
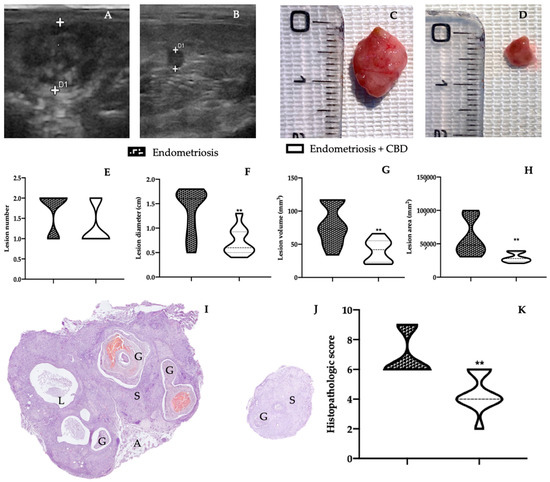
“Endometriosis, a chronic condition affecting around 10-14% of women, is challenging to manage, due to its complex pathogenesis and limited treatment options. Research has suggested a potential role of the gut microbiota and the endocannabinoid system in the development and progression of endometriosis. This narrative review aims to explore the role of, and any potential interactions between, the endocannabinoid system (ECS) and the gut microbiota in endometriosis. This review found that both the ECS and microbiota influence endometriosis, with the former regulating inflammation and pain perception and the latter influencing immune responses and hormonal balance. There is evidence that a dysregulation of the endocannabinoid system and the gut microbiota influence endometriosis symptoms and progression via changes in CB1 receptor expression and increased circulating levels of endocannabinoids. Microbial imbalances in the gut, such as increases in Prevotella, have been directly correlated to increased bloating, a common endometriosis symptom, while increases in E. coli have supported the bacterial contamination hypothesis as a potential pathway for endometriosis pathogenesis. These microbial imbalances have been correlated with increases in inflammatory markers such as TNF-α and IL-6, both often raised in those with endometriosis. Protective effects of the ECS on the gut were observed by increases in endocannabinoids, including 2-AG, resulting in decreased inflammation and improved gut permeability. Given these findings, both the ECS and the gut microbiota may be targets for therapeutic interventions for endometriosis; however, clinical studies are required to determine effectiveness.”



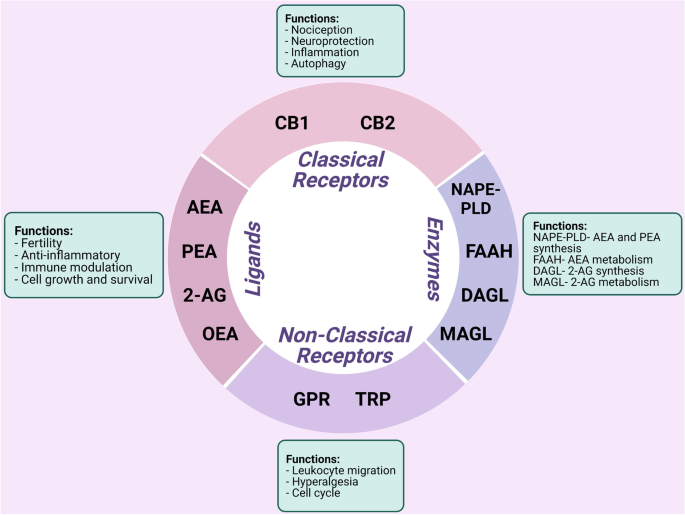



 “Endometriosis affects a large proportion of women during their reproductive years and is associated with pain and infertility, also affecting psychological wellbeing and quality of life. The pathogenesis of the disease remains unclear, although it is believed to be multifactorial.
“Endometriosis affects a large proportion of women during their reproductive years and is associated with pain and infertility, also affecting psychological wellbeing and quality of life. The pathogenesis of the disease remains unclear, although it is believed to be multifactorial.