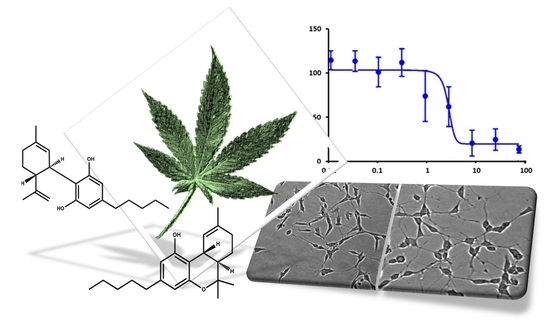
 “In this proof-of-concept study, the antioxidant activity of phytocannabinoids, namely cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9- tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), were investigated using an in vitro system of differentiated human neuronal SY-SH5Y cells.
“In this proof-of-concept study, the antioxidant activity of phytocannabinoids, namely cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9- tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), were investigated using an in vitro system of differentiated human neuronal SY-SH5Y cells.
We showed that THC had a high potency to combat oxidative stress in both in vitro models, while CBD did not show a remarkable antioxidant activity. The cannabis extracts also exhibited a significant antioxidant activity, which depended on the ratio of the THC and CBD. However, our results did not suggest any antagonist effect of the CBD on the antioxidant activity of THC. The effect of cannabis extracts on the cell viability of differentiated human neuronal SY-SH5Y cells was also investigated, which emphasized the differences between the bioactivity of cannabis extracts due to their composition.
Our preliminary results demonstrated that cannabis extracts and phytocannabinoids have a promising potential as antioxidants, which can be further investigated to develop novel pharmaceuticals targeting oxidative stress therapy.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33105840/
https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/13/11/328

 “Evidence details how cannabis can influence the use of other psychoactive substances, including prescription medications, alcohol, tobacco and illicit drugs, but very little research has examined the factors associated with these changes in substance use patterns. This paper explores the self-reported use of cannabis as a substitute for alcohol among a Canadian medical cannabis patient population.
“Evidence details how cannabis can influence the use of other psychoactive substances, including prescription medications, alcohol, tobacco and illicit drugs, but very little research has examined the factors associated with these changes in substance use patterns. This paper explores the self-reported use of cannabis as a substitute for alcohol among a Canadian medical cannabis patient population. “Cannabis is a historical plant which has been used as a medicine in East Asia.
“Cannabis is a historical plant which has been used as a medicine in East Asia. “We aimed to comprehensively evaluate the effects of medical marijuana on symptoms that are relevant to movement disorders with a focus on Huntington disease (HD).
“We aimed to comprehensively evaluate the effects of medical marijuana on symptoms that are relevant to movement disorders with a focus on Huntington disease (HD). “Although studied in a few randomized controlled trials (RCTs), the efficacy of medical cannabis (MC) for chronic pain remains controversial. Using an alternative approach, this multicenter, questionnaire-based prospective cohort was aimed to assess the long-term effects of MC on chronic pain of various etiologies and to identify predictors for MC treatment success.
“Although studied in a few randomized controlled trials (RCTs), the efficacy of medical cannabis (MC) for chronic pain remains controversial. Using an alternative approach, this multicenter, questionnaire-based prospective cohort was aimed to assess the long-term effects of MC on chronic pain of various etiologies and to identify predictors for MC treatment success. “This study evaluated the synergistic anti-cancer potential of cannabinoid combinations across the MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 human breast cancer cell lines. Cannabinoids were combined and their synergistic interactions were evaluated using median effect analysis.
“This study evaluated the synergistic anti-cancer potential of cannabinoid combinations across the MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 human breast cancer cell lines. Cannabinoids were combined and their synergistic interactions were evaluated using median effect analysis. “Background: Little is known about the the acute effects of cannabis on symptoms of OCD in humans. Therefore, this study sought to: 1) examine whether symptoms of OCD are significantly reduced after inhaling cannabis, 2) examine predictors (gender, dose, cannabis constituents, time) of these symptom changes and 3) explore potential long-term consequences of repeatedly using cannabis to self-medicate for OCD symptoms, including changes in dose and baseline symptom severity over time.
“Background: Little is known about the the acute effects of cannabis on symptoms of OCD in humans. Therefore, this study sought to: 1) examine whether symptoms of OCD are significantly reduced after inhaling cannabis, 2) examine predictors (gender, dose, cannabis constituents, time) of these symptom changes and 3) explore potential long-term consequences of repeatedly using cannabis to self-medicate for OCD symptoms, including changes in dose and baseline symptom severity over time. “The purpose of this study was to evaluate the antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of two extracts from a new Chinese accession (G-309) of Cannabis sativa L. (Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabinol <0.2%) with high content of propyl side chain phytocannabinoids.
“The purpose of this study was to evaluate the antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of two extracts from a new Chinese accession (G-309) of Cannabis sativa L. (Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabinol <0.2%) with high content of propyl side chain phytocannabinoids. “The inflammatory sequence is the first phase of wound healing. Macrophages (MPhs) and mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) respond to an inflammatory microenvironment by adapting their functional activity, which polarizes them into the pro-inflammatory phenotypes M1 and MSC1. Prolongation of the inflammatory phase results in the formation of chronic wounds. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) possesses immunomodulatory properties that may impede this cellular phenotypic switch.
“The inflammatory sequence is the first phase of wound healing. Macrophages (MPhs) and mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) respond to an inflammatory microenvironment by adapting their functional activity, which polarizes them into the pro-inflammatory phenotypes M1 and MSC1. Prolongation of the inflammatory phase results in the formation of chronic wounds. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) possesses immunomodulatory properties that may impede this cellular phenotypic switch. “Graft versus host disease (GVHD) pathophysiology is a complex interplay between cells that comprise the adaptive and innate arms of the immune system. Effective prophylactic strategies are therefore contingent upon approaches that address contributions from both immune cell compartments.
“Graft versus host disease (GVHD) pathophysiology is a complex interplay between cells that comprise the adaptive and innate arms of the immune system. Effective prophylactic strategies are therefore contingent upon approaches that address contributions from both immune cell compartments.