 “Hepatic cardiomyopathy, a special type of heart failure develops in up to 50% of patients with cirrhosis and is a major determinant of survival. However, there is no reliable model of hepatic cardiomyopathy in mice. Herein we aimed to characterize the detailed hemodynamics of mice with bile-duct ligation (BDL)-induced liver fibrosis, by monitoring echocardiography and intracardiac pressure-volume (PV) relationships and myocardial structural alterations. Treatment of mice with a selective cannabinoid-2 receptor (CB2 -R) agonist, known to attenuate inflammation and fibrosis, was used to explore the impact of liver inflammation, fibrosis on cardiac function.
“Hepatic cardiomyopathy, a special type of heart failure develops in up to 50% of patients with cirrhosis and is a major determinant of survival. However, there is no reliable model of hepatic cardiomyopathy in mice. Herein we aimed to characterize the detailed hemodynamics of mice with bile-duct ligation (BDL)-induced liver fibrosis, by monitoring echocardiography and intracardiac pressure-volume (PV) relationships and myocardial structural alterations. Treatment of mice with a selective cannabinoid-2 receptor (CB2 -R) agonist, known to attenuate inflammation and fibrosis, was used to explore the impact of liver inflammation, fibrosis on cardiac function.
MAIN RESULTS:
BDL induced massive inflammation (increased leukocyte infiltration, inflammatory cytokines and chemokines), oxidative stress, microvascular dysfunction, and fibrosis in the liver. These pathological changes were accompanied by impaired diastolic, systolic and macrovascular functions, cardiac inflammation (increased MIP1, interleukin-1, P-selectin, CD45+ cells) and oxidative stress (increased malondialdehyde, 3-nitrotyrosine and NADPH-oxidases). CB2 -R up-regulation was observed both in livers and hearts of mice exposed to BDL. CB2 -R activation markedly improved hepatic inflammation, impaired microcirculation, fibrosis. CB2 -R activation also decreased serum TNF-alpha levels, and improved cardiac dysfunction, myocardial inflammation and oxidative stress underlining the importance of inflammatory mediators in the pathology of hepatic cardiomyopathy.
CONCLUSION:
We propose BDL-induced cardiomyopathy in mice as a model for hepatic/cirrhotic cardiomyopathy. This cardiomyopathy, similarly to cirrhotic cardiomyopathy in humans, is characterized by systemic hypotension, impaired macro- and microvascular function accompanied by both systolic and diastolic dysfunction. Our results indicate that the liver-heart inflammatory axis has a pivotal pathophysiological role in the development of hepatic cardiomyopathy. Thus, controlling liver and/or myocardial inflammation (e.g. with selective CB2-R agonists) may delay/prevent the development of cardiomyopathy in severe liver disease. ”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31469200
https://aasldpubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/hep.30916
 “The synthetic atypical cannabinoid Abn-CBD, a cannabidiol (CBD) derivative, has been recently shown to modulate the immune system in different organs, but its impact in obesity-related meta-inflammation remains unstudied.
“The synthetic atypical cannabinoid Abn-CBD, a cannabidiol (CBD) derivative, has been recently shown to modulate the immune system in different organs, but its impact in obesity-related meta-inflammation remains unstudied.
 “Confident relationships between diabetes and liver damage have previously been established.
“Confident relationships between diabetes and liver damage have previously been established. “Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a life-threatening complication of end-stage liver disease characterized by the rapid decline of kidney function. Herein, we explored the therapeutic potential of targeting the
“Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a life-threatening complication of end-stage liver disease characterized by the rapid decline of kidney function. Herein, we explored the therapeutic potential of targeting the 
 “Hepatic fibrosis is the consequence of an unresolved wound healing process in response to chronic liver injury and involves multiple cell types and molecular mechanisms. The hepatic endocannabinoid and apelin systems are two signalling pathways with a substantial role in the liver fibrosis pathophysiology-both are upregulated in patients with advanced liver disease. Endogenous
“Hepatic fibrosis is the consequence of an unresolved wound healing process in response to chronic liver injury and involves multiple cell types and molecular mechanisms. The hepatic endocannabinoid and apelin systems are two signalling pathways with a substantial role in the liver fibrosis pathophysiology-both are upregulated in patients with advanced liver disease. Endogenous 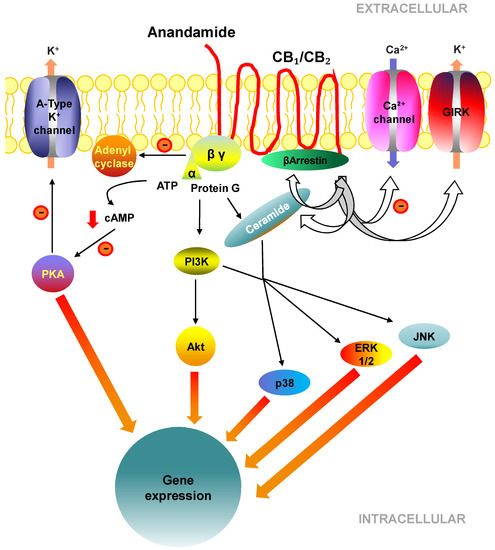
 “The endocannabinoid (EC) system has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several metabolic diseases, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
“The endocannabinoid (EC) system has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several metabolic diseases, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
 “Hepatic cardiomyopathy, a special type of heart failure develops in up to 50% of patients with cirrhosis and is a major determinant of survival. However, there is no reliable model of hepatic cardiomyopathy in mice. Herein we aimed to characterize the detailed hemodynamics of mice with bile-duct ligation (BDL)-induced liver fibrosis, by monitoring echocardiography and intracardiac pressure-volume (PV) relationships and myocardial structural alterations. Treatment of mice with a selective
“Hepatic cardiomyopathy, a special type of heart failure develops in up to 50% of patients with cirrhosis and is a major determinant of survival. However, there is no reliable model of hepatic cardiomyopathy in mice. Herein we aimed to characterize the detailed hemodynamics of mice with bile-duct ligation (BDL)-induced liver fibrosis, by monitoring echocardiography and intracardiac pressure-volume (PV) relationships and myocardial structural alterations. Treatment of mice with a selective  “Formation of schistosomal granulomata surrounding the ova can result in schistosomiasis-associated liver fibrosis (SSLF). The current standard of treatment is praziquantel (PZQ), which cannot effectively reverse SSLF.
“Formation of schistosomal granulomata surrounding the ova can result in schistosomiasis-associated liver fibrosis (SSLF). The current standard of treatment is praziquantel (PZQ), which cannot effectively reverse SSLF. “Increased incidence of obesity and excess weight lead to an increased incidence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Recent evidence indicates a protective effect of
“Increased incidence of obesity and excess weight lead to an increased incidence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Recent evidence indicates a protective effect of