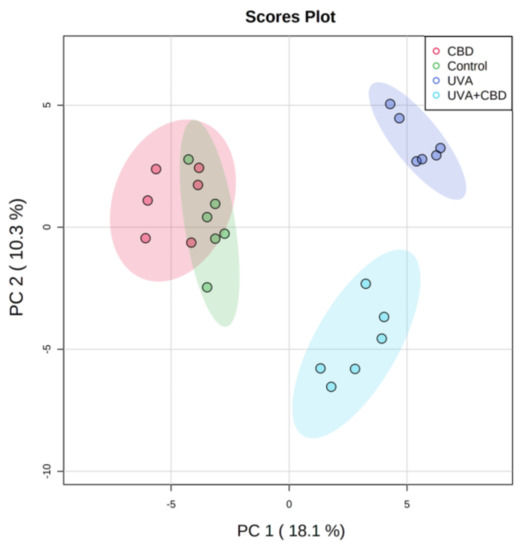
 “UV radiation is a well-established environmental risk factor known to cause oxidative stress and disrupt the metabolism of keratinocyte phospholipids. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
“UV radiation is a well-established environmental risk factor known to cause oxidative stress and disrupt the metabolism of keratinocyte phospholipids. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
In this study, we examined changes in the keratinocyte phospholipid profile from nude rat skin exposed to UVA and UVB radiation that was also treated topically with CBD.
UVA and UVB radiation promoted up-regulation of phosphatidylcholines (PC), lysophosphatidylcholines (LPC), phosphatidylethanolamines (PE) and down-regulation of sphingomyelin (SM) levels and enhanced the activity of phospholipase A2 (PLA2) and sphingomyelinase (SMase).
Application of CBD to the skin of control rats led to down-regulation of SM and up-regulation of SMase activity. After CBD treatment of rats irradiated with UVA or UVB, SM was up-regulated and down-regulated, respectively, while ceramide (CER) levels and SMase activity were down-regulated and up-regulated, respectively. CBD applied to the skin of UV-irradiated rats down-regulated LPC, up-regulated PE and phosphatidylserines (PS) and reduced PLA2 activity.
In conclusion, up-regulation of PS may suggest that CBD inhibits their oxidative modification, while changes in the content of PE and SM may indicate a role of CBD in promoting autophagy and improving the status of the transepidermal barrier.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33255796/
https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3921/9/12/1178

 “Leukocytes are part of the tumor microenvironment (TME) and are critical determinants of tumor progression. Because of the immunoregulatory properties of cannabinoids, the endocannabinoid system (ECS) may have an important role in shaping the TME.
“Leukocytes are part of the tumor microenvironment (TME) and are critical determinants of tumor progression. Because of the immunoregulatory properties of cannabinoids, the endocannabinoid system (ECS) may have an important role in shaping the TME.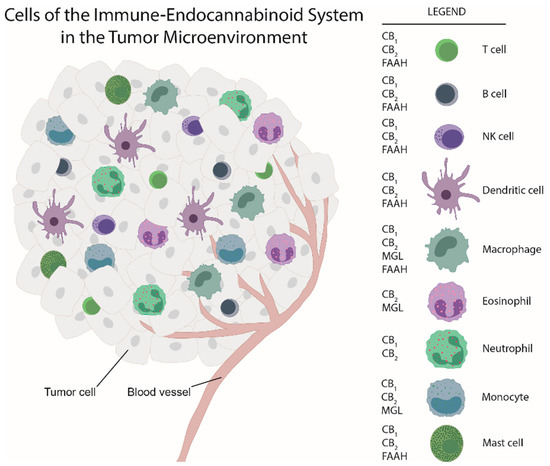
 “There is not a single pharmacological agent with demonstrated therapeutic efficacy for traumatic brain injury (TBI). With recent legalization efforts and the growing popularity of medical cannabis, patients with TBI will inevitably consider medical cannabis as a treatment option.
“There is not a single pharmacological agent with demonstrated therapeutic efficacy for traumatic brain injury (TBI). With recent legalization efforts and the growing popularity of medical cannabis, patients with TBI will inevitably consider medical cannabis as a treatment option. “Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by structural damage, death, and functional disruption of cholinergic neurons (ChNs) as a result of intracellular amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregation, extracellular neuritic plaques, and hyperphosphorylation of protein tau (p-Tau) overtime.
“Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by structural damage, death, and functional disruption of cholinergic neurons (ChNs) as a result of intracellular amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregation, extracellular neuritic plaques, and hyperphosphorylation of protein tau (p-Tau) overtime. “Chronic pelvic pain (CPP) affects up to 15% of women in the United States. The endocannabinoid system is a potential pharmacological target for pelvic pain as cannabinoid receptors are highly expressed in the uterus and other nonreproductive tissues.
“Chronic pelvic pain (CPP) affects up to 15% of women in the United States. The endocannabinoid system is a potential pharmacological target for pelvic pain as cannabinoid receptors are highly expressed in the uterus and other nonreproductive tissues. “Opioid misuse and overuse has contributed to a widespread overdose crisis and many patients and physicians are considering medical cannabis to support opioid tapering and chronic pain control. Using a five-step modified Delphi process, we aimed to develop consensus-based recommendations on: 1) when and how to safely initiate and titrate cannabinoids in the presence of opioids, 2) when and how to safely taper opioids in the presence of cannabinoids, and 3) how to monitor patients and evaluate outcomes when treating with opioids and cannabinoids.
“Opioid misuse and overuse has contributed to a widespread overdose crisis and many patients and physicians are considering medical cannabis to support opioid tapering and chronic pain control. Using a five-step modified Delphi process, we aimed to develop consensus-based recommendations on: 1) when and how to safely initiate and titrate cannabinoids in the presence of opioids, 2) when and how to safely taper opioids in the presence of cannabinoids, and 3) how to monitor patients and evaluate outcomes when treating with opioids and cannabinoids. “Low tetrahydrocannabinol Cannabis sativa products, also known as hemp products, have become widely available and their use in veterinary patients has become increasingly popular. Despite prevalence of use, the veterinary literature is lacking and evidence-based resource for cannabinoid efficacy.
“Low tetrahydrocannabinol Cannabis sativa products, also known as hemp products, have become widely available and their use in veterinary patients has become increasingly popular. Despite prevalence of use, the veterinary literature is lacking and evidence-based resource for cannabinoid efficacy. “Cannabis has long been used for healing and recreation in several regions of the world. Over 400 bioactive constituents, including more than 100 phytocannabinoids, have been isolated from this plant. The non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) and the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) are the major and widely studied constituents from this plant.
“Cannabis has long been used for healing and recreation in several regions of the world. Over 400 bioactive constituents, including more than 100 phytocannabinoids, have been isolated from this plant. The non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) and the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) are the major and widely studied constituents from this plant. “Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a highly infectious respiratory disease caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. A significant proportion of COVID-19 patients develop Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) resulting from hyperactivation of the immune system and cytokine storm, which leads to respiratory and multi-organ failure, and death. Currently, there are no effective treatments against hyperimmune syndrome and ARDS.
“Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a highly infectious respiratory disease caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. A significant proportion of COVID-19 patients develop Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) resulting from hyperactivation of the immune system and cytokine storm, which leads to respiratory and multi-organ failure, and death. Currently, there are no effective treatments against hyperimmune syndrome and ARDS.