 “Highly purified cannabidiol (CBD) (approved as Epidiolex® in the United States) has demonstrated efficacy with an acceptable safety profile in patients with Lennox-Gastaut or Dravet syndrome in four randomized controlled trials. CBD possesses affinity for many target classes with functional effects relevant to the pathophysiology of many disease types, including epilepsy.
“Highly purified cannabidiol (CBD) (approved as Epidiolex® in the United States) has demonstrated efficacy with an acceptable safety profile in patients with Lennox-Gastaut or Dravet syndrome in four randomized controlled trials. CBD possesses affinity for many target classes with functional effects relevant to the pathophysiology of many disease types, including epilepsy.
Although the mechanism of action of CBD underlying the reduction of seizures in humans is unknown, transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) represents a plausible target because (1) CBD activates and then desensitizes TRPV1, (2) TRPV1 is overexpressed in models of temporal lobe epilepsy and patients with epilepsy, (3) and TRPV1 modulates neuronal excitability.
Methods: To investigate a potential role of TRPV1 in the anticonvulsive effects of CBD, the effect of CBD on seizure threshold was assessed using a mouse maximal electroshock threshold model of generalized seizure in TRPV1 knockout and wildtype mice. The dose dependence of the CBD effect was determined and compared with that of the positive comparator diazepam and vehicle.
Results: At 50 and 100 mg/kg, CBD significantly (p<0.0001) increased seizure threshold in wildtype mice compared with TRPV1 knockout and vehicle controls. This effect was observed only at 100 mg/kg in TRPV1 knockout mice compared with knockout vehicle mice, in which gene deletion partially attenuated the CBD-increased seizure threshold. The effect of high-dose CBD in wildtype mice was nevertheless significantly different from vehicle-treated TRPV1 knockout mice (p<0.0001). Bioanalysis confirmed that genotype-specific differential brain exposure to CBD was not responsible for the observed effect on seizure threshold.
Conclusion: These data strongly implicate TRPV1 in the potential mechanisms of action for the anticonvulsive effects of CBD. The partial inhibition of the anticonvulsive effect of high-dose CBD in TRPV1 knockout mice may indicate the involvement of targets other than TRPV1. Further characterization of TRPV1 in the anticonvulsive effect of CBD in validated models of seizure is warranted, as is pharmacological investigation of the molecular interaction between CBD and TRPV1.”

 “Phytocannabinoids are bioactive natural products found in some flowering
“Phytocannabinoids are bioactive natural products found in some flowering  “Cannabinoids may have an important therapeutic potential for the treatment of dependence on crack cocaine.
“Cannabinoids may have an important therapeutic potential for the treatment of dependence on crack cocaine.

 “Like most modern molecular biology and natural product chemistry, understanding cannabinoid pharmacology centers around molecular interactions, in this case, between the cannabinoids and their putative targets, the G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2). Understanding the complex structure and interplay between the partners in this molecular dance is required to understand the mechanism of action of synthetic, endogenous, and phytochemical cannabinoids. This review, with 91 references, surveys our understanding of the structural biology of the cannabinoids and their target receptors including both a critical comparison of the extant crystal structures and the computationally derived homology models, as well as an in-depth discussion about the binding modes of the major cannabinoids. The aim is to assist in situating structural biochemists, synthetic chemists, and molecular biologists who are new to the field of cannabis research.”
“Like most modern molecular biology and natural product chemistry, understanding cannabinoid pharmacology centers around molecular interactions, in this case, between the cannabinoids and their putative targets, the G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2). Understanding the complex structure and interplay between the partners in this molecular dance is required to understand the mechanism of action of synthetic, endogenous, and phytochemical cannabinoids. This review, with 91 references, surveys our understanding of the structural biology of the cannabinoids and their target receptors including both a critical comparison of the extant crystal structures and the computationally derived homology models, as well as an in-depth discussion about the binding modes of the major cannabinoids. The aim is to assist in situating structural biochemists, synthetic chemists, and molecular biologists who are new to the field of cannabis research.” “Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid derived from Cannabis sativa. CBD initially drew scientific interest due to its anticonvulsant properties but increasing evidence of other therapeutic effects has attracted the attention of additional clinical and non-clinical populations, including athletes.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid derived from Cannabis sativa. CBD initially drew scientific interest due to its anticonvulsant properties but increasing evidence of other therapeutic effects has attracted the attention of additional clinical and non-clinical populations, including athletes. “Hempseeds, the edible fruits of the Cannabis sativa L. plant, were initially considered a by-product of the hemp technical fibre industry. Nowadays, following the restorationing of the cultivation of C. sativa L. plants containing an amount of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) <0.3% or 0.2% (industrial hemp) there is a growing interest for the hempseeds production due to their high nutritional value and functional features.
“Hempseeds, the edible fruits of the Cannabis sativa L. plant, were initially considered a by-product of the hemp technical fibre industry. Nowadays, following the restorationing of the cultivation of C. sativa L. plants containing an amount of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) <0.3% or 0.2% (industrial hemp) there is a growing interest for the hempseeds production due to their high nutritional value and functional features.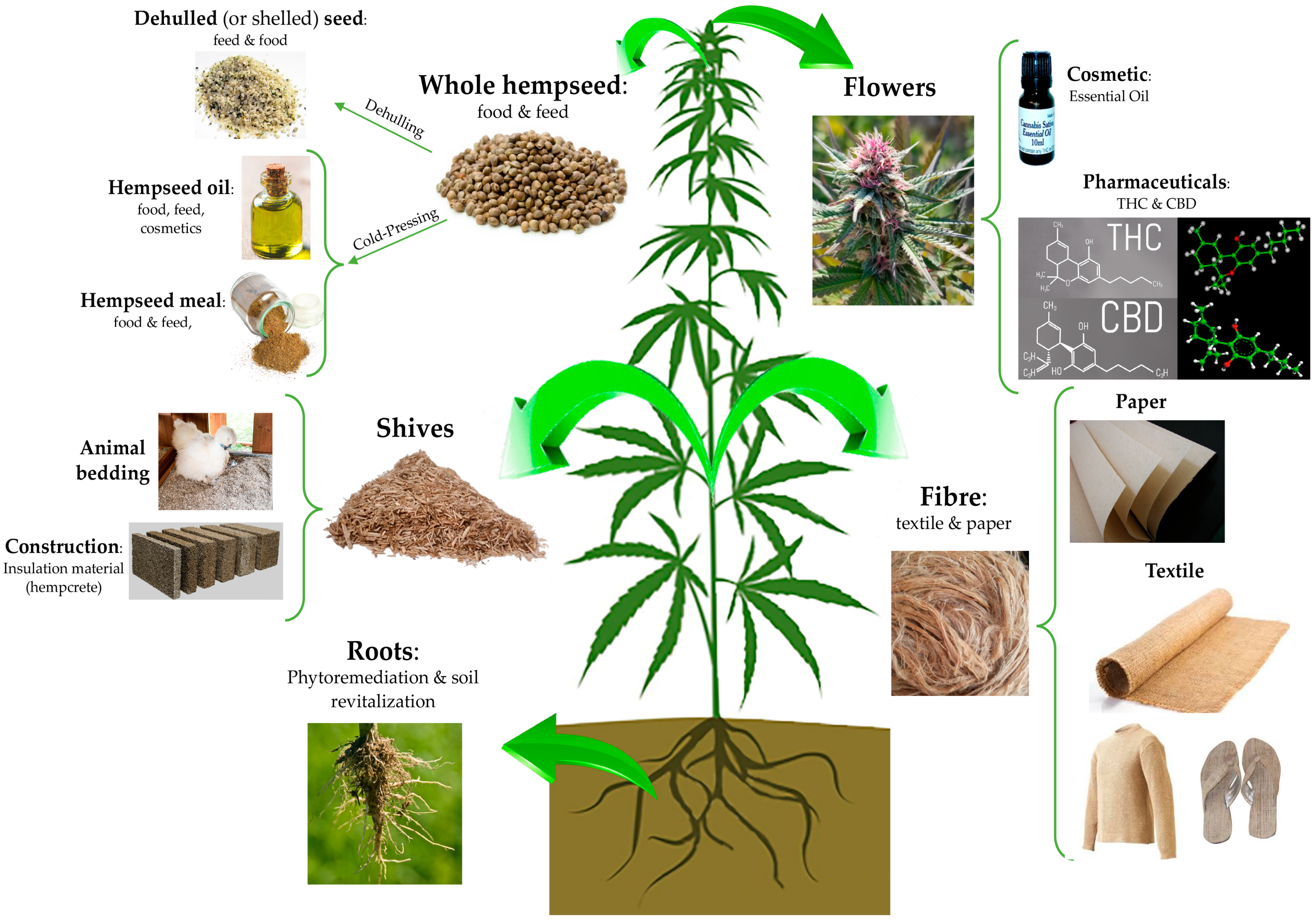
 “Embase and Pubmed were systematically searched for articles addressing the neuroprotective properties of phytocannabinoids, aside from cannabidiol and Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabinol, including Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (Δ9 -THCA), Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabivarin (Δ9 -THCV), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), cannabidivarin (CBDV), cannabichromene (CBC), cannabichromenic acid (CBCA), cannabichromevarin (CBCV), cannabigerol (CBG), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), cannabigerivarin (CBGV), cannabigerovarinic acid (CBGVA), cannabichromevarinic acid (CBCVA) cannabidivarinic acid (CBDVA) and cannabinol (CBN).
“Embase and Pubmed were systematically searched for articles addressing the neuroprotective properties of phytocannabinoids, aside from cannabidiol and Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabinol, including Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (Δ9 -THCA), Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabivarin (Δ9 -THCV), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), cannabidivarin (CBDV), cannabichromene (CBC), cannabichromenic acid (CBCA), cannabichromevarin (CBCV), cannabigerol (CBG), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), cannabigerivarin (CBGV), cannabigerovarinic acid (CBGVA), cannabichromevarinic acid (CBCVA) cannabidivarinic acid (CBDVA) and cannabinol (CBN). “Scientific research on how consumption of whole, natural Cannabis flower affects low mood and behavioral motivations more generally is largely nonexistent, and few studies to date have measured how common and commercially available Cannabis flower used in vivo may affect the experience of “depression” in real-time.
“Scientific research on how consumption of whole, natural Cannabis flower affects low mood and behavioral motivations more generally is largely nonexistent, and few studies to date have measured how common and commercially available Cannabis flower used in vivo may affect the experience of “depression” in real-time. “Genus Cannabis belong to family Cannabaceae and is traditionally used as medicinal plant against many diseases notably asthma, malaria, treatment of skin diseases, diabetes and headache. The plant Cannabis sativa L. is flowering and an annual herbaceous plant located to eastern Asia but now of cosmopolitan distribution due to extensive cultivation.
“Genus Cannabis belong to family Cannabaceae and is traditionally used as medicinal plant against many diseases notably asthma, malaria, treatment of skin diseases, diabetes and headache. The plant Cannabis sativa L. is flowering and an annual herbaceous plant located to eastern Asia but now of cosmopolitan distribution due to extensive cultivation.