 “Cannabinoid oils are being increasingly used to treat Dravet syndrome, yet the long-term costs and outcomes of this approach are unknown. Thus, we examined the cost effectiveness of cannabinoid oil as an adjunctive treatment (added to clobazam and valproate), compared with adjunctive stiripentol or with clobazam and valproate alone, for the treatment of Dravet syndrome in children.
“Cannabinoid oils are being increasingly used to treat Dravet syndrome, yet the long-term costs and outcomes of this approach are unknown. Thus, we examined the cost effectiveness of cannabinoid oil as an adjunctive treatment (added to clobazam and valproate), compared with adjunctive stiripentol or with clobazam and valproate alone, for the treatment of Dravet syndrome in children.
METHODS:
We performed a probabilistic cost-utility analysis from the perspective of the Canadian public health care system, comparing cannabinoid oil and stiripentol (both on a background of clobazam and valproate) with clobazam and valproate alone. Costs and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) were estimated using a Markov model that followed a cohort of children aged from 5 to 18 years through model states related to seizure frequency. Model inputs were obtained from the literature. The cost effectiveness of adjunctive cannabinoid oil, adjunctive stiripentol, and clobazam/valproate alone was assessed through sequential analysis. The influence of perspective and other assumptions were explored in scenario analyses. All costs are expressed in 2019 Canadian dollars, and costs and QALYs were discounted at a rate of 1.5% per year.
RESULTS:
The incremental cost per QALY gained with the use of adjunctive cannabinoid oil, from the health care system perspective, was $32,399 compared with clobazam and valproate. Stiripentol was dominated by cannabinoid oil, producing fewer QALYs at higher costs. At a willingness-to-pay threshold of $50,000, cannabinoid oil was the optimal treatment in 76% of replications. From a societal perspective, cannabinoid oil dominated stiripentol and clobazam/valproate. The interpretation of the results was insensitive to model and input assumptions.
CONCLUSION:
Compared with clobazam/valproate, adjunctive cannabinoid oil may be a cost-effective treatment for Dravet syndrome, if a decision maker is willing to pay at least $32,399 for each QALY gained. The opportunity costs of continuing to fund stiripentol, but not cannabinoid oil, should be considered.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32406036
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs40273-020-00923-5

 “Opioid prescriptions and abuse remain a significant national concern.
“Opioid prescriptions and abuse remain a significant national concern. “Modern day research, in an attempt to determine the potential therapeutic and adverse effects of illicit substances, is a growing field, but one that faces many regulatory challenges. Due to the potential abuse of illicit substances such as
“Modern day research, in an attempt to determine the potential therapeutic and adverse effects of illicit substances, is a growing field, but one that faces many regulatory challenges. Due to the potential abuse of illicit substances such as 

 “The intraperitoneal administration of chemotherapeutics has emerged as a potential route in ovarian cancer treatment. Nanoparticles as carriers for these agents could be interesting by increasing the retention of chemotherapeutics within the peritoneal cavity. Moreover, nanoparticles could be internalised by cancer cells and let the drug release near the biological target, which could increase the anticancer efficacy.
“The intraperitoneal administration of chemotherapeutics has emerged as a potential route in ovarian cancer treatment. Nanoparticles as carriers for these agents could be interesting by increasing the retention of chemotherapeutics within the peritoneal cavity. Moreover, nanoparticles could be internalised by cancer cells and let the drug release near the biological target, which could increase the anticancer efficacy.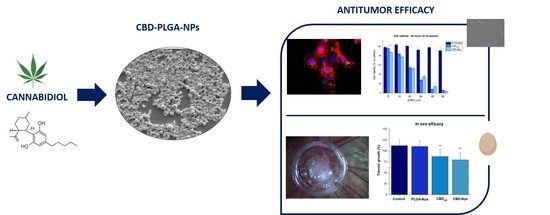
.jpg) “Despite limited data demonstrating pronounced negative effects of prenatal cannabis exposure, popular opinion and public policies still reflect the belief that cannabis is fetotoxic.
“Despite limited data demonstrating pronounced negative effects of prenatal cannabis exposure, popular opinion and public policies still reflect the belief that cannabis is fetotoxic. “An emerging area of preclinical research has investigated whether drug use in parents prior to conception influences drug responsivity in their offspring.
“An emerging area of preclinical research has investigated whether drug use in parents prior to conception influences drug responsivity in their offspring. “Cannabis sativa and its principal components, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and
“Cannabis sativa and its principal components, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and  “The therapeutic effect of the Cannabis plant largely depends on the presence and specific ratio of a spectrum of phytocannabinoids. While prescription of medicinal Cannabis for various conditions constantly grows, its consumption is mostly limited to oral or respiratory pathways, impeding its duration of action, bioavailability and efficacy. Herein, a long-acting formulation in the form of melt-printed polymeric microdepots for full-spectrum
“The therapeutic effect of the Cannabis plant largely depends on the presence and specific ratio of a spectrum of phytocannabinoids. While prescription of medicinal Cannabis for various conditions constantly grows, its consumption is mostly limited to oral or respiratory pathways, impeding its duration of action, bioavailability and efficacy. Herein, a long-acting formulation in the form of melt-printed polymeric microdepots for full-spectrum 
