 “In the process of neonatal encephalopathy, oxidative stress and neuroinflammation have a prominent role after perinatal asphyxia. With the exception of therapeutic hypothermia, no therapeutic interventions are available in the clinical setting to target either the oxidative stress or inflammation, despite the high prevalence of neurological sequelae of this devastating condition.
“In the process of neonatal encephalopathy, oxidative stress and neuroinflammation have a prominent role after perinatal asphyxia. With the exception of therapeutic hypothermia, no therapeutic interventions are available in the clinical setting to target either the oxidative stress or inflammation, despite the high prevalence of neurological sequelae of this devastating condition.
The endocannabinoid system (ECS), recently recognized as a widespread neuromodulatory system, plays an important role in the development of the central nervous system (CNS).
This study aims to evaluate the potential effect of the cannabinoid (CB) agonist WIN 55,212-2 (WIN) on reactive oxygen species (ROS) and early inflammatory cytokine production after hypoxia-ischemia (HI) in fetal lambs.
Hypoxic-ischemic animals were subjected to 60 min of HI by partial occlusion of the umbilical cord. A group of lambs received a single dose of 0.01 μg/kg WIN, whereas non-asphyctic animals served as controls. WIN reduced the widespread and notorious increase in inflammatory markers tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6 induced by HI, a modulatory effect not observed for oxidative stress.
Our study suggests that treatment with a low dose of WIN can alter the profile of pro-inflammatory cytokines 3 h after HI.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32074976
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/4/1283

 “To determine whether differences in disability status, spasticity severity, and spasticity duration at treatment start in patients with resistant multiple sclerosis (MS) spasticity might influence response to add-on tetrahydrocannabinol:
“To determine whether differences in disability status, spasticity severity, and spasticity duration at treatment start in patients with resistant multiple sclerosis (MS) spasticity might influence response to add-on tetrahydrocannabinol: “Phytocannabinoids (and synthetic analogs thereof) are gaining significant attention as promising leads in modern medicine. Considering this, new directions for the design of phytocannabinoid-inspired molecules is of immediate interest. In this regard, we have hypothesized that axially-chiral-cannabinols (ax-CBNs), unnatural and unknown isomers of cannabinol (CBN) may be valuable scaffolds for
“Phytocannabinoids (and synthetic analogs thereof) are gaining significant attention as promising leads in modern medicine. Considering this, new directions for the design of phytocannabinoid-inspired molecules is of immediate interest. In this regard, we have hypothesized that axially-chiral-cannabinols (ax-CBNs), unnatural and unknown isomers of cannabinol (CBN) may be valuable scaffolds for  “Patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) develop resistance to antitumor agents by mechanisms that involve the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This necessitates the development of new complementary drugs, e.g.,
“Patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) develop resistance to antitumor agents by mechanisms that involve the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This necessitates the development of new complementary drugs, e.g.,  “Plant phytochemicals have potential decontaminating properties, however, their role in the amelioration of hydrophobic water filtration membranes have not been elucidated yet.
“Plant phytochemicals have potential decontaminating properties, however, their role in the amelioration of hydrophobic water filtration membranes have not been elucidated yet.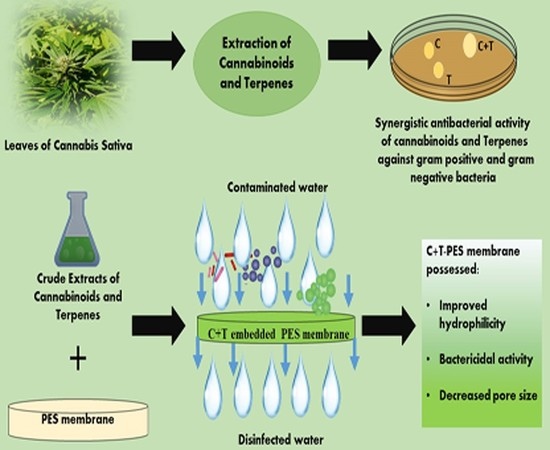
 “Septic lung injury is one of main causes of high mortality in severe patients. Inhibition of excessive inflammatory response is considered as an effective strategy for septic lung injury.
“Septic lung injury is one of main causes of high mortality in severe patients. Inhibition of excessive inflammatory response is considered as an effective strategy for septic lung injury. “Most of the drugs of abuse affect the brain by interacting with naturally expressed molecular receptors. Marihuana affects a series of receptors including
“Most of the drugs of abuse affect the brain by interacting with naturally expressed molecular receptors. Marihuana affects a series of receptors including  “Critically ill patients with sepsis require a multidisciplinary approach, as this situation implies multiorgan distress, with most of the bodily biochemical and cellular systems being affected by the condition. Moreover, sepsis is characterized by a multitude of biochemical interactions and by dynamic changes of the immune system. At the moment, there is a gap in our understanding of the cellular, genetic, and molecular mechanisms involved in sepsis.
“Critically ill patients with sepsis require a multidisciplinary approach, as this situation implies multiorgan distress, with most of the bodily biochemical and cellular systems being affected by the condition. Moreover, sepsis is characterized by a multitude of biochemical interactions and by dynamic changes of the immune system. At the moment, there is a gap in our understanding of the cellular, genetic, and molecular mechanisms involved in sepsis.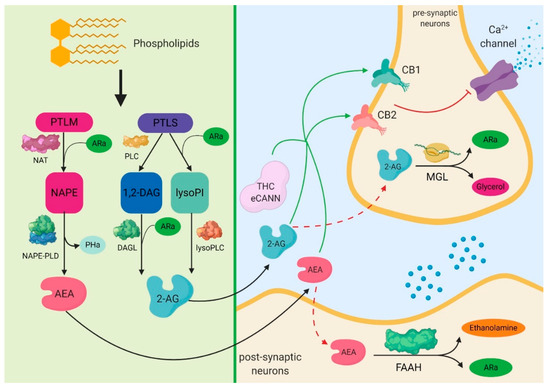
 “Human adipose tissue includes large quantities of mesenchymal stromal cells (atMSCs), which represent an abundant cell source for therapeutic applications in the field of regenerative medicine.
“Human adipose tissue includes large quantities of mesenchymal stromal cells (atMSCs), which represent an abundant cell source for therapeutic applications in the field of regenerative medicine.
 “Activation of
“Activation of