 “Proteins from hemp bran (HPB), a byproduct of the hemp seed food-processing chain, were chemically extracted, hydrolyzed by Alcalase, and separated by membrane ultrafiltration into four fractions (MW <1, 1-3, 3-5, and >5 kDa).
“Proteins from hemp bran (HPB), a byproduct of the hemp seed food-processing chain, were chemically extracted, hydrolyzed by Alcalase, and separated by membrane ultrafiltration into four fractions (MW <1, 1-3, 3-5, and >5 kDa).
The antioxidant and antihypertensive properties of the initial extract and the fractions were evaluated by in vitro assays for their ability to scavenge radical species, bind with metal ions, reduce ferric ions, and inhibit angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) activity.
The hydrolysate was strongly antioxidant and ACE-inhibiting; the most bioactive peptides were further concentrated by ultrafiltration. Of the 239 peptides identified, 47 (12 antioxidant and 35 ACE-inhibitory) exhibited structural features correlated with the specific bioactivity.
These results highlight the promise of hydrolysate and size-based HPB fractions as natural functional ingredients for the food or pharmaceutical industry.”
“In conclusion, this study highlights the potential use of HPB hydrolysate and fractions as multifunctional ingredients for the development of new healthy foods or for the pharmaceutical industry. ”
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c01487


 “In recent decades, a lot of attention has been paid to Cannabis sativa L. due to its useful applications, including in fibers, oil, food for humans and animals, and therapeutics.
“In recent decades, a lot of attention has been paid to Cannabis sativa L. due to its useful applications, including in fibers, oil, food for humans and animals, and therapeutics.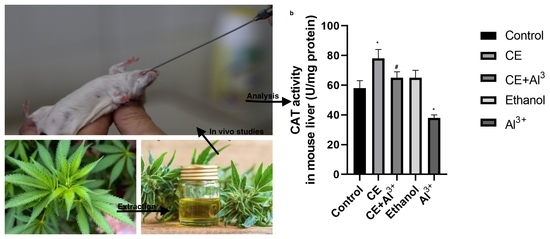
 “Cannabidiol (CBD), a phytochemical derived from
“Cannabidiol (CBD), a phytochemical derived from  “Background:
“Background:  “Nowadays cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the major causes for the reduction of the quality of life.
“Nowadays cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the major causes for the reduction of the quality of life. “Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) were isolated from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUCMSCs) and were further encapsulated with cannabidiol (CBD) through sonication method (CBD EVs). CBD EVs displayed an average particle size of 114.1±1.02 nm, zeta potential of -30.26±0.12 mV, entrapment efficiency of 92.3±2.21% and stability for several months at 4 °C. CBD release from the EVs was observed as 50.74±2.44% and 53.99±1.4% at pH 6.8 and pH 7.4, respectively after 48 h. Ourin-vitrostudies demonstrated that CBD either alone or in EVs form significantly sensitized MDA-MB-231 cells to doxorubicin (DOX) (*P<0.05). Flow cytometry and migration studies revealed that CBD EVs either alone or in combination with DOX induced G1 phase cell cycle arrest and decreased migration of MDA-MB-231 cells, respectively. CBD EVs and DOX combination significantly reduced tumor burden (***P<0.001) in MDA-MB-231 xenograft tumor model. Western blotting and immunocytochemical analysis demonstrated that CBD EVs and DOX combination decreased the expression of proteins involved in inflammation, metastasis and increased the expression of proteins involved in apoptosis. CBD EVs and DOX combination will have profound clinical significance in not only decreasing the side effects but also increasing the therapeutic efficacy of DOX in TNBC.”
“Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) were isolated from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUCMSCs) and were further encapsulated with cannabidiol (CBD) through sonication method (CBD EVs). CBD EVs displayed an average particle size of 114.1±1.02 nm, zeta potential of -30.26±0.12 mV, entrapment efficiency of 92.3±2.21% and stability for several months at 4 °C. CBD release from the EVs was observed as 50.74±2.44% and 53.99±1.4% at pH 6.8 and pH 7.4, respectively after 48 h. Ourin-vitrostudies demonstrated that CBD either alone or in EVs form significantly sensitized MDA-MB-231 cells to doxorubicin (DOX) (*P<0.05). Flow cytometry and migration studies revealed that CBD EVs either alone or in combination with DOX induced G1 phase cell cycle arrest and decreased migration of MDA-MB-231 cells, respectively. CBD EVs and DOX combination significantly reduced tumor burden (***P<0.001) in MDA-MB-231 xenograft tumor model. Western blotting and immunocytochemical analysis demonstrated that CBD EVs and DOX combination decreased the expression of proteins involved in inflammation, metastasis and increased the expression of proteins involved in apoptosis. CBD EVs and DOX combination will have profound clinical significance in not only decreasing the side effects but also increasing the therapeutic efficacy of DOX in TNBC.”
 “Our laboratory is interested in searching for a new plant-based therapeutics to treat ovarian cancer.
“Our laboratory is interested in searching for a new plant-based therapeutics to treat ovarian cancer.
 “Introduction:
“Introduction: