 “The cannabis plant (Cannabis sativa L.) produces an estimated 545 chemical compounds of different biogenetic classes. In addition to economic value, many of these phytochemicals have medicinal and physiological activity. The plant is most popularly known for its two most-prominent and most-studied secondary metabolites-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Both Δ9-THC and CBD have a wide therapeutic window across many ailments and form part of a class of secondary metabolites called cannabinoids-of which approximately over 104 exist.
“The cannabis plant (Cannabis sativa L.) produces an estimated 545 chemical compounds of different biogenetic classes. In addition to economic value, many of these phytochemicals have medicinal and physiological activity. The plant is most popularly known for its two most-prominent and most-studied secondary metabolites-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Both Δ9-THC and CBD have a wide therapeutic window across many ailments and form part of a class of secondary metabolites called cannabinoids-of which approximately over 104 exist.
This review will focus on non-cannabinoid metabolites of Cannabis sativa that also have therapeutic potential, some of which share medicinal properties similar to those of cannabinoids. The most notable of these non-cannabinoid phytochemicals are flavonoids and terpenes. We will also discuss future directions in cannabis research and development of cannabis-based pharmaceuticals. Caflanone, a flavonoid molecule with selective activity against the human viruses including the coronavirus OC43 (HCov-OC43) that is responsible for COVID-19, and certain cancers, is one of the most promising non-cannabinoid molecules that is being advanced into clinical trials.
As validated by thousands of years of the use of cannabis for medicinal purposes, vast anecdotal evidence abounds on the medicinal benefits of the plant. These benefits are attributed to the many phytochemicals in this plant, including non-cannabinoids. The most promising non-cannabinoids with potential to alleviate global disease burdens are discussed.”

 “Non-Uremic Calciphylaxis (NUC) is a rare condition that often manifests as intractable and painful integumentary wounds, afflicting patients with a high burden of co-morbidity.
“Non-Uremic Calciphylaxis (NUC) is a rare condition that often manifests as intractable and painful integumentary wounds, afflicting patients with a high burden of co-morbidity.
 “Cannflavins are a group of prenylflavonoids derived from Cannabis sativa L.. Cannflavin A (CFL-A), B (CFL-B) and C (CFL-C) have been heralded for their anti-inflammatory properties in pre-clinical evaluations.
“Cannflavins are a group of prenylflavonoids derived from Cannabis sativa L.. Cannflavin A (CFL-A), B (CFL-B) and C (CFL-C) have been heralded for their anti-inflammatory properties in pre-clinical evaluations. “Hemp (Cannabis sativa) is an angiosperm plant belonging to the Cannabaceae family. Its cultivation dates back to centuries. It has always been cultivated due to the possibility of exploiting almost all the parts of the plant: paper, fabrics, ropes, bio-compounds with excellent insulating capacity, fuel, biodegradable plastic, antibacterial detergents, and food products, such as flour, oils, seeds, herbal teas, and beer, are indeed obtained from hemp.
“Hemp (Cannabis sativa) is an angiosperm plant belonging to the Cannabaceae family. Its cultivation dates back to centuries. It has always been cultivated due to the possibility of exploiting almost all the parts of the plant: paper, fabrics, ropes, bio-compounds with excellent insulating capacity, fuel, biodegradable plastic, antibacterial detergents, and food products, such as flour, oils, seeds, herbal teas, and beer, are indeed obtained from hemp. “Purpose of review: To evaluate the impact of flavonoids and cannabinoids as anti-inflammatory and antiallergic treatments on the anterior surface of the eye.
“Purpose of review: To evaluate the impact of flavonoids and cannabinoids as anti-inflammatory and antiallergic treatments on the anterior surface of the eye. “In recent years, and even more since its legalization in several jurisdictions, cannabis and the endocannabinoid system have received an increasing amount of interest related to their potential exploitation in clinical settings. Cannabinoids have been suggested and shown to be effective in the treatment of various conditions. In cancer, the endocannabinoid system is altered in numerous types of tumours and can relate to cancer prognosis and disease outcome. Additionally, cannabinoids display anticancer effects in several models by suppressing the proliferation, migration and/or invasion of cancer cells, as well as tumour angiogenesis. However, the therapeutic use of cannabinoids is currently limited to the treatment of symptoms and pain associated with chemotherapy, while their potential use as cytotoxic drugs in chemotherapy still requires validation in patients. Along with cannabinoids, cannabis contains several other compounds that have also been shown to exert anti-tumorigenic actions. The potential anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids, present in cannabis, are explored in this literature review.”
“In recent years, and even more since its legalization in several jurisdictions, cannabis and the endocannabinoid system have received an increasing amount of interest related to their potential exploitation in clinical settings. Cannabinoids have been suggested and shown to be effective in the treatment of various conditions. In cancer, the endocannabinoid system is altered in numerous types of tumours and can relate to cancer prognosis and disease outcome. Additionally, cannabinoids display anticancer effects in several models by suppressing the proliferation, migration and/or invasion of cancer cells, as well as tumour angiogenesis. However, the therapeutic use of cannabinoids is currently limited to the treatment of symptoms and pain associated with chemotherapy, while their potential use as cytotoxic drugs in chemotherapy still requires validation in patients. Along with cannabinoids, cannabis contains several other compounds that have also been shown to exert anti-tumorigenic actions. The potential anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids, present in cannabis, are explored in this literature review.”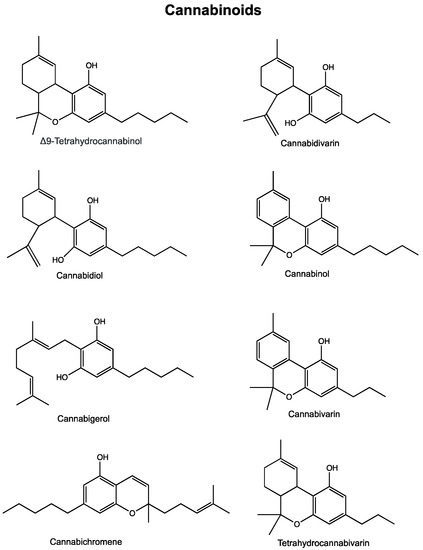

 “Hempseed (Cannabis sativa L.) has beneficial impact on human health mainly because of its wide variability of bioactive compounds. However, many of them are not fully characterized yet. In this work, hempseed was defatted and through a bio-guided studied, two fractions (F03 and F05) with the highest content of phenols, flavonoids and antioxidant capacity were selected. Fractions were chemically analyzed by UHPLC HRMS/MS. The anti-inflammatory capacities of these compounds were evaluated on human monocytes using flow cytometry, RT-qPCR and Elisa procedures. A high amount of phenolic compounds were identified, with the major compound being: N-trans-caffeoyltyramine (6.36 mg g-1 in F05 and 1.28 mg g-1 in F03). Both, F03 and F05 significantly reduced the inflammatory competence of LPS-treated human primary monocytes, decreasing TNF-α and IL-6 gene expression and secretion. These findings indicate that in the defatted fraction of the hempseed there are a wide number of compounds with beneficial potential to prevent and treat inflammatory disorders, as well as other processes caused by oxidative stress.”
“Hempseed (Cannabis sativa L.) has beneficial impact on human health mainly because of its wide variability of bioactive compounds. However, many of them are not fully characterized yet. In this work, hempseed was defatted and through a bio-guided studied, two fractions (F03 and F05) with the highest content of phenols, flavonoids and antioxidant capacity were selected. Fractions were chemically analyzed by UHPLC HRMS/MS. The anti-inflammatory capacities of these compounds were evaluated on human monocytes using flow cytometry, RT-qPCR and Elisa procedures. A high amount of phenolic compounds were identified, with the major compound being: N-trans-caffeoyltyramine (6.36 mg g-1 in F05 and 1.28 mg g-1 in F03). Both, F03 and F05 significantly reduced the inflammatory competence of LPS-treated human primary monocytes, decreasing TNF-α and IL-6 gene expression and secretion. These findings indicate that in the defatted fraction of the hempseed there are a wide number of compounds with beneficial potential to prevent and treat inflammatory disorders, as well as other processes caused by oxidative stress.” “Cannabis has been used for thousands of years in many cultures for the treatment of several ailments including pain.
“Cannabis has been used for thousands of years in many cultures for the treatment of several ailments including pain. “Cannabis research has historically focused on the most prevalent
“Cannabis research has historically focused on the most prevalent