 “The potential therapeutic use of some Cannabis sativa plant compounds has been attracting great interest, especially for managing neuropsychiatric disorders due to the relative lack of efficacy of the current treatments.
“The potential therapeutic use of some Cannabis sativa plant compounds has been attracting great interest, especially for managing neuropsychiatric disorders due to the relative lack of efficacy of the current treatments.
Numerous studies have been carried out using the main phytocannabinoids, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). CBD displays an interesting pharmacological profile without the potential for becoming a drug of abuse, unlike THC.
In this review, we focused on the anxiolytic, antidepressant, and antipsychotic effects of CBD found in animal and human studies. In rodents, results suggest that the effects of CBD depend on the dose, the strain, the administration time course (acute vs. chronic), and the route of administration. In addition, certain key targets have been related with these CBD pharmacological actions, including cannabinoid receptors (CB1r and CB2r), 5-HT1A receptor and neurogenesis factors.
Preliminary clinical trials also support the efficacy of CBD as an anxiolytic, antipsychotic, and antidepressant, and more importantly, a positive risk-benefit profile. These promising results support the development of large-scale studies to further evaluate CBD as a potential new drug for the treatment of these psychiatric disorders.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33228239/
https://www.mdpi.com/2218-273X/10/11/1575
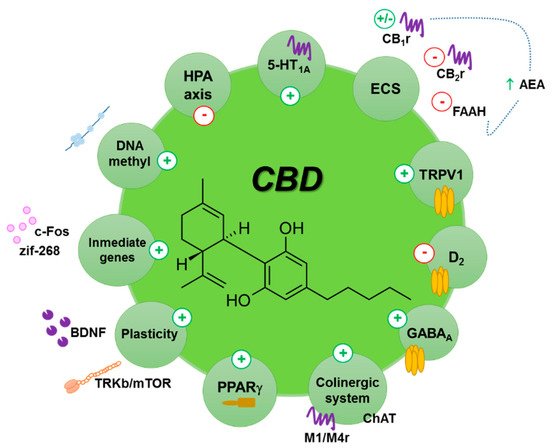

 “The endocannabinoid (eCB) system encompasses the eCBs anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol, their anabolic/catabolic enzymes, and the cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Its expansion to include several eCB-like lipid mediators, their metabolic enzymes, and their molecular targets, forms the endocannabinoidome (eCBome).
“The endocannabinoid (eCB) system encompasses the eCBs anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol, their anabolic/catabolic enzymes, and the cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Its expansion to include several eCB-like lipid mediators, their metabolic enzymes, and their molecular targets, forms the endocannabinoidome (eCBome).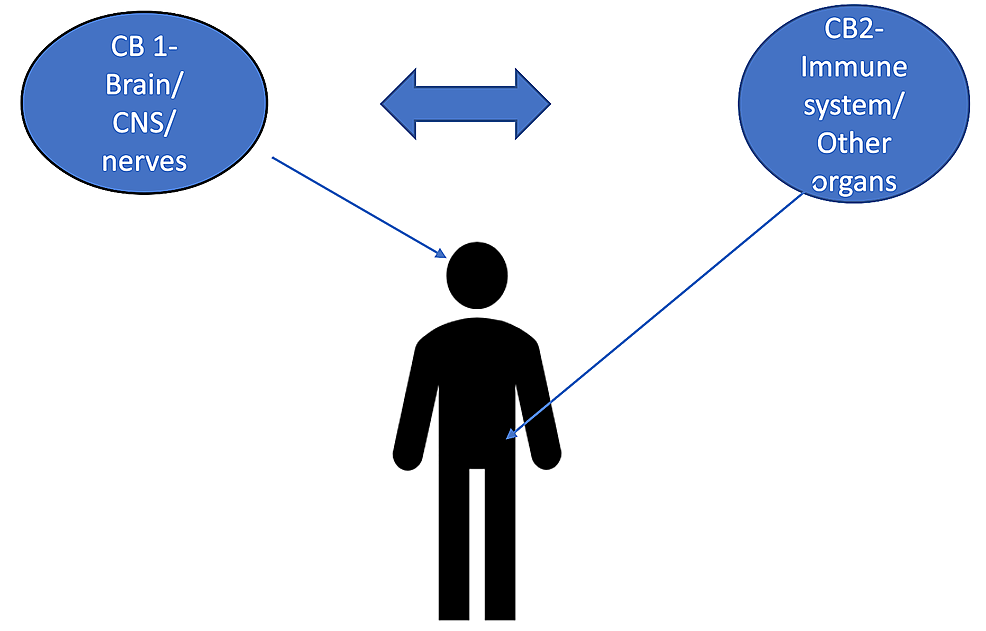 “The burden of chronic pain has affected many individuals leading to distress and discomfort, alongside numerous side effects with conventional therapeutic approaches.
“The burden of chronic pain has affected many individuals leading to distress and discomfort, alongside numerous side effects with conventional therapeutic approaches. “The identification of the human cannabinoid receptors and their roles in health and disease, has been one of the most significant biochemical and pharmacological advancements to have occurred in the past few decades. In spite of the major strides made in furthering endocannabinoid research, therapeutic exploitation of the endocannabinoid system has often been a challenging task.
“The identification of the human cannabinoid receptors and their roles in health and disease, has been one of the most significant biochemical and pharmacological advancements to have occurred in the past few decades. In spite of the major strides made in furthering endocannabinoid research, therapeutic exploitation of the endocannabinoid system has often been a challenging task. “Cannabinoids help in pain treatment through their action on CB1 and CB2 receptors.
“Cannabinoids help in pain treatment through their action on CB1 and CB2 receptors. “∆ 9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (∆9 -THC), the active phytocannabinoid in cannabis, is virtually an adjunct to the endogenous endocannabinoid signaling system.
“∆ 9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (∆9 -THC), the active phytocannabinoid in cannabis, is virtually an adjunct to the endogenous endocannabinoid signaling system. “Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with metabolic syndrome, which often includes obesity, diabetes, and dyslipidemia. Several studies in mice and humans have implicated the involvement of the gut microbiome in NAFLD.
“Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with metabolic syndrome, which often includes obesity, diabetes, and dyslipidemia. Several studies in mice and humans have implicated the involvement of the gut microbiome in NAFLD. “Δ9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the main bioactive compound found in the plant Cannabis sativa, exerts its effects by activating cannabinoid receptors present in many neural cells.
“Δ9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the main bioactive compound found in the plant Cannabis sativa, exerts its effects by activating cannabinoid receptors present in many neural cells. “Cannabis is an annual plant with a long history of use as food, feed, fiber, oil, medicine, and narcotics. Despite realizing its true value, it has not yet found its true place. Cannabis has had a long history with many ups and downs, and now it is our turn to promote it.
“Cannabis is an annual plant with a long history of use as food, feed, fiber, oil, medicine, and narcotics. Despite realizing its true value, it has not yet found its true place. Cannabis has had a long history with many ups and downs, and now it is our turn to promote it.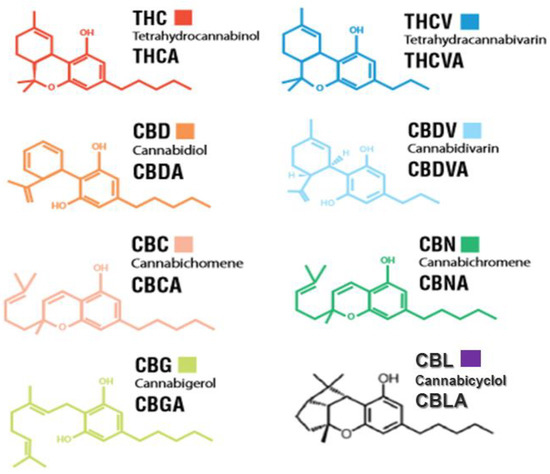
 “Cannabidiol (CBD) is considered a non-psychoactive, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory compound derived from the Cannabis sativa plant.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is considered a non-psychoactive, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory compound derived from the Cannabis sativa plant.