 “Plant-based therapies date back centuries. Cannabis sativa is one such plant that was used medicinally up until the early part of the 20th century.
“Plant-based therapies date back centuries. Cannabis sativa is one such plant that was used medicinally up until the early part of the 20th century.
Although rich in diverse and interesting phytochemicals, cannabis was largely ignored by the modern scientific community due to its designation as a schedule 1 narcotic and restrictions on access for research purposes. There was renewed interest in the early 1990s when the endocannabinoid system (ECS) was discovered, a complex network of signaling pathways responsible for physiological homeostasis. Two key components of the ECS, cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2), were identified as the molecular targets of the phytocannabinoid Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC).
Restrictions on access to cannabis have eased worldwide, leading to a resurgence in interest in the therapeutic potential of cannabis. Much of the focus has been on the two major constituents, Δ9-THC and cannabidiol (CBD). Cannabis contains over 140 phytocannabinoids, although only a handful have been tested for pharmacological activity. Many of these minor cannabinoids potently modulate receptors, ionotropic channels, and enzymes associated with the ECS and show therapeutic potential individually or synergistically with other phytocannabinoids.
The following review will focus on the pharmacological developments of the next generation of phytocannabinoid therapeutics.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33356248/
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c00965


 “Anticancer activity of different phenols is documented, but underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Recently, we have shown that cannabidiol kills the cells of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) by a direct interaction with mitochondria, with their consequent dysfunction.
“Anticancer activity of different phenols is documented, but underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Recently, we have shown that cannabidiol kills the cells of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) by a direct interaction with mitochondria, with their consequent dysfunction.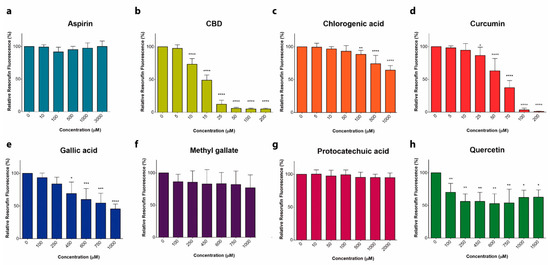
 “Objectives: This article presents findings from a large prospective examination of Canadian medical cannabis patients, with a focus on the impacts of cannabis on prescription opioid use and quality of life over a 6-month period.
“Objectives: This article presents findings from a large prospective examination of Canadian medical cannabis patients, with a focus on the impacts of cannabis on prescription opioid use and quality of life over a 6-month period.
 “Cannabis sativa L. is an aromatic annual herb belonging to the family Cannabaceae and it is widely distributed worldwide. Cultivation, selling, and consumption of cannabis and cannabis related products, regardless of its use, was prohibited in Lebanon until April 22, 2020. Nevertheless, cannabis oil has been traditionally used unlawfully for many years in Lebanon to treat diseases such as arthritis, diabetes, cancer and few neurological disorders.
“Cannabis sativa L. is an aromatic annual herb belonging to the family Cannabaceae and it is widely distributed worldwide. Cultivation, selling, and consumption of cannabis and cannabis related products, regardless of its use, was prohibited in Lebanon until April 22, 2020. Nevertheless, cannabis oil has been traditionally used unlawfully for many years in Lebanon to treat diseases such as arthritis, diabetes, cancer and few neurological disorders.
 “Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder with a multifactorial etiology. Latest researches are raising the hypothesis of a link between the onset of the main behavioral symptoms of ASD and the chronic neuroinflammatory condition of the autistic brain; increasing evidence of this connection is shedding light on new possible players in the pathogenesis of ASD.
“Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder with a multifactorial etiology. Latest researches are raising the hypothesis of a link between the onset of the main behavioral symptoms of ASD and the chronic neuroinflammatory condition of the autistic brain; increasing evidence of this connection is shedding light on new possible players in the pathogenesis of ASD. “Stem cell therapy promotes tissue regeneration and wound healing. Efforts have been made to prime stem cells to enhance their regenerative abilities.
“Stem cell therapy promotes tissue regeneration and wound healing. Efforts have been made to prime stem cells to enhance their regenerative abilities. “Melanoma causes the highest number of skin cancer-related deaths worldwide. New treatment methods are essential for the management of this life-threatening disease.
“Melanoma causes the highest number of skin cancer-related deaths worldwide. New treatment methods are essential for the management of this life-threatening disease. “A significant number of cannabinoids are known to have analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties in various diseases. Due to their presynaptic/terminal location, cannabinoid receptors can inhibit synaptic transmission and have the potential to regulate neurogenic inflammation. Neurogenic inflammation occurs when a noxious signal is detected in the periphery initiating an antidromic axon reflex in the same sensory neurone leading to depolarization of the afferent terminal. Neuropeptides are subsequently released and contribute to vasodilation, plasma extravasation and modulation of immune cells. Endocannabinoids, synthetic cannabinoids and phytocannabinoids can reduce neuroinflammation by inhibiting afferent firing and inflammatory neuropeptide release. Thus, in addition to a direct effect on vascular smooth muscle and inflammatory cells, cannabinoids can reduce inflammation by silencing small diameter neurones. This review examines the neuropharmacological processes involved in regulating antidromic depolarization of afferent nerve terminals by cannabinoids and the control of neurogenic inflammation in different diseases.”
“A significant number of cannabinoids are known to have analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties in various diseases. Due to their presynaptic/terminal location, cannabinoid receptors can inhibit synaptic transmission and have the potential to regulate neurogenic inflammation. Neurogenic inflammation occurs when a noxious signal is detected in the periphery initiating an antidromic axon reflex in the same sensory neurone leading to depolarization of the afferent terminal. Neuropeptides are subsequently released and contribute to vasodilation, plasma extravasation and modulation of immune cells. Endocannabinoids, synthetic cannabinoids and phytocannabinoids can reduce neuroinflammation by inhibiting afferent firing and inflammatory neuropeptide release. Thus, in addition to a direct effect on vascular smooth muscle and inflammatory cells, cannabinoids can reduce inflammation by silencing small diameter neurones. This review examines the neuropharmacological processes involved in regulating antidromic depolarization of afferent nerve terminals by cannabinoids and the control of neurogenic inflammation in different diseases.” “Effective treatment choices to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) are limited because of the absence of effective target-based therapeutics. The main object of the current research was to estimate the antiviral activity of cannabinoids (CBDs) against the human coronavirus SARS-CoV-2.
“Effective treatment choices to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) are limited because of the absence of effective target-based therapeutics. The main object of the current research was to estimate the antiviral activity of cannabinoids (CBDs) against the human coronavirus SARS-CoV-2.