged scientists to identify novel molecular targets and develop alternative pain therapeutics.
Increasing preclinical and clinical evidence suggests that cannabis has several beneficial pharmacological activities, including pain relief.
Cannabis sativa contains more than 500 chemical compounds, with two principle phytocannabinoids, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Beyond phytocannabinoids, more than 150 terpenes have been identified in different cannabis chemovars. Although the predominant cannabinoids, Δ9-THC and CBD, are thought to be the primary medicinal compounds, terpenes including the monoterpenes β-myrcene, α-pinene, limonene, and linalool, as well as the sesquiterpenes β-caryophyllene and α-humulene may contribute to many pharmacological properties of cannabis, including anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects.
The aim of this review is to summarize our current knowledge about terpene compounds in cannabis and to analyze the available scientific evidence for a role of cannabis-derived terpenes in modern pain management.
SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Decades of research have improved our knowledge of cannabis polypharmacy and contributing phytochemicals, including terpenes. Reform of the legal status for cannabis possession and increased availability (medicinal and recreational) have resulted in cannabis use to combat the increasing prevalence of pain and may help to address the opioid crisis. Better understanding of the pharmacological effects of cannabis and its active components, including terpenes, may assist in identifying new therapeutic approaches and optimizing the use of cannabis and/or terpenes as analgesic agents.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34663685/
“Cannabis sativa has been used for medical, recreational, and spiritual purposes for thousands of years. Modern scientific studies have provided increasing amounts of preclinical and clinical evidence about its beneficial pharmacological effects, including pain relief. Recent changes in the legislation of cannabis usage and possession have resulted in cannabis-based products becoming widely used alternatives in fighting against many different illnesses. Medical marijuana has been applied to treat a host of indications, but the most frequent, and evidence-backed indication, is pain. Overall, cannabis terpenes have a high potential for pain management, alone or as adjunctive therapeutics, and are attractive compounds for the development of terpene-based analgesics given their generally-recognized-as-safe status with low side effect and toxicity profiles.”

 “Aging is a complex phenomenon associated with a wide spectrum of physical and physiological changes affecting every part of all metazoans, if they escape death prior to reaching maturity. Critical to survival, the immune system evolved as the principal component of response to injury and defense against pathogen invasions. Because how significantly immune system affects and is affected by aging, several neologisms now appear to encapsulate these reciprocal relationships, such as Immunosenescence. The central part of Immunosenescence is Inflammaging -a sustained, low-grade, sterile inflammation occurring after reaching reproductive prime. Once initiated, the impact of Inflammaging and its adverse effects determine the direction and magnitudes of further Inflammaging. In this article, we review the nature of this vicious cycle, we will propose that phytocannabinoids as immune regulators may possess the potential as effective adjunctive therapies to slow and, in certain cases, reverse the pathologic senescence to permit a more healthy aging.”
“Aging is a complex phenomenon associated with a wide spectrum of physical and physiological changes affecting every part of all metazoans, if they escape death prior to reaching maturity. Critical to survival, the immune system evolved as the principal component of response to injury and defense against pathogen invasions. Because how significantly immune system affects and is affected by aging, several neologisms now appear to encapsulate these reciprocal relationships, such as Immunosenescence. The central part of Immunosenescence is Inflammaging -a sustained, low-grade, sterile inflammation occurring after reaching reproductive prime. Once initiated, the impact of Inflammaging and its adverse effects determine the direction and magnitudes of further Inflammaging. In this article, we review the nature of this vicious cycle, we will propose that phytocannabinoids as immune regulators may possess the potential as effective adjunctive therapies to slow and, in certain cases, reverse the pathologic senescence to permit a more healthy aging.” “HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND) persist despite the advent of antiretroviral therapy (ART), suggesting underlying systemic and central nervous system (CNS) inflammatory mechanisms.
“HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND) persist despite the advent of antiretroviral therapy (ART), suggesting underlying systemic and central nervous system (CNS) inflammatory mechanisms. “Purpose:
“Purpose: 
 “Interest in CBG (cannabigerol) has been growing in the past few years, due to its anti-inflammatory properties and other therapeutic benefits.
“Interest in CBG (cannabigerol) has been growing in the past few years, due to its anti-inflammatory properties and other therapeutic benefits. 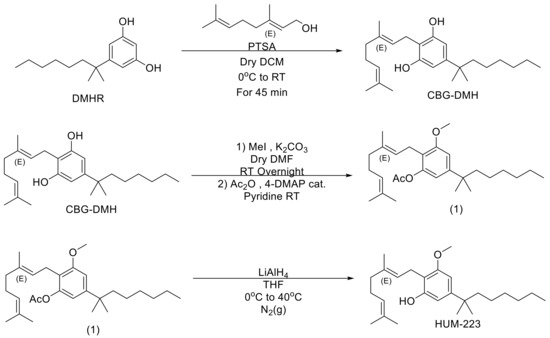
 “The global incidence of respiratory diseases and complications is increasing. Therefore, new methods of treatment, as well as prevention, need to be investigated.
“The global incidence of respiratory diseases and complications is increasing. Therefore, new methods of treatment, as well as prevention, need to be investigated.  “Given the abundancy of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE-2) receptors density, beyond the lung, the intestine is considered as an alternative site of infection and replication for severe acute respiratory syndrome by coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
“Given the abundancy of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE-2) receptors density, beyond the lung, the intestine is considered as an alternative site of infection and replication for severe acute respiratory syndrome by coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2).  “The generation of functional regulatory T cells (Tregs) is essential to keep tissue homeostasis and restore healthy immune responses in many biological and inflammatory contexts.
“The generation of functional regulatory T cells (Tregs) is essential to keep tissue homeostasis and restore healthy immune responses in many biological and inflammatory contexts.  “Objective: Joint injury-induced perturbations to the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a regulator of both inflammation and nociception, remain largely uncharacterized. We employed a mouse model of ACL rupture to assess alterations to nociception, inflammation, and the ECS while using in vitro models to determine whether CB2 agonism can mitigate inflammatory signaling in macrophages and fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS).
“Objective: Joint injury-induced perturbations to the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a regulator of both inflammation and nociception, remain largely uncharacterized. We employed a mouse model of ACL rupture to assess alterations to nociception, inflammation, and the ECS while using in vitro models to determine whether CB2 agonism can mitigate inflammatory signaling in macrophages and fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS). “Aged skeletal muscle undergoes metabolic and structural alterations eventually resulting in a loss of muscle strength and mass, i.e. age-related sarcopenia. Therefore, novel targets for muscle growth purposes in elderly are needed.
“Aged skeletal muscle undergoes metabolic and structural alterations eventually resulting in a loss of muscle strength and mass, i.e. age-related sarcopenia. Therefore, novel targets for muscle growth purposes in elderly are needed.