 “Cognitive impairment is a major source of disability in schizophrenia and current antipsychotic drugs (APDs) have minimal efficacy for this symptom domain.
“Cognitive impairment is a major source of disability in schizophrenia and current antipsychotic drugs (APDs) have minimal efficacy for this symptom domain.
Cannabidiol (CBD), the major non-intoxicating component of Cannabis sativa L., exhibits antipsychotic and neuroprotective properties.
We recently reported the effects of CBD on cognition in male offspring of a maternal immune activation (polyinosinic-polycytidilic acid (poly I:C)) model relevant to the aetiology of schizophrenia; however, the effects of CBD treatment in females are unknown. Sex differences are observed in the onset of schizophrenia symptoms and response to APD treatment.
Furthermore, the endogenous cannabinoid system, a direct target of CBD, is sexually dimorphic in humans and rodents. Therefore, the present work aimed to assess the therapeutic impact of CBD treatment on behaviour and neurochemical signalling markers in female poly I:C offspring.
Overall, the findings of this study support the therapeutic benefits of CBD on recognition memory and sociability in female poly I:C offspring, and provide insight into the neurochemical changes that may underlie the therapeutic benefits of CBD in the poly I:C model.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31326506
“These findings suggest that CBD is an efficacious treatment for behavioural and neurochemical changes in a female rodent model relevant to schizophrenia.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0889159119302806?via%3Dihub


 “Herein, we report the antioxidant activity of
“Herein, we report the antioxidant activity of 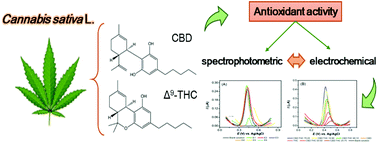
 “Currently, there are no approved pharmacotherapies for addiction to cocaine and other psychostimulant drugs. Several studies have proposed that
“Currently, there are no approved pharmacotherapies for addiction to cocaine and other psychostimulant drugs. Several studies have proposed that  “Current pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is palliative and unable to modify the progression of neurodegeneration. Treatments that can improve patients’ quality of life with fewer side effects are needed, but not yet available.
“Current pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is palliative and unable to modify the progression of neurodegeneration. Treatments that can improve patients’ quality of life with fewer side effects are needed, but not yet available. “Osteoporosis is a skeletal disease with decreased bone mass and alteration in microarchitecture of bone tissue, and these changes put patients in risk of bone fracture. As a common symptom of osteoporosis and complication of osteoporotic fracture, chronic pain is a headache for clinicians. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), selective COX-2 inhibitors and opioid drugs can temporarily reduce osteoporotic pain but have relevant side effects, such as addiction, tolerability and safety. The review summarized the recent advancements in the study of CB receptors in osteoporosis and osteoporotic pain and related mechanisms.
“Osteoporosis is a skeletal disease with decreased bone mass and alteration in microarchitecture of bone tissue, and these changes put patients in risk of bone fracture. As a common symptom of osteoporosis and complication of osteoporotic fracture, chronic pain is a headache for clinicians. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), selective COX-2 inhibitors and opioid drugs can temporarily reduce osteoporotic pain but have relevant side effects, such as addiction, tolerability and safety. The review summarized the recent advancements in the study of CB receptors in osteoporosis and osteoporotic pain and related mechanisms. “Cardiac disease is accounted as the leading cause of worldwide morbidity and mortality, mainly in association with induction of inflammation and oxidative stress. The disease is characterized by the overproduction of reactive oxygen and/or nitrogen species (ROS/RNS), and reduced antioxidant capacity.
“Cardiac disease is accounted as the leading cause of worldwide morbidity and mortality, mainly in association with induction of inflammation and oxidative stress. The disease is characterized by the overproduction of reactive oxygen and/or nitrogen species (ROS/RNS), and reduced antioxidant capacity.