 “Cannabis sativa L. turned out to be a valuable source of chemical compounds of various structures, showing pharmacological activity. The most important groups of compounds include phytocannabinoids and terpenes.
“Cannabis sativa L. turned out to be a valuable source of chemical compounds of various structures, showing pharmacological activity. The most important groups of compounds include phytocannabinoids and terpenes.
The pharmacological activity of Cannabis (in epilepsy, sclerosis multiplex (SM), vomiting and nausea, pain, appetite loss, inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs), Parkinson’s disease, Tourette’s syndrome, schizophrenia, glaucoma, and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)), which has been proven so far, results from the affinity of these compounds predominantly for the receptors of the endocannabinoid system (the cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1), type two (CB2), and the G protein-coupled receptor 55 (GPR55)) but, also, for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR), glycine receptors, serotonin receptors (5-HT), transient receptor potential channels (TRP), and GPR, opioid receptors.
The synergism of action of phytochemicals present in Cannabis sp. raw material is also expressed in their increased bioavailability and penetration through the blood-brain barrier. This review provides an overview of phytochemistry and pharmacology of compounds present in Cannabis extracts in the context of the current knowledge about their synergistic actions and the implications of clinical use in the treatment of selected diseases.”
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/22/2/778

 “The potential therapeutic use of some Cannabis sativa plant compounds has been attracting great interest, especially for managing neuropsychiatric disorders due to the relative lack of efficacy of the current treatments.
“The potential therapeutic use of some Cannabis sativa plant compounds has been attracting great interest, especially for managing neuropsychiatric disorders due to the relative lack of efficacy of the current treatments.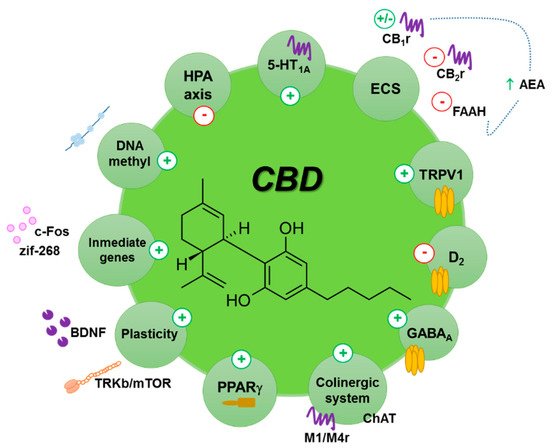
 “Emotional dysregulation and anxiety are common in people at clinical high risk for psychosis (CHR) and are associated with altered neural responses to emotional stimuli in the striatum and medial temporal lobe.
“Emotional dysregulation and anxiety are common in people at clinical high risk for psychosis (CHR) and are associated with altered neural responses to emotional stimuli in the striatum and medial temporal lobe. “During the last decades, researchers have investigated the functional relevance of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in normal brain function as well as in the pathogenesis of diverse psychiatric conditions.
“During the last decades, researchers have investigated the functional relevance of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in normal brain function as well as in the pathogenesis of diverse psychiatric conditions. “Cannabidiol (
“Cannabidiol ( “Gestational methylazoxymethanol acetate (MAM) treatment produces offspring with adult phenotype relevant to schizophrenia, including positive- and negative-like symptoms, cognitive deficits, dopaminergic dysfunction, structural and functional abnormalities.
“Gestational methylazoxymethanol acetate (MAM) treatment produces offspring with adult phenotype relevant to schizophrenia, including positive- and negative-like symptoms, cognitive deficits, dopaminergic dysfunction, structural and functional abnormalities.
 “Considering data from in vitro and in vivo studies,
“Considering data from in vitro and in vivo studies,  “Preclinical and clinical data indicate that
“Preclinical and clinical data indicate that  “The most recent studies published or initiated in the last 18 months, investigating cannabidiol in the treatment of symptoms of schizophrenia and related conditions are summarized, including observed tolerability and reported side-effects.
“The most recent studies published or initiated in the last 18 months, investigating cannabidiol in the treatment of symptoms of schizophrenia and related conditions are summarized, including observed tolerability and reported side-effects.