 “Chronic inflammation is considered to be a silent killer because it is the underlying cause of a wide range of clinical disorders, from cardiovascular to neurological diseases, and from cancer to obesity. In addition, there are over 80 different types of debilitating autoimmune diseases for which there are no cure. Currently, the drugs that are available to suppress chronic inflammation are either ineffective or overtly suppress the inflammation, thereby causing increased susceptibility to infections and cancer. Thus, the development of a new class of drugs that can suppress chronic inflammation is imperative.
“Chronic inflammation is considered to be a silent killer because it is the underlying cause of a wide range of clinical disorders, from cardiovascular to neurological diseases, and from cancer to obesity. In addition, there are over 80 different types of debilitating autoimmune diseases for which there are no cure. Currently, the drugs that are available to suppress chronic inflammation are either ineffective or overtly suppress the inflammation, thereby causing increased susceptibility to infections and cancer. Thus, the development of a new class of drugs that can suppress chronic inflammation is imperative.
Cannabinoids are a group of compounds produced in the body (endocannabinoids) or found in cannabis (phytocannabinoids) that act through cannabinoid receptors and various other receptors expressed widely in the brain and immune system. In the last decade, cannabinoids have been well established experimentally to mediate anti-inflammatory properties. Research has shown that they suppress inflammation through multiple pathways, including apoptosis and inducing immunosuppressive T regulatory cells (Tregs) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs).
Interestingly, cannabinoids also mediate epigenetic alterations in genes that regulate inflammation. In the current review, we highlight how the epigenetic modulations caused by cannabinoids lead to the suppression of inflammation and help identify novel pathways that can be used to target autoimmune diseases.”
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/22/14/7302
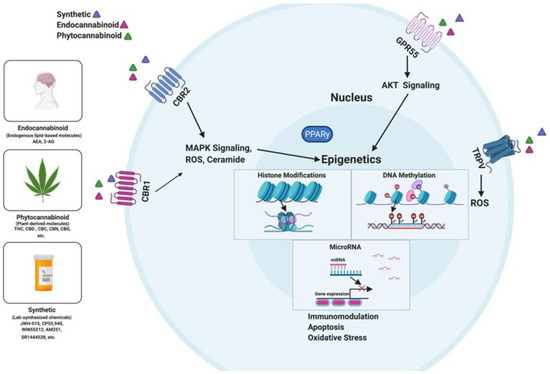

 “The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a composite cell-signaling system that allows endogenous cannabinoid ligands to control cell functions through the interaction with cannabinoid receptors. Modifications of the ECS might contribute to the pathogenesis of different diseases, including cancers. However, the use of these compounds as antitumor agents remains debatable.
“The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a composite cell-signaling system that allows endogenous cannabinoid ligands to control cell functions through the interaction with cannabinoid receptors. Modifications of the ECS might contribute to the pathogenesis of different diseases, including cancers. However, the use of these compounds as antitumor agents remains debatable. 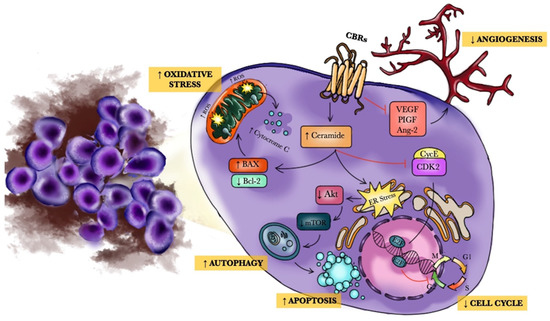
 “Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and antiretroviral therapy can independently induce HIV-associated neuropathic pain (HIV-NP).
“Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and antiretroviral therapy can independently induce HIV-associated neuropathic pain (HIV-NP). “The therapeutic potential of
“The therapeutic potential of 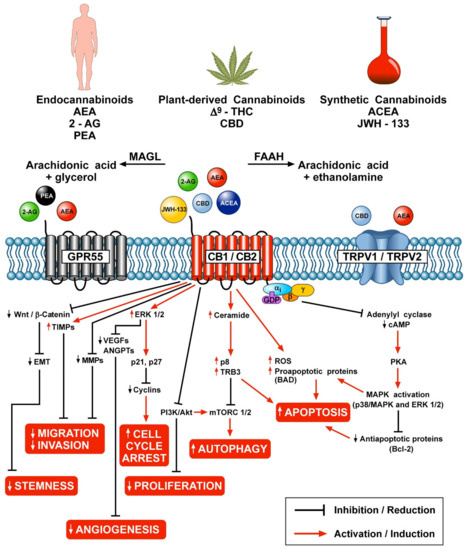
 “Venous Leg Ulcers are highly prevalent lower limb integumentary wounds that remain challenging to heal despite the use of evidence-based compression therapies. A multitude of adjuvant treatments have been studied but none have demonstrated enough efficacy to gain adoption into treatment guidelines.
“Venous Leg Ulcers are highly prevalent lower limb integumentary wounds that remain challenging to heal despite the use of evidence-based compression therapies. A multitude of adjuvant treatments have been studied but none have demonstrated enough efficacy to gain adoption into treatment guidelines.  “Cannabinoids such as ▵-9-THC and CBD can downregulate the immune response by modulating the endocannabinoid system. This modulation is relevant for the treatment of prevalent autoimmune diseases (ADs), such as multiple sclerosis (MS), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), diabetes mellitus type 1 (DMT1), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). These conditions require new therapeutic options with fewer side effects for the control of the autoimmune response. Objective: to conduct a literature review of preclinical scientific evidence that supports further clinical investigations for the use of cannabinoids (natural or synthetic) as potential immunomodulators of the immune response in ADs.
“Cannabinoids such as ▵-9-THC and CBD can downregulate the immune response by modulating the endocannabinoid system. This modulation is relevant for the treatment of prevalent autoimmune diseases (ADs), such as multiple sclerosis (MS), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), diabetes mellitus type 1 (DMT1), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). These conditions require new therapeutic options with fewer side effects for the control of the autoimmune response. Objective: to conduct a literature review of preclinical scientific evidence that supports further clinical investigations for the use of cannabinoids (natural or synthetic) as potential immunomodulators of the immune response in ADs.  “Agents targeting the endocannabinoid system (ECS) have gained attention as potential cancer treatments. Given recent evidence that cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2R) regulates lymphocyte development and inflammation, we performed studies on CB2R in the immune response against melanoma. Analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data revealed a strong positive correlation between CB2R expression and survival, as well as B cell infiltration in human melanoma. In a murine melanoma model, CB2R expression reduced the growth of melanoma as well as the B cell frequencies in the tumor microenvironment (TME), compared to CB2R-deficient mice. In depth analysis of tumor-infiltrating B cells using single-cell RNA sequencing suggested a less differentiated phenotype in tumors from
“Agents targeting the endocannabinoid system (ECS) have gained attention as potential cancer treatments. Given recent evidence that cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2R) regulates lymphocyte development and inflammation, we performed studies on CB2R in the immune response against melanoma. Analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data revealed a strong positive correlation between CB2R expression and survival, as well as B cell infiltration in human melanoma. In a murine melanoma model, CB2R expression reduced the growth of melanoma as well as the B cell frequencies in the tumor microenvironment (TME), compared to CB2R-deficient mice. In depth analysis of tumor-infiltrating B cells using single-cell RNA sequencing suggested a less differentiated phenotype in tumors from 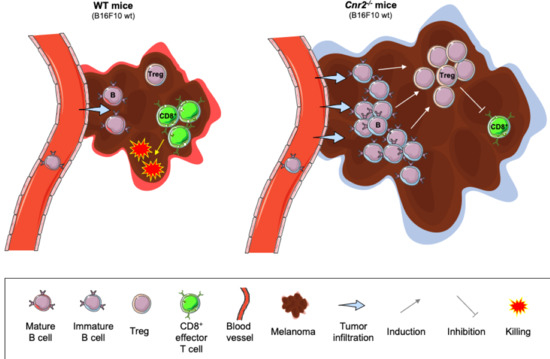

 “Cannabis was extensively utilized for its medicinal properties till the 19th century. A steep decline in its medicinal usage was observed later due to its emergence as an illegal recreational drug. Advances in technology and scientific findings led to the discovery of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound of cannabis, that further led to the discovery of endogenous cannabinoids system consisting of G-protein-coupled receptors – cannabinoid receptor 1 and cannabinoid receptor 2 along with their ligands, mainly anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Endocannabinoid (EC) is shown to be a modulator not only for physiological functions but also for the immune system, endocrine network, and central nervous system. Medicinal research and meta-data analysis over the last few decades have shown a significant potential for both THC and cannabidiol (CBD) to exert palliative effects. People suffering from many forms of advanced stages of cancers undergo chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting followed by severe and chronic neuropathic pain and weight loss. THC and CBD exhibit effective analgesic, anxiolytic, and appetite-stimulating effect on patients suffering from cancer. Drugs currently available in the market to treat such chemotherapy-induced cancer-related ailments are Sativex (GW Pharmaceutical), Dronabinol (Unimed Pharmaceuticals), and Nabilone (Valeant Pharmaceuticals). Apart from exerting palliative effects, THC also shows promising role in the treatment of cancer growth, neurodegenerative diseases (multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease), and alcohol addiction and hence should be exploited for potential benefits. The current review discusses the nature and role of CB receptors, specific applications of cannabinoids, and major studies that have assessed the role of cannabinoids in cancer management.”
“Cannabis was extensively utilized for its medicinal properties till the 19th century. A steep decline in its medicinal usage was observed later due to its emergence as an illegal recreational drug. Advances in technology and scientific findings led to the discovery of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound of cannabis, that further led to the discovery of endogenous cannabinoids system consisting of G-protein-coupled receptors – cannabinoid receptor 1 and cannabinoid receptor 2 along with their ligands, mainly anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Endocannabinoid (EC) is shown to be a modulator not only for physiological functions but also for the immune system, endocrine network, and central nervous system. Medicinal research and meta-data analysis over the last few decades have shown a significant potential for both THC and cannabidiol (CBD) to exert palliative effects. People suffering from many forms of advanced stages of cancers undergo chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting followed by severe and chronic neuropathic pain and weight loss. THC and CBD exhibit effective analgesic, anxiolytic, and appetite-stimulating effect on patients suffering from cancer. Drugs currently available in the market to treat such chemotherapy-induced cancer-related ailments are Sativex (GW Pharmaceutical), Dronabinol (Unimed Pharmaceuticals), and Nabilone (Valeant Pharmaceuticals). Apart from exerting palliative effects, THC also shows promising role in the treatment of cancer growth, neurodegenerative diseases (multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease), and alcohol addiction and hence should be exploited for potential benefits. The current review discusses the nature and role of CB receptors, specific applications of cannabinoids, and major studies that have assessed the role of cannabinoids in cancer management.”