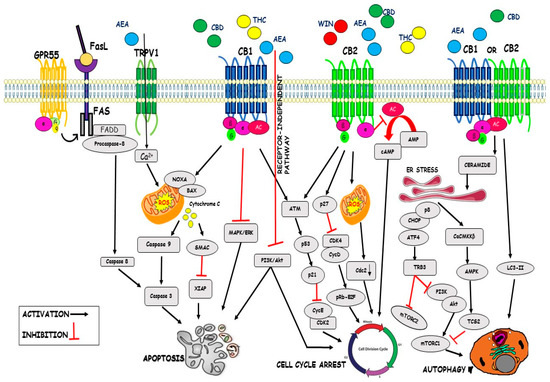
“Cannabinoids are a family of heterogeneous compounds that mostly interact with receptors eliciting several physiological effects both in the central and peripheral nervous systems and in peripheral organs. They exert anticancer action by modulating signaling pathways involved in cancer progression; furthermore, the effects induced by their use depend on both the type of tumor and their action on the components of the endocannabinoid system. This review will explore the mechanism of action of the cannabinoids in signaling pathways involved in cancer proliferation, neovascularisation, migration, invasion, metastasis, and tumor angiogenesis.”
“Cannabinoids are a family of heterogeneous compounds that mostly interact with receptors eliciting several physiological effects both in the central and peripheral nervous systems and in peripheral organs. They exert anticancer action by modulating signaling pathways involved in cancer progression; furthermore, the effects induced by their use depend on both the type of tumor and their action on the components of the endocannabinoid system. This review will explore the mechanism of action of the cannabinoids in signaling pathways involved in cancer proliferation, neovascularisation, migration, invasion, metastasis, and tumor angiogenesis.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33916164/

 “Agents targeting the endocannabinoid system (ECS) have gained attention as potential cancer treatments. Given recent evidence that cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2R) regulates lymphocyte development and inflammation, we performed studies on CB2R in the immune response against melanoma. Analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data revealed a strong positive correlation between CB2R expression and survival, as well as B cell infiltration in human melanoma. In a murine melanoma model, CB2R expression reduced the growth of melanoma as well as the B cell frequencies in the tumor microenvironment (TME), compared to CB2R-deficient mice. In depth analysis of tumor-infiltrating B cells using single-cell RNA sequencing suggested a less differentiated phenotype in tumors from
“Agents targeting the endocannabinoid system (ECS) have gained attention as potential cancer treatments. Given recent evidence that cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2R) regulates lymphocyte development and inflammation, we performed studies on CB2R in the immune response against melanoma. Analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data revealed a strong positive correlation between CB2R expression and survival, as well as B cell infiltration in human melanoma. In a murine melanoma model, CB2R expression reduced the growth of melanoma as well as the B cell frequencies in the tumor microenvironment (TME), compared to CB2R-deficient mice. In depth analysis of tumor-infiltrating B cells using single-cell RNA sequencing suggested a less differentiated phenotype in tumors from 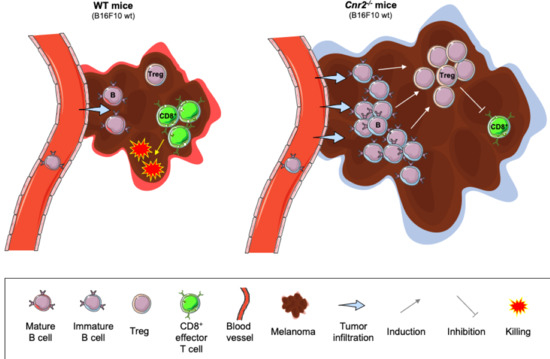
 “Colorectal cancer (CRC) is between the top three occurring cancers worldwide. The anticancer effects of Cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB
“Colorectal cancer (CRC) is between the top three occurring cancers worldwide. The anticancer effects of Cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB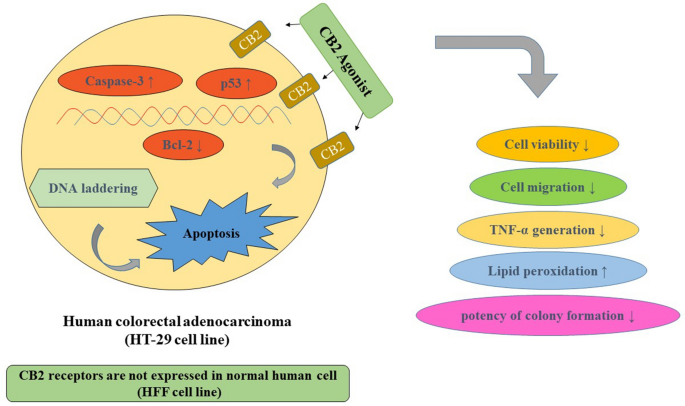
 “In recent years, evidence has accumulated that cannabinoids-especially the non-psychoactive compound, cannabidiol (CBD)-possess promising medical and pharmacological activities that might qualify them as potential anti-tumor drugs. This review is based on multiple studies summarizing different mechanisms for how CBD can target tumor cells including cannabinoid receptors or other constituents of the endocannabinoid system, and their complex activation of biological systems that results in the inhibition of tumor growth. CBD also participates in anti-inflammatory activities which are related to tumor progression, as demonstrated in preclinical models. Although the numbers of clinical trials and tested tumor entities are limited, there is clear evidence that CBD has anti-tumor efficacy and is well tolerated in human cancer patients. In summary, it appears that CBD has potential as a neoadjuvant and/or adjuvant drug in therapy for cancer.”
“In recent years, evidence has accumulated that cannabinoids-especially the non-psychoactive compound, cannabidiol (CBD)-possess promising medical and pharmacological activities that might qualify them as potential anti-tumor drugs. This review is based on multiple studies summarizing different mechanisms for how CBD can target tumor cells including cannabinoid receptors or other constituents of the endocannabinoid system, and their complex activation of biological systems that results in the inhibition of tumor growth. CBD also participates in anti-inflammatory activities which are related to tumor progression, as demonstrated in preclinical models. Although the numbers of clinical trials and tested tumor entities are limited, there is clear evidence that CBD has anti-tumor efficacy and is well tolerated in human cancer patients. In summary, it appears that CBD has potential as a neoadjuvant and/or adjuvant drug in therapy for cancer.”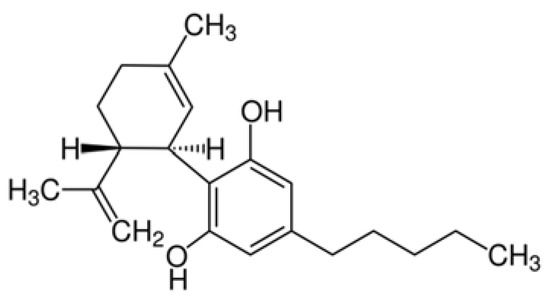
 “
“ “We previously reported that cannabidiol (CBD), a cannabinoid with a low toxicity profile, downregulated the expression of the prometastatic gene inhibitor of DNA binding 1 (
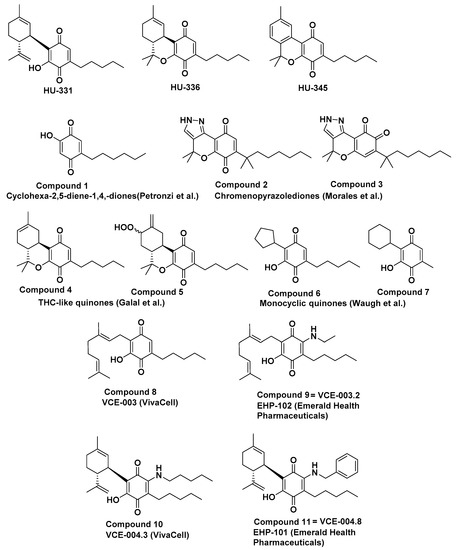
“We previously reported that cannabidiol (CBD), a cannabinoid with a low toxicity profile, downregulated the expression of the prometastatic gene inhibitor of DNA binding 1 ( “A cannabinoid anticancer para-quinone, HU-331, which was synthesized by our group five decades ago, was shown to have very high efficacy against human cancer cell lines in-vitro and against in-vivo grafts of human tumors in nude mice. The main mechanism was topoisomerase IIα catalytic inhibition. Later, several groups synthesized related compounds. In the present presentation, we review the publications on compounds synthesized on the basis of HU-331, summarize their published activities and mechanisms of action and report the synthesis and action of novel quinones, thus expanding the structure-activity relationship in these series.”
“A cannabinoid anticancer para-quinone, HU-331, which was synthesized by our group five decades ago, was shown to have very high efficacy against human cancer cell lines in-vitro and against in-vivo grafts of human tumors in nude mice. The main mechanism was topoisomerase IIα catalytic inhibition. Later, several groups synthesized related compounds. In the present presentation, we review the publications on compounds synthesized on the basis of HU-331, summarize their published activities and mechanisms of action and report the synthesis and action of novel quinones, thus expanding the structure-activity relationship in these series.”