 “∆ 9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (∆9 -THC), the active phytocannabinoid in cannabis, is virtually an adjunct to the endogenous endocannabinoid signaling system.
“∆ 9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (∆9 -THC), the active phytocannabinoid in cannabis, is virtually an adjunct to the endogenous endocannabinoid signaling system.
By interacting with G-protein-coupled receptors CB1 and CB2, ∆9 -THC affects peripheral and central circulation by lowering sympathetic activity, altering gene expression, cell proliferation, and differentiation, decreasing leukocyte migration, modulating neurotransmitter release thereby modulating cardiovascular functioning, tumorigenesis, immune responses, behavioral and locomotory activities respectively.
∆ 9 -THC is effective in suppressing chemotherapy-induced vomiting, retards malignant tumor growth, inhibits metastasis, and promotes apoptosis. Other mechanisms involved are targeting cell cycle at the G2-M phase in human breast cancer, downregulation of E2F transcription factor 1 (E2F1) in human glioblastoma multiforme, and stimulation of ER stress-induced autophagy.
∆ 9 -THC also plays a role in ameliorating neuroinflammation, excitotoxicity, neuroplasticity, trauma, and stroke and is associated with reliving childhood epilepsy, brain trauma, and neurodegenerative diseases.
∆9 -THC via CB1 receptors affects nociception, emotion, memory, and reduces neuronal excitability and excitotoxicity in epilepsy. It also increases renal blood flow, reduces intraocular pressure via a sympathetic pathway, and modulates hormonal release, thereby decreasing the reproductive function and increasing glucose metabolism.
Versatile medical marijuana has stimulated abundant research demonstrating substantial therapeutic promise, suggesting the possibilities of first-in-class drugs in diverse therapeutic segments. In this review, we represent the current pharmacological status of the phytocannabinoid, ∆ 9 -THC, and synthetic analogs in cancer, cardiovascular, and neurodegenerative disorders.”

 “Cannabis is an annual plant with a long history of use as food, feed, fiber, oil, medicine, and narcotics. Despite realizing its true value, it has not yet found its true place. Cannabis has had a long history with many ups and downs, and now it is our turn to promote it.
“Cannabis is an annual plant with a long history of use as food, feed, fiber, oil, medicine, and narcotics. Despite realizing its true value, it has not yet found its true place. Cannabis has had a long history with many ups and downs, and now it is our turn to promote it.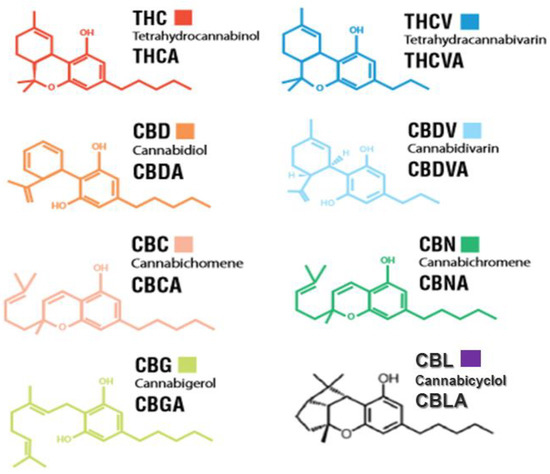
 “Attenuating emesis elicited by both disease and medical treatments of disease remains a critical
“Attenuating emesis elicited by both disease and medical treatments of disease remains a critical  “There is increasing interest in the use of purified
“There is increasing interest in the use of purified  “Cannabis has been used to relieve the symptoms of disease for thousands of years. However, social and political biases have limited effective interrogation of the potential benefits of cannabis and polarised public opinion.
“Cannabis has been used to relieve the symptoms of disease for thousands of years. However, social and political biases have limited effective interrogation of the potential benefits of cannabis and polarised public opinion.
 “In the last decade, we have observed an increased public and scientific interest in the clinical applications of medical cannabis.
“In the last decade, we have observed an increased public and scientific interest in the clinical applications of medical cannabis. “Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabinol (CBN) affect the human endocannabinoid system.
“Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabinol (CBN) affect the human endocannabinoid system. “This study evaluated the potential of combined cannabis constituents to reduce nausea.
“This study evaluated the potential of combined cannabis constituents to reduce nausea.