 “High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is a late phase inflammatory mediator in many inflammatory diseases. Extracellular HMGB1 could bind to many membrane receptors to activate downstream signaling molecules and promote inflammation resulting in cell and tissue damage.
“High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is a late phase inflammatory mediator in many inflammatory diseases. Extracellular HMGB1 could bind to many membrane receptors to activate downstream signaling molecules and promote inflammation resulting in cell and tissue damage.
In our previous work, we found cannabinoid receptor Ⅱ(CB2R) inhibited the expression of HMGB1 in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced septic models in vivo and in vitro, but the underlying mechanism is still unclear.
The present study was aimed to explore the possible pathway through which CB2R suppressed HMGB1.
Here, we found that the specific agonist of CB2R, GW405833 (GW) could induce intracellular HMGB1 degradation without influencing HMGB1 mRNA in peritoneal macrophages. Then we observed that autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine (3-MA) but not proteasome inhibitor MG-132 (MG) could block GW-induced HMGB1 degradation, which indicated that the autophagy-lysosome but not the ubiquitination pathway was involved in this process.
Further study showed that GW could promote the integrity of autophagy flux in macrophages in terms of increased level of LC3Ⅱand decreased expression of p62 protein. It also observed that inhibition of autophagy blocked GW-induced nuclear translocation of HMGB1 in macrophages. GW could up-regulate expression of Cathepsin B (CTSB), and inhibition of CTSB blocked GW-induced HMGB1 degradation.
In summary, all the data showed that activation of CB2R could promote the intracellular degradation of HMGB1 via the autophagy-lysosome pathway in macrophage.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31806570
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1567576919321186?via%3Dihub

 “Aging and HIV have adverse effects on the central nervous system, including increased inflammation and neural injury and confer risk of neurocognitive impairment (NCI).
“Aging and HIV have adverse effects on the central nervous system, including increased inflammation and neural injury and confer risk of neurocognitive impairment (NCI). “The endocannabinoid system (ECS) has emerged in recent years as a potential treatment target for alcohol use disorders (AUD).
“The endocannabinoid system (ECS) has emerged in recent years as a potential treatment target for alcohol use disorders (AUD). “This study attempted to provide the effects and mechanisms of two cannabinoids, O-1602 and
“This study attempted to provide the effects and mechanisms of two cannabinoids, O-1602 and  “Inflammation is a common feature of many neurodegenerative diseases.
“Inflammation is a common feature of many neurodegenerative diseases. “A 64 year old male heating engineer was investigated for a persistent cough and found to have epithelioid mesothelioma with pleural effusion, lung nodules and increased thoracic lymph nodes. He declined standard of care treatment following his own research and he was enrolled in a named patient programme of IMM-101. He was advised to correct his low vitamin D3 level and to start using anti-inflammatories such as aspirin, bromelain and low dose Naltrexone. At review one year later a CT scan showed no change and he continued on the regimen. Four years after the diagnosis a CT scan showed that there was a modest but definite progression of the left malignant pleural thickening, and a new right-sided effusion, enlargement of several intrathoracic nodes which had been noted on the early scans. The chest wall lump eventually broke down and required local radiotherapy. He then developed abdominal pain and found to have peritoneal disease. Last year he obtained the
“A 64 year old male heating engineer was investigated for a persistent cough and found to have epithelioid mesothelioma with pleural effusion, lung nodules and increased thoracic lymph nodes. He declined standard of care treatment following his own research and he was enrolled in a named patient programme of IMM-101. He was advised to correct his low vitamin D3 level and to start using anti-inflammatories such as aspirin, bromelain and low dose Naltrexone. At review one year later a CT scan showed no change and he continued on the regimen. Four years after the diagnosis a CT scan showed that there was a modest but definite progression of the left malignant pleural thickening, and a new right-sided effusion, enlargement of several intrathoracic nodes which had been noted on the early scans. The chest wall lump eventually broke down and required local radiotherapy. He then developed abdominal pain and found to have peritoneal disease. Last year he obtained the  “Endometriosis affects a large proportion of women during their reproductive years and is associated with pain and infertility, also affecting psychological wellbeing and quality of life. The pathogenesis of the disease remains unclear, although it is believed to be multifactorial.
“Endometriosis affects a large proportion of women during their reproductive years and is associated with pain and infertility, also affecting psychological wellbeing and quality of life. The pathogenesis of the disease remains unclear, although it is believed to be multifactorial.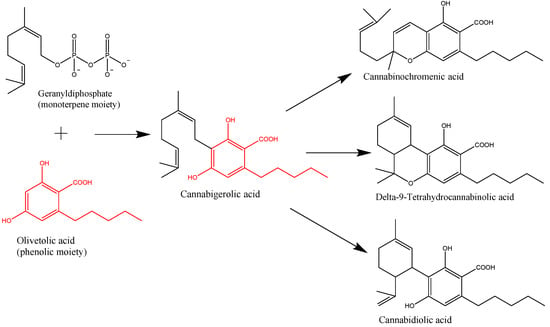
 “Endocannabinoid system consists of
“Endocannabinoid system consists of 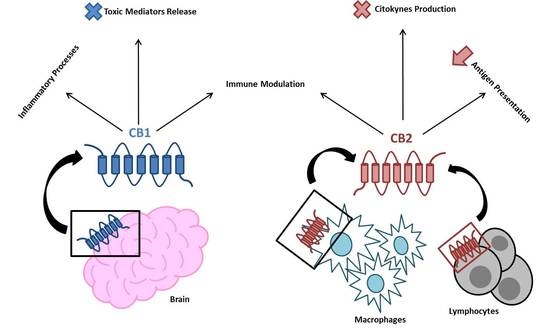
 “As we learn more about the endocannabinoid system (ECS), our understanding and grasp of the system’s ubiquitous presence is expanding. In light of this, there is also a growing body of evidence for the therapeutic potential of ECS modulation in a range of clinical situations. Strategies include for example manipulation of the
“As we learn more about the endocannabinoid system (ECS), our understanding and grasp of the system’s ubiquitous presence is expanding. In light of this, there is also a growing body of evidence for the therapeutic potential of ECS modulation in a range of clinical situations. Strategies include for example manipulation of the