
“Reduced brain glucose consumption arising from impaired glucose uptake and utilization has been linked to the pathogenesis and complications of neurodegenerative diseases. The ability of Cannabis sativa L. tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)-rich extracts to stimulate brain glucose uptake and utilization as well as its modulatory effect on gluconeogenesis, antioxidative, purinergic and cholinergic activities were investigated in isolated rats’ brains. C. sativa leaves were sequentially extracted to yield the hexane and dichloromethane extracts. The extracts were incubated at 37°C with freshly harvested brains in the presence of glucose for 2 h. The control consisted of incubation without the extracts, while brains without the extracts and glucose served as the normal control. Metformin was used as the standard drug. C. sativa extracts caused a significant (p < 0.05) increase in brain glucose uptake, with concomitant elevation of glutathione level, superoxide dismutase, catalase, and ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase activities compared to the controls. Incubation with C. sativa extracts also led to depletion in malondialdehyde and nitric oxide levels, acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase, glucose 6-phosphatase and fructose-1,6-biphosphatase activities. GC-MS analysis of the extracts revealed the presence of THC. In silico analysis predicted THC to be permeable across the blood-brain-barrier. THC was also predicted to have an oral LD50 and toxicity class values of 482 mg/kg and 4 respectively. These results indicate that C. sativa improves glucose consumption with concomitant suppression of oxidative stress and cholinergic dysfunction, and modulation of purinergic and gluconeogenic activities in brain tissues.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33390972/
“As portrayed by these results, C. sativa improves glucose consumption with concomitant suppression of oxidative stress and cholinergic dysfunction, and modulation of purinergic and gluconeogenic activities in brain tissues. Further studies are recommended to decipher the molecular mechanisms that may be involved in these neuroprotective activities in in vivo studies.”
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2020.592981/full

 “The concept of neurons as irreplaceable cells does not hold true today. Experiments and evidence of neurogenesis, also, in the adult brain give hope that some compounds or drugs can enhance this process, helping to reverse the outcomes of diseases or traumas that once were thought to be everlasting.
“The concept of neurons as irreplaceable cells does not hold true today. Experiments and evidence of neurogenesis, also, in the adult brain give hope that some compounds or drugs can enhance this process, helping to reverse the outcomes of diseases or traumas that once were thought to be everlasting.  “HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND) persist despite the advent of antiretroviral therapy (ART), suggesting underlying systemic and central nervous system (CNS) inflammatory mechanisms.
“HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND) persist despite the advent of antiretroviral therapy (ART), suggesting underlying systemic and central nervous system (CNS) inflammatory mechanisms. “”Medicinal cannabis” is defined as the use of cannabis-based products for the treatment of an illness. Investigations of cannabis compounds in psychiatric and neurological illnesses primarily focus on the major cannabinoids, cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ
“”Medicinal cannabis” is defined as the use of cannabis-based products for the treatment of an illness. Investigations of cannabis compounds in psychiatric and neurological illnesses primarily focus on the major cannabinoids, cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ “Clinical and preclinical evidence has indicated that estrogen depletion leads to memory impairments and increases the susceptibility to neural damage.
“Clinical and preclinical evidence has indicated that estrogen depletion leads to memory impairments and increases the susceptibility to neural damage.  “Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the Substantia Nigra pars compacta, leading to classical PD motor symptoms. Current therapies are purely symptomatic and do not modify disease progression.
“Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the Substantia Nigra pars compacta, leading to classical PD motor symptoms. Current therapies are purely symptomatic and do not modify disease progression.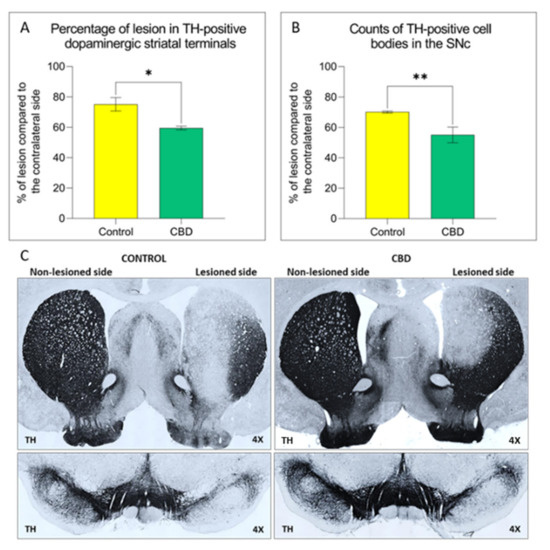
 “Despite the high incidence of traumatic brain injury (TBI), there is no universal treatment to safely treat patients. Blunt brain injuries destroy primary neural tissue that results in impaired perfusion, excessive release of glutamate, inflammation, excitotoxicity, and progressive secondary neuronal cell death.
“Despite the high incidence of traumatic brain injury (TBI), there is no universal treatment to safely treat patients. Blunt brain injuries destroy primary neural tissue that results in impaired perfusion, excessive release of glutamate, inflammation, excitotoxicity, and progressive secondary neuronal cell death.  “Introduction:
“Introduction: “Background and purpose:
“Background and purpose: