“Cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG) are Cannabis sativa terpenophenols.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG) are Cannabis sativa terpenophenols.
Although CBD’s effectiveness against neurological diseases has already been demonstrated, nothing is known about CBG. Therefore, a comparison of the effects of these compounds was performed in two experimental models mimicking the oxidative stress and neurotoxicity occurring in neurological diseases.
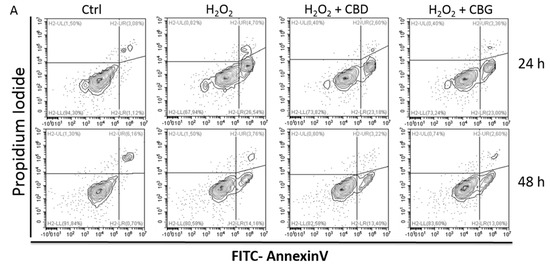
Rat astrocytes were exposed to hydrogen peroxide and cell viability, reactive oxygen species production and apoptosis occurrence were investigated. Cortexes were exposed to K+ 60 mM depolarizing stimulus and serotonin (5-HT) turnover, 3-hydroxykinurenine and kynurenic acid levels were measured. A proteomic analysis and bioinformatics and docking studies were performed.
Both compounds exerted antioxidant effects in astrocytes and restored the cortex level of 5-HT depleted by neurotoxic stimuli, whereas sole CBD restored the basal levels of 3-hydroxykinurenine and kynurenic acid. CBG was less effective than CBD in restoring the levels of proteins involved in neurotransmitter exocytosis. Docking analyses predicted the inhibitory effects of these compounds towards the neurokinin B receptor.
Conclusion: The results in the in vitro system suggest brain non-neuronal cells as a target in the treatment of oxidative conditions, whereas findings in the ex vivo system and docking analyses imply the potential roles of CBD and CBG as neuroprotective agents.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32443623/
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/10/3575