
“Neurodegenerative diseases are an increasing cause of global morbidity and mortality. They occur in the central nervous system (CNS) and lead to functional and mental impairment due to loss of neurons. Recent evidence highlights the link between neurodegenerative and inflammatory diseases of the CNS. These are typically associated with several neurological disorders. These diseases have fundamental differences regarding their underlying physiology and clinical manifestations, although there are aspects that overlap.
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is comprised of receptors (type-1 (CB1R) and type-2 (CB2R) cannabinoid-receptors, as well as transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1)), endogenous ligands and enzymes that synthesize and degrade endocannabinoids (ECBs). Recent studies revealed the involvement of the ECS in different pathological aspects of these neurodegenerative disorders.
The present review will explore the roles of cannabinoid receptors (CBRs) and pharmacological agents that modulate CBRs or ECS activity with reference to Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Parkinson’s Disease (PD), Huntington’s Disease (HD) and multiple sclerosis (MS).”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35336814/
“Neurodegenerative diseases represent an important cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Existing therapeutic options are limited and focus mostly on improving symptoms and reducing exacerbations. The endocannabinoid system is involved in the pathophysiology of such disorders, an idea which has been highlighted by recent scientific work. The current work focusses its attention on the importance and implications of this system and its synthetic and natural ligands in disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s and multiple sclerosis.”
https://www.mdpi.com/2079-7737/11/3/440/htm



 “Cannabis sativa
“Cannabis sativa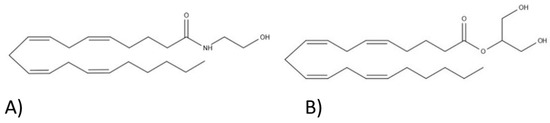
 “Background and purpose:
“Background and purpose:  “In humans, various sites like cannabinoid receptors (CBR) having a binding affinity with cannabinoids are distributed on the surface of different cell types, where endocannabinoids (ECs) and derivatives of fatty acid can bind. The binding of these substance(s) triggers the activation of specific receptors required for various physiological functions, including pain sensation, memory, and appetite.
“In humans, various sites like cannabinoid receptors (CBR) having a binding affinity with cannabinoids are distributed on the surface of different cell types, where endocannabinoids (ECs) and derivatives of fatty acid can bind. The binding of these substance(s) triggers the activation of specific receptors required for various physiological functions, including pain sensation, memory, and appetite. 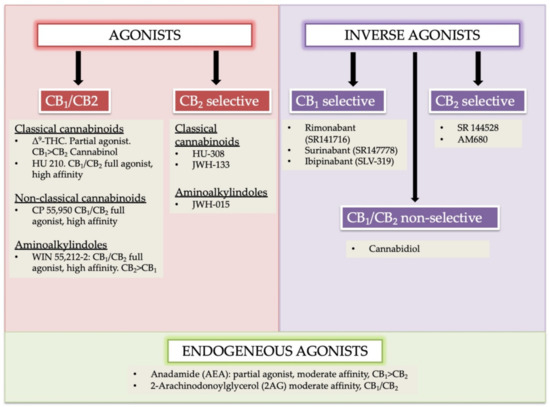
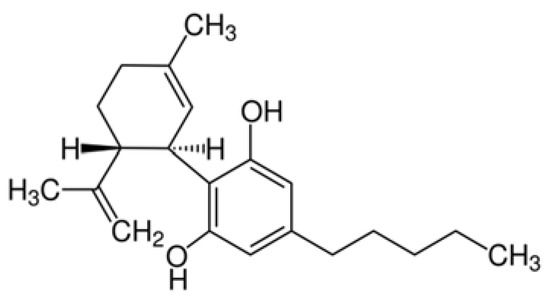
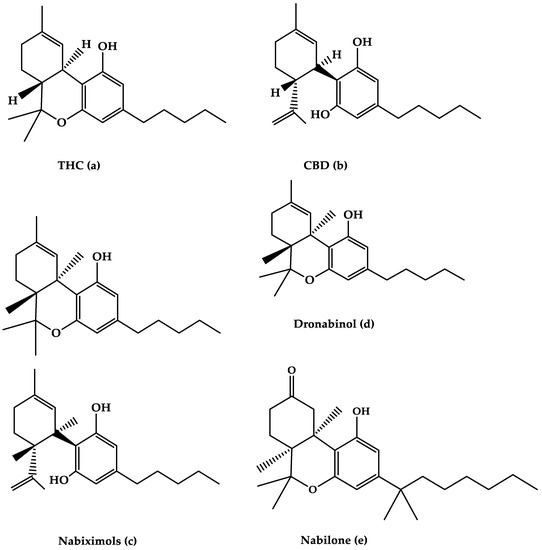
 “Medical cannabis and individual cannabinoids, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), are receiving growing attention in both the media and the scientific literature. The Cannabis plant, however, produces over 100 different cannabinoids, and cannabigerol (CBG) serves as the precursor molecule for the most abundant phytocannabinoids.
“Medical cannabis and individual cannabinoids, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), are receiving growing attention in both the media and the scientific literature. The Cannabis plant, however, produces over 100 different cannabinoids, and cannabigerol (CBG) serves as the precursor molecule for the most abundant phytocannabinoids.