“Drugs targeting the endocannabinoid system are of interest as potential systemic chemotherapeutic treatments and for palliative care in cancer.
In this context, cannabinoid compounds have been successfully tested as a systemic therapeutic option in preclinical models over the past decades. Recent findings have suggested an essential function of the endocannabinoid system in the homeostasis of various skin functions and indicated that cannabinoids could also be considered for the treatment and prophylaxis of tumour diseases of the skin.
Cannabinoids have been shown to exert their anticarcinogenic effects at different levels of skin cancer progression, such as inhibition of tumour growth, proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis, as well as inducing apoptosis and autophagy. This review provides an insight into the current literature on cannabinoid compounds as potential pharmaceuticals for the treatment of melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35406541/
“Recent research has suggested that the endocannabinoid system offers several pharmacotherapeutic targets for drug administration as new options for the treatment and prophylaxis of skin cancer. This review focused on the anticarcinogenic mechanisms of cannabinoids at the different levels of skin cancer progression, such as inhibition of tumour growth, proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis, as well as inducing apoptosis and autophagy.”
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/14/7/1769

 “Melanoma is one of the most aggressive malignances in human. Recently developed therapies improved overall survival rate, however, the treatment of melanoma still remains a challenging issue.
“Melanoma is one of the most aggressive malignances in human. Recently developed therapies improved overall survival rate, however, the treatment of melanoma still remains a challenging issue. 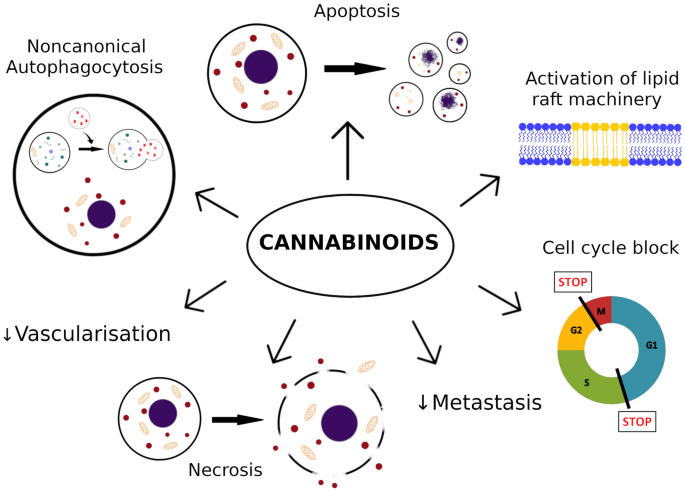
 “Agents targeting the endocannabinoid system (ECS) have gained attention as potential cancer treatments. Given recent evidence that cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2R) regulates lymphocyte development and inflammation, we performed studies on CB2R in the immune response against melanoma. Analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data revealed a strong positive correlation between CB2R expression and survival, as well as B cell infiltration in human melanoma. In a murine melanoma model, CB2R expression reduced the growth of melanoma as well as the B cell frequencies in the tumor microenvironment (TME), compared to CB2R-deficient mice. In depth analysis of tumor-infiltrating B cells using single-cell RNA sequencing suggested a less differentiated phenotype in tumors from
“Agents targeting the endocannabinoid system (ECS) have gained attention as potential cancer treatments. Given recent evidence that cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2R) regulates lymphocyte development and inflammation, we performed studies on CB2R in the immune response against melanoma. Analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data revealed a strong positive correlation between CB2R expression and survival, as well as B cell infiltration in human melanoma. In a murine melanoma model, CB2R expression reduced the growth of melanoma as well as the B cell frequencies in the tumor microenvironment (TME), compared to CB2R-deficient mice. In depth analysis of tumor-infiltrating B cells using single-cell RNA sequencing suggested a less differentiated phenotype in tumors from 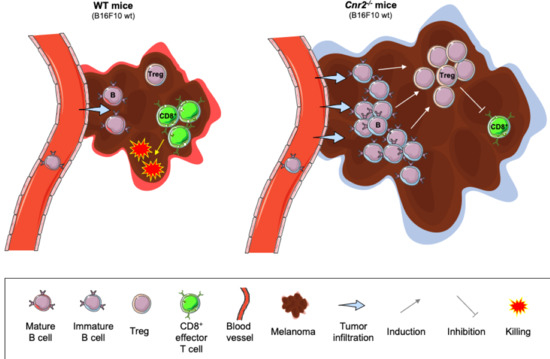
 “Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the most popular emerging plant extracts that is being investigated for its wide range of potential health benefits.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the most popular emerging plant extracts that is being investigated for its wide range of potential health benefits. “Melanoma causes the highest number of skin cancer-related deaths worldwide. New treatment methods are essential for the management of this life-threatening disease.
“Melanoma causes the highest number of skin cancer-related deaths worldwide. New treatment methods are essential for the management of this life-threatening disease. “UV phototherapy used in chronic skin diseases causes redox imbalance and pro-inflammatory reactions, especially in the case of unchanged skin cells.
“UV phototherapy used in chronic skin diseases causes redox imbalance and pro-inflammatory reactions, especially in the case of unchanged skin cells.