“The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is natural physiological system in the humans. The presence of the ECS system involves different roles in body. The endocannabinoid system involves regulation of most of the centers, which regulates the hunger and leads to changes in the weight.
“The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is natural physiological system in the humans. The presence of the ECS system involves different roles in body. The endocannabinoid system involves regulation of most of the centers, which regulates the hunger and leads to changes in the weight.
In the present article, we reviewed the role of natural cannabinoid compounds in metabolic disorders and related complications. We studied variety of a plant-derived cannabinoids in treating the metabolic syndrome including stoutness, fatty acid liver diseases, insulin obstruction, dementia, hypertension, lipid abnormalities, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, endothelial damage, and polycystic ovarian syndrome and so on.
The activation of cannabinoid receptors demonstrates a significant number of beneficial approaches concerning metabolic syndrome and reduces the pro-inflammatory cytokines on account of aggravation, decreased oxidative stress and uneasiness, diminishes liver fibrosis, with reduces adiponectin.
Pre-clinical investigations of plant-derived cannabinoids resulted in promising outcomes.
The different distinctive plant-derived cannabinoids were discovered like cannabidiol (CBD), cannabinol (CBN), cannabichromene (CBC), and cannabidiol (CBG). It has been observed that endogenous cannabinoids and plant-derived cannabinoids have an advantageous impact on limiting the metabolic disorder arising due to lifestyle changes.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33113429/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0753332220310817?via%3Dihub

 “This article provides a concise overview of how cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system (ECS) have significant implications for the prevention and treatment of metabolic syndrome (MetS) and for the treatment of cardiovascular disorders, including cardiac fibrosis.
“This article provides a concise overview of how cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system (ECS) have significant implications for the prevention and treatment of metabolic syndrome (MetS) and for the treatment of cardiovascular disorders, including cardiac fibrosis. “Numerous studies showed that sustained obesity results in accumulation of bioactive lipid derivatives in several tissues, including skeletal muscle, which further contributes to the development of metabolic disturbances and insulin resistance (IR).
“Numerous studies showed that sustained obesity results in accumulation of bioactive lipid derivatives in several tissues, including skeletal muscle, which further contributes to the development of metabolic disturbances and insulin resistance (IR). “Literature on the association between cannabis use and body mass index (BMI) among adults suggests that greater cannabis use is associated with a lower BMI. However, results are mixed among adolescents, with both cross-sectional and longitudinal studies finding positive, negative, and nonsignificant associations between cannabis use and BMI.
“Literature on the association between cannabis use and body mass index (BMI) among adults suggests that greater cannabis use is associated with a lower BMI. However, results are mixed among adolescents, with both cross-sectional and longitudinal studies finding positive, negative, and nonsignificant associations between cannabis use and BMI. “The synthetic atypical cannabinoid Abn-CBD, a
“The synthetic atypical cannabinoid Abn-CBD, a  “The cellular microenvironment plays a critical role in the maintenance of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) and their subsequent cell lineage differentiation. Recent studies suggested that individuals with adipocyte-related metabolic disorders have altered function and adipogenic potential of adipose stem cell subpopulations, primarily BM-MSCs, increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke or diabetes.
“The cellular microenvironment plays a critical role in the maintenance of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) and their subsequent cell lineage differentiation. Recent studies suggested that individuals with adipocyte-related metabolic disorders have altered function and adipogenic potential of adipose stem cell subpopulations, primarily BM-MSCs, increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke or diabetes.
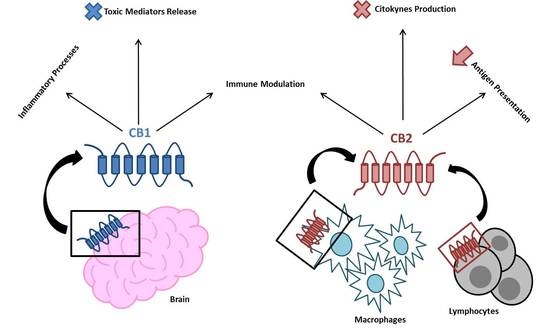
 “Endocannabinoid system consists of
“Endocannabinoid system consists of