 “Opioid misuse and overuse has contributed to a widespread overdose crisis and many patients and physicians are considering medical cannabis to support opioid tapering and chronic pain control. Using a five-step modified Delphi process, we aimed to develop consensus-based recommendations on: 1) when and how to safely initiate and titrate cannabinoids in the presence of opioids, 2) when and how to safely taper opioids in the presence of cannabinoids, and 3) how to monitor patients and evaluate outcomes when treating with opioids and cannabinoids.
“Opioid misuse and overuse has contributed to a widespread overdose crisis and many patients and physicians are considering medical cannabis to support opioid tapering and chronic pain control. Using a five-step modified Delphi process, we aimed to develop consensus-based recommendations on: 1) when and how to safely initiate and titrate cannabinoids in the presence of opioids, 2) when and how to safely taper opioids in the presence of cannabinoids, and 3) how to monitor patients and evaluate outcomes when treating with opioids and cannabinoids.
Results: In patients with chronic pain taking opioids not reaching treatment goals, there was consensus that cannabinoids may be considered for patients experiencing or displaying opioid-related complications, despite psychological or physical interventions. There was consensus observed to initiate with a cannabidiol (CBD)-predominant oral extract in the daytime and consider adding tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). When adding THC, start with 0.5-3 mg, and increase by 1-2 mg once or twice weekly up to 30-40 mg/day. Initiate opioid tapering when the patient reports a minor/major improvement in function, seeks less as-needed medication to control pain, and/or the cannabis dose has been optimized. The opioid tapering schedule may be 5%-10% of the morphine equivalent dose (MED) every 1 to 4 weeks. Clinical success could be defined by an improvement in function/quality of life, a ≥ 30% reduction in pain intensity, a ≥ 25% reduction in opioid dose, a reduction in opioid dose to < 90 mg MED, and/or reduction in opioid-related adverse events.
Conclusions: This five-stage modified Delphi process led to the development of consensus-based recommendations surrounding the safe introduction and titration of cannabinoids in concert with tapering opioids.”

 “Chronic pelvic pain affects women across all demographics. Its management is complex and requires a multimodal approach.
“Chronic pelvic pain affects women across all demographics. Its management is complex and requires a multimodal approach. “Although studied in a few randomized controlled trials (RCTs), the efficacy of medical cannabis (MC) for chronic pain remains controversial. Using an alternative approach, this multicenter, questionnaire-based prospective cohort was aimed to assess the long-term effects of MC on chronic pain of various etiologies and to identify predictors for MC treatment success.
“Although studied in a few randomized controlled trials (RCTs), the efficacy of medical cannabis (MC) for chronic pain remains controversial. Using an alternative approach, this multicenter, questionnaire-based prospective cohort was aimed to assess the long-term effects of MC on chronic pain of various etiologies and to identify predictors for MC treatment success.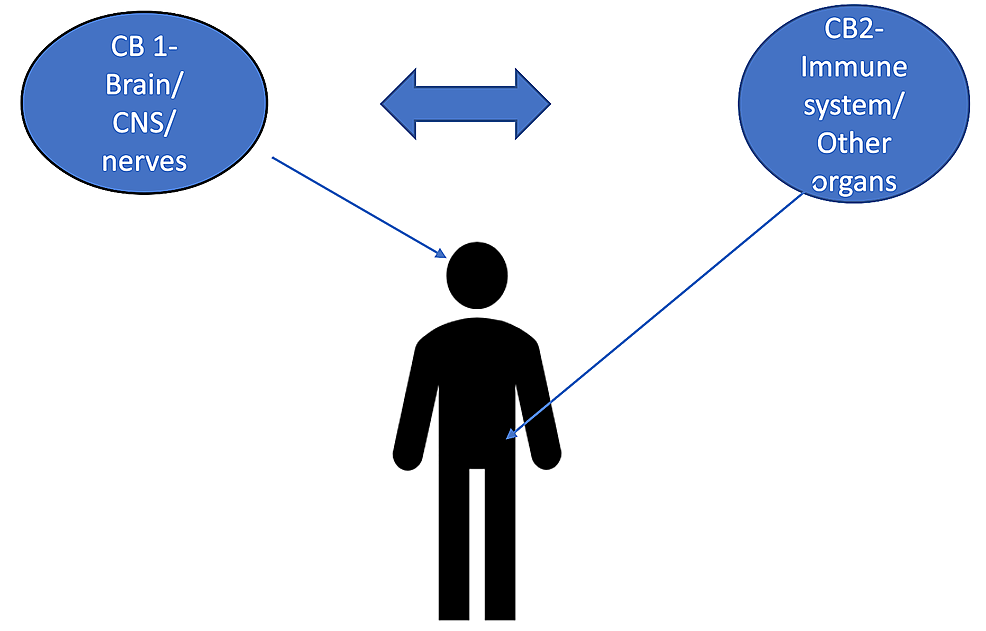 “The burden of chronic pain has affected many individuals leading to distress and discomfort, alongside numerous side effects with conventional therapeutic approaches.
“The burden of chronic pain has affected many individuals leading to distress and discomfort, alongside numerous side effects with conventional therapeutic approaches. “Cannabinoids help in pain treatment through their action on CB1 and CB2 receptors.
“Cannabinoids help in pain treatment through their action on CB1 and CB2 receptors. “Chronic pain can be recurrent or constant pain that lasts for longer than 3 months and can result in disability, suffering, and a physical disturbance. Related to the complex nature of chronic pain, treatments have a pharmacological and non-pharmacological approach.
“Chronic pain can be recurrent or constant pain that lasts for longer than 3 months and can result in disability, suffering, and a physical disturbance. Related to the complex nature of chronic pain, treatments have a pharmacological and non-pharmacological approach. “Cannabidiol (CBD) is reported to produce pain relief, but the clinically relevant cellular and molecular mechanisms remain uncertain.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is reported to produce pain relief, but the clinically relevant cellular and molecular mechanisms remain uncertain. “Cannabis exposure is becoming more common in older age but little is known about how it is associated with brain health in this population.
“Cannabis exposure is becoming more common in older age but little is known about how it is associated with brain health in this population. “To determine if cannabis may be used as an alternative or adjunct treatment for intermittent and chronic prescription opioid users.
“To determine if cannabis may be used as an alternative or adjunct treatment for intermittent and chronic prescription opioid users.