
We describe the novel use of a cannabidiol-based extract that incidentally improved core social deficits and overall functioning in a patient with autism spectrum disorder, at a lower dose than has been previously reported in autism spectrum disorder.
Case presentation: The parents of a 15-year-old boy, of South African descent, with autism spectrum disorder, selective mutism, anxiety, and controlled epilepsy, consulted a medical cannabis physician to trial cannabis extract to replace seizure medications. Incidentally, at a very low cannabidiol-based extract dose, he experienced unanticipated positive effects on behavioral symptoms and core social deficits.
Conclusion: This case report provides evidence that a lower than previously reported dose of a phytocannabinoid in the form of a cannabidiol-based extract may be capable of aiding in autism spectrum disorder-related behavioral symptoms, core social communication abilities, and comorbid anxiety, sleep difficulties, and weight control. Further research is needed to elucidate the clinical role and underlying biological mechanisms of action of cannabidiol-based extract in patients with autism spectrum disorder.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32958062/
https://jmedicalcasereports.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13256-020-02478-7

 “Cannabis products have been used for centuries by humans for recreational and medical purposes. Resent research, proposed the promising therapeutic potential of cannabis and related cannabinoids for a wide range of medical conditions, including psychiatric and neurological diseases.
“Cannabis products have been used for centuries by humans for recreational and medical purposes. Resent research, proposed the promising therapeutic potential of cannabis and related cannabinoids for a wide range of medical conditions, including psychiatric and neurological diseases. “Cannabis is an annual plant with a long history of use as food, feed, fiber, oil, medicine, and narcotics. Despite realizing its true value, it has not yet found its true place. Cannabis has had a long history with many ups and downs, and now it is our turn to promote it.
“Cannabis is an annual plant with a long history of use as food, feed, fiber, oil, medicine, and narcotics. Despite realizing its true value, it has not yet found its true place. Cannabis has had a long history with many ups and downs, and now it is our turn to promote it.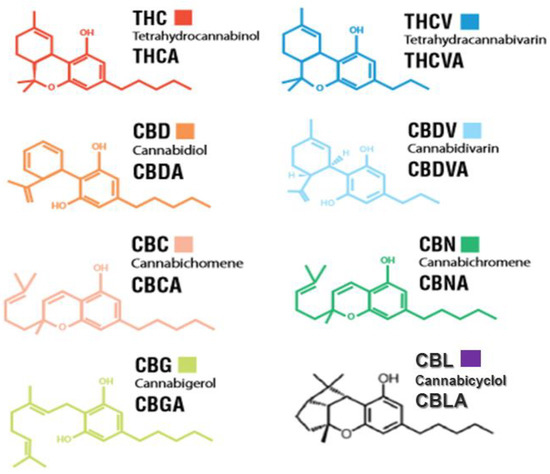
 “Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a multifactorial, pervasive neurodevelopmental disorder defined by the core symptoms of significant impairment in social interaction and communication as well as restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior. In addition to these core behaviors, persons with ASD frequently have associated noncore behavioral disturbance (ie, self-injury, aggression), as well as several medical comorbidities. Currently, no effective treatment exists for the core symptoms of ASD.
“Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a multifactorial, pervasive neurodevelopmental disorder defined by the core symptoms of significant impairment in social interaction and communication as well as restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior. In addition to these core behaviors, persons with ASD frequently have associated noncore behavioral disturbance (ie, self-injury, aggression), as well as several medical comorbidities. Currently, no effective treatment exists for the core symptoms of ASD. “Precise cannabis treatment dosing remains a major challenge, leading to physicians’ reluctance to prescribe medical cannabis.
“Precise cannabis treatment dosing remains a major challenge, leading to physicians’ reluctance to prescribe medical cannabis.
 “Attenuating emesis elicited by both disease and medical treatments of disease remains a critical
“Attenuating emesis elicited by both disease and medical treatments of disease remains a critical  “Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is an often chronic condition for which currently available medications have limited efficacy.
“Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is an often chronic condition for which currently available medications have limited efficacy. “Cannabidiol (
“Cannabidiol ( “Medical cannabis (MC) treatment for migraine is practically emerging, although sufficient clinical data are not available for this indication. This cross-sectional questionnaire-based study aimed to investigate the associations between phytocannabinoid treatment and migraine frequency.
“Medical cannabis (MC) treatment for migraine is practically emerging, although sufficient clinical data are not available for this indication. This cross-sectional questionnaire-based study aimed to investigate the associations between phytocannabinoid treatment and migraine frequency.