 “Uterus transplantation is a complex surgical procedure. Uterine ischemia/reperfusion (IR) damage occurring in this process may cause loss of function in the uterus. Cell damage must be prevented for a healthy uterine function and successful transplantation.
“Uterus transplantation is a complex surgical procedure. Uterine ischemia/reperfusion (IR) damage occurring in this process may cause loss of function in the uterus. Cell damage must be prevented for a healthy uterine function and successful transplantation.
Cannabinoids, with their increasing clinical use, are substances with strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects and have a role in immune system regulation. However, their efficacy in uterine IR damage is still unknown.
This study provides information on the potential applications cannabinoids agonist JWH-133 in uterine IR damage and, hence, in the transplant process.
Results: In the uterine IR group, NF-κB expression and MDA levels were detected at high levels. Histopathological examinations and TUNEL staining revealed extensive cell damage. On the other hand, in groups treated with JWH-133, dose-dependent NF-κB expression and MDA levels decreased (p < 0.05). Depending on the dose, the rate of surviving cells increased in TUNEL staining results.
Conclusion: The results showed that JWH-133 was effective in reducing uterine IR damage. Cannabinoids may be a new alternative that may be used in the transplantation process in the future.”

 “The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between work-related injury and cannabis use in the past year.
“The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between work-related injury and cannabis use in the past year. “These data support the notion that CBD and CBDV act as functional partial agonists on dopamine D2-like receptors in vivo.
“These data support the notion that CBD and CBDV act as functional partial agonists on dopamine D2-like receptors in vivo. “In this proof-of-concept study, the antioxidant activity of phytocannabinoids, namely cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9- tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), were investigated using an in vitro system of differentiated human neuronal SY-SH5Y cells.
“In this proof-of-concept study, the antioxidant activity of phytocannabinoids, namely cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9- tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), were investigated using an in vitro system of differentiated human neuronal SY-SH5Y cells.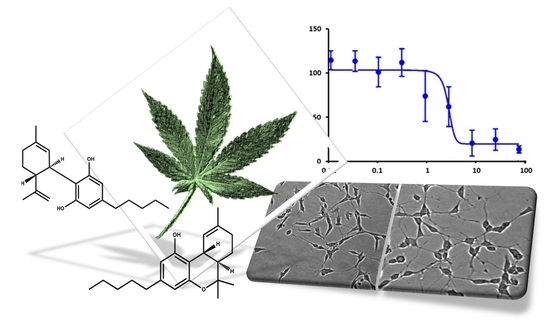
 “Evidence details how cannabis can influence the use of other psychoactive substances, including prescription medications, alcohol, tobacco and illicit drugs, but very little research has examined the factors associated with these changes in substance use patterns. This paper explores the self-reported use of cannabis as a substitute for alcohol among a Canadian medical cannabis patient population.
“Evidence details how cannabis can influence the use of other psychoactive substances, including prescription medications, alcohol, tobacco and illicit drugs, but very little research has examined the factors associated with these changes in substance use patterns. This paper explores the self-reported use of cannabis as a substitute for alcohol among a Canadian medical cannabis patient population. “Cannabis is a historical plant which has been used as a medicine in East Asia.
“Cannabis is a historical plant which has been used as a medicine in East Asia. “The identification of the human cannabinoid receptors and their roles in health and disease, has been one of the most significant biochemical and pharmacological advancements to have occurred in the past few decades. In spite of the major strides made in furthering endocannabinoid research, therapeutic exploitation of the endocannabinoid system has often been a challenging task.
“The identification of the human cannabinoid receptors and their roles in health and disease, has been one of the most significant biochemical and pharmacological advancements to have occurred in the past few decades. In spite of the major strides made in furthering endocannabinoid research, therapeutic exploitation of the endocannabinoid system has often been a challenging task. “Considering lack of target-specific antiviral treatment and vaccination for COVID-19, it is absolutely exigent to have an effective therapeutic modality to reduce hospitalization and mortality rate as well as to improve COVID-19-infected patient outcomes.
“Considering lack of target-specific antiviral treatment and vaccination for COVID-19, it is absolutely exigent to have an effective therapeutic modality to reduce hospitalization and mortality rate as well as to improve COVID-19-infected patient outcomes. “The inflammatory sequence is the first phase of wound healing. Macrophages (MPhs) and mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) respond to an inflammatory microenvironment by adapting their functional activity, which polarizes them into the pro-inflammatory phenotypes M1 and MSC1. Prolongation of the inflammatory phase results in the formation of chronic wounds. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) possesses immunomodulatory properties that may impede this cellular phenotypic switch.
“The inflammatory sequence is the first phase of wound healing. Macrophages (MPhs) and mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) respond to an inflammatory microenvironment by adapting their functional activity, which polarizes them into the pro-inflammatory phenotypes M1 and MSC1. Prolongation of the inflammatory phase results in the formation of chronic wounds. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) possesses immunomodulatory properties that may impede this cellular phenotypic switch. “Cannabinoids have long been used for their psychotropic and possible medical properties of symptom relief. In the past few years, a vast literature shows that cannabinoids are neuroprotective under different pathological situations.
“Cannabinoids have long been used for their psychotropic and possible medical properties of symptom relief. In the past few years, a vast literature shows that cannabinoids are neuroprotective under different pathological situations.