 “Recently, cannabinoids, such as cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), have been the subject of intensive research and heavy scrutiny. Cannabinoids encompass a wide array of organic molecules, including those that are physiologically produced in humans, synthesized in laboratories, and extracted primarily from the Cannabis sativa plant. These organic molecules share similarities in their chemical structures as well as in their protein binding profiles. However, pronounced differences do exist in their mechanisms of action and clinical applications, which will be briefly compared and contrasted in this review. The mechanism of action of CBD and its potential applications in cancer therapy will be the major focus of this review article.”
“Recently, cannabinoids, such as cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), have been the subject of intensive research and heavy scrutiny. Cannabinoids encompass a wide array of organic molecules, including those that are physiologically produced in humans, synthesized in laboratories, and extracted primarily from the Cannabis sativa plant. These organic molecules share similarities in their chemical structures as well as in their protein binding profiles. However, pronounced differences do exist in their mechanisms of action and clinical applications, which will be briefly compared and contrasted in this review. The mechanism of action of CBD and its potential applications in cancer therapy will be the major focus of this review article.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33143283/
“The use of cannabinoids containing plant extracts as herbal medicine can be traced back to as early as 500 BC. In recent years, the medical and health-related applications of one of the non-psychotic cannabinoids, cannabidiol or CBD, has garnered tremendous attention. In this review, we will discuss the most recent findings that strongly support the further development of CBD as a promising anti-cancer drug.”
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/12/11/3203
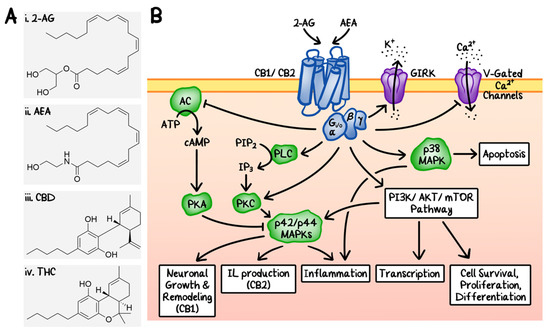

 “Chronic pelvic pain affects women across all demographics. Its management is complex and requires a multimodal approach.
“Chronic pelvic pain affects women across all demographics. Its management is complex and requires a multimodal approach. “These data support the notion that CBD and CBDV act as functional partial agonists on dopamine D2-like receptors in vivo.
“These data support the notion that CBD and CBDV act as functional partial agonists on dopamine D2-like receptors in vivo. “Evidence details how cannabis can influence the use of other psychoactive substances, including prescription medications, alcohol, tobacco and illicit drugs, but very little research has examined the factors associated with these changes in substance use patterns. This paper explores the self-reported use of cannabis as a substitute for alcohol among a Canadian medical cannabis patient population.
“Evidence details how cannabis can influence the use of other psychoactive substances, including prescription medications, alcohol, tobacco and illicit drugs, but very little research has examined the factors associated with these changes in substance use patterns. This paper explores the self-reported use of cannabis as a substitute for alcohol among a Canadian medical cannabis patient population. “We aimed to comprehensively evaluate the effects of medical marijuana on symptoms that are relevant to movement disorders with a focus on Huntington disease (HD).
“We aimed to comprehensively evaluate the effects of medical marijuana on symptoms that are relevant to movement disorders with a focus on Huntington disease (HD). “Although studied in a few randomized controlled trials (RCTs), the efficacy of medical cannabis (MC) for chronic pain remains controversial. Using an alternative approach, this multicenter, questionnaire-based prospective cohort was aimed to assess the long-term effects of MC on chronic pain of various etiologies and to identify predictors for MC treatment success.
“Although studied in a few randomized controlled trials (RCTs), the efficacy of medical cannabis (MC) for chronic pain remains controversial. Using an alternative approach, this multicenter, questionnaire-based prospective cohort was aimed to assess the long-term effects of MC on chronic pain of various etiologies and to identify predictors for MC treatment success. “Cannabinoids have long been used for their psychotropic and possible medical properties of symptom relief. In the past few years, a vast literature shows that cannabinoids are neuroprotective under different pathological situations.
“Cannabinoids have long been used for their psychotropic and possible medical properties of symptom relief. In the past few years, a vast literature shows that cannabinoids are neuroprotective under different pathological situations. “Background/objectives: Use of cannabis is increasing in a variety of populations in the United States; however, few investigations about how and for what reasons cannabis is used in older populations exist.
“Background/objectives: Use of cannabis is increasing in a variety of populations in the United States; however, few investigations about how and for what reasons cannabis is used in older populations exist. “Cannabis exposure is becoming more common in older age but little is known about how it is associated with brain health in this population.
“Cannabis exposure is becoming more common in older age but little is known about how it is associated with brain health in this population. “To determine if cannabis may be used as an alternative or adjunct treatment for intermittent and chronic prescription opioid users.
“To determine if cannabis may be used as an alternative or adjunct treatment for intermittent and chronic prescription opioid users.