 “Background: Various factors trigger the inflammatory response and cytokine activation in skeletal muscle. Inflamed muscle will exhibit significant levels of inflammation and cytokine activity. Interleukin-6 (IL-6), a pro-inflammatory cytokine, exerts pleiotropic effects on skeletal muscle. Endocannabinoid produced by all cell types binds to a class of G protein-coupled receptors, in particular cannabinoid CB1 receptors, to induce skeletal muscle actions.
“Background: Various factors trigger the inflammatory response and cytokine activation in skeletal muscle. Inflamed muscle will exhibit significant levels of inflammation and cytokine activity. Interleukin-6 (IL-6), a pro-inflammatory cytokine, exerts pleiotropic effects on skeletal muscle. Endocannabinoid produced by all cell types binds to a class of G protein-coupled receptors, in particular cannabinoid CB1 receptors, to induce skeletal muscle actions.
Objective: The purpose of this research was to discover whether activation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in L6 skeletal muscle cells may promote IL-6 gene expression.
Materials and methods: L6 skeletal muscle cells were cultured in 25 cm2 flasks and quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (probe-based) utilised to quantify IL-6 gene expression levels among different treatment settings.
Results: Arachidonyl-2′-chloroethylamide (ACEA) 10 nM, a persistent selective CB1 receptor agonist, promotes IL-6 gene expression in a time-dependent manner. Rimonabant 100 nM, a selective cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, blocks the impact of ACEA. However, insulin does not change IL-6 gene expression.
Conclusion: For the first time, a unique link between ACEA and IL-6 up-regulation has been established; IL-6 up-regulation generated by ACEA is mediated in skeletal muscle through cannabinoid CB1 receptor activation. As a result, cannabinoid CB1 receptors may be useful pharmaceutical targets in the treatment of inflammation and related disorders in skeletal muscle tissues.”
“In the present study, I have demonstrated that when cannabinoid CB1 receptors are activated, the expression of IL-6 increases in a way that is influenced by time. Such findings deliver a novel mechanism characterised by cannabinoid analogue playing the role of a pro-inflammatory mediator in the skeletal muscle tissue. The findings from the present study also imply that there may be a possible therapeutic use of cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist at acute early states for skeletal muscle dysfunction related to inflammation. My findings point to skeletal muscle cell cannabinoid CB1 receptor as a therapeutic target, and expand its potential to include anti-inflammatory effects in diabetes, obesity, and sarcopenia.”

 “Despite the high incidence of traumatic brain injury (TBI), there is no universal treatment to safely treat patients. Blunt brain injuries destroy primary neural tissue that results in impaired perfusion, excessive release of glutamate, inflammation, excitotoxicity, and progressive secondary neuronal cell death.
“Despite the high incidence of traumatic brain injury (TBI), there is no universal treatment to safely treat patients. Blunt brain injuries destroy primary neural tissue that results in impaired perfusion, excessive release of glutamate, inflammation, excitotoxicity, and progressive secondary neuronal cell death.  “Introduction:
“Introduction: “Oral ulcer is a common oral inflammatory lesion accompanied by severe pain but with few effective treatments. Cannabidiol (CBD) is recently emerging for its therapeutic potential in a range of diseases, including inflammatory conditions and cancers.
“Oral ulcer is a common oral inflammatory lesion accompanied by severe pain but with few effective treatments. Cannabidiol (CBD) is recently emerging for its therapeutic potential in a range of diseases, including inflammatory conditions and cancers. “Significant growth of interest in cannabis (
“Significant growth of interest in cannabis (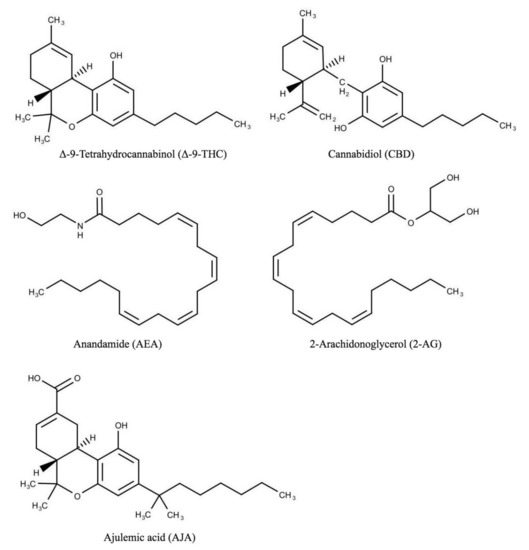
 “Background:
“Background:  “Objectives:
“Objectives: