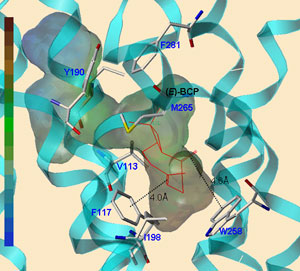
“Considering the advantages of using medicinal herbs as supplementary treatments to sensitize conventional anti-cancer drugs, studying functional mechanisms and regulatory effects of Echinacea purpurea (as a non-cannabinoid plant)
“Considering the advantages of using medicinal herbs as supplementary treatments to sensitize conventional anti-cancer drugs, studying functional mechanisms and regulatory effects of Echinacea purpurea (as a non-cannabinoid plant) 
and Cannabis sativa (as a cannabinoid plant) are timely and required.
The potential effects of such herbs on lung cancer cell growth, apoptosis, cell cycle distribution, cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) level, caspase activity and their cannabinomimetic properties on the CB2 receptor are addressed in the current study.
Results: Echinacea purpurea (EP) root extract induced a considerable decrease in A549 viable cells, showing a time and dose-dependent response. The cell toxicity of EP was accompanied by induction of early apoptosis and cell accumulation at the sub G1 phase of the cell cycle. The elevation of cellular ROS level and caspase 3 activity indicate ROS-induced caspase-dependent apoptosis following the treatment of A549 cells by EP extract. The observed effects of EP extract on A549 growth and death were abrogated following blockage of CB2 using AM630, a specific antagonist of the CB2 receptor. Increasing concentrations of Cannabis sativa (CS) induced A549 cell death in a time-dependent manner, followed by induction of early apoptosis, cell cycle arrest at sub G1 phase, elevation of ROS level, and activation of caspase 3. The CB2 blockage caused attenuation of CS effects on A549 cell death which revealed consistency with the effects of EP extract on A549 cells.
Conclusions: The pro-apoptotic effects of EP and CS extracts on A549 cells and their possible regulatory role of CB2 activity might be attributed to metabolites of both herbs. These effects deserve receiving more attention as alternative anti-cancer agents.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33446187/
“Both cannabinoid receptors and naturally occurring cannabinoids, known as phytocannabinoids, have potential therapeutic applications based on their pivotal roles in regulating immunologic responses, alleviating inflammation, tumor cell proliferation, angiogenesis, invasion, and migration. Based on the findings, it can be postulated that EP and CS extracts can inhibit lung cancer cell growth and induce apoptosis and should be considered as an alternative anti-cancer agent in lung cancer.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7809807/


 “Beta-caryophyllene is an odoriferous bicyclic sesquiterpene found in various herbs and spices.
“Beta-caryophyllene is an odoriferous bicyclic sesquiterpene found in various herbs and spices. “Depression is a widespread psychological disorder that affects up to 20% of the world’s population. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), with its unique curative effect in depression treatment, is gaining increasing attention as the discovery of novel antidepressant drug has become the pursuit of pharmaceutical. This article summarizes the work done on the natural products from TCM that have been reported to conceive antidepressant effects in the past two decades, which can be classified according to various mechanisms including increasing synaptic concentrations of monoamines, alleviating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis dysfunctions, lightening the impairment of neuroplasticity, fighting towards immune and inflammatory dysregulation. The antidepressant active ingredients identified can be generally divided into saponins, flavonoids, alkaloids, polysaccharides and others. Albiflorin, Baicalein, Berberine chloride, beta-Asarone, cannabidiol, Curcumin, Daidzein, Echinocystic acid (EA), Emodin, Ferulic acid, Gastrodin, Genistein, Ginsenoside Rb1, Ginsenoside Rg1, Ginsenoside Rg3, Hederagenin, Hesperidin, Honokiol, Hyperoside, Icariin, Isoliquiritin, Kaempferol, Liquiritin, L-theanine, Magnolol, Paeoniflorin, Piperine, Proanthocyanidin, Puerarin, Quercetin, Resveratrol (trans), Rosmarinic acid, Saikosaponin A, Senegenin, Tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside and Vanillic acid are Specified in this review. Simultaneously, chemical structures of the active ingredients with antidepressant activities are listed and their sources, models, efficacy and mechanisms are described. Chinese compound prescription and extracts that exert antidepressant effects are also introduced, which may serve as a source of inspiration for further development. In the view of present study, the antidepressant effect of certain TCMs are affirmative and encouraging. However, there are a lot of work needs to be done to evaluate the exact therapeutic effects and mechanisms of those active ingredients, specifically, to establish a unified standard for diagnosis and evaluation of curative effect.”
“Depression is a widespread psychological disorder that affects up to 20% of the world’s population. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), with its unique curative effect in depression treatment, is gaining increasing attention as the discovery of novel antidepressant drug has become the pursuit of pharmaceutical. This article summarizes the work done on the natural products from TCM that have been reported to conceive antidepressant effects in the past two decades, which can be classified according to various mechanisms including increasing synaptic concentrations of monoamines, alleviating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis dysfunctions, lightening the impairment of neuroplasticity, fighting towards immune and inflammatory dysregulation. The antidepressant active ingredients identified can be generally divided into saponins, flavonoids, alkaloids, polysaccharides and others. Albiflorin, Baicalein, Berberine chloride, beta-Asarone, cannabidiol, Curcumin, Daidzein, Echinocystic acid (EA), Emodin, Ferulic acid, Gastrodin, Genistein, Ginsenoside Rb1, Ginsenoside Rg1, Ginsenoside Rg3, Hederagenin, Hesperidin, Honokiol, Hyperoside, Icariin, Isoliquiritin, Kaempferol, Liquiritin, L-theanine, Magnolol, Paeoniflorin, Piperine, Proanthocyanidin, Puerarin, Quercetin, Resveratrol (trans), Rosmarinic acid, Saikosaponin A, Senegenin, Tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside and Vanillic acid are Specified in this review. Simultaneously, chemical structures of the active ingredients with antidepressant activities are listed and their sources, models, efficacy and mechanisms are described. Chinese compound prescription and extracts that exert antidepressant effects are also introduced, which may serve as a source of inspiration for further development. In the view of present study, the antidepressant effect of certain TCMs are affirmative and encouraging. However, there are a lot of work needs to be done to evaluate the exact therapeutic effects and mechanisms of those active ingredients, specifically, to establish a unified standard for diagnosis and evaluation of curative effect.”