 “Breast cancer (BC) is the most common cancer in women worldwide. Approximately 70-80% of BCs express estrogen receptors (ER), which predict the response to endocrine therapy (ET), and are therefore hormone receptor-positive (HR+).
“Breast cancer (BC) is the most common cancer in women worldwide. Approximately 70-80% of BCs express estrogen receptors (ER), which predict the response to endocrine therapy (ET), and are therefore hormone receptor-positive (HR+).
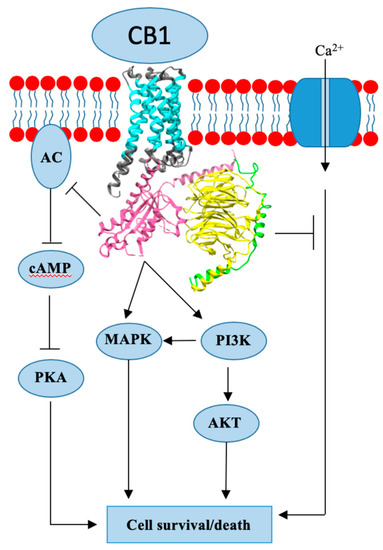
Endogenous cannabinoids together with cannabinoid receptor 1 and 2 (CB1, CB2) constitute the basis of the endocannabinoid system.
Interactions of cannabinoids with hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis hormones are well documented, and two studies found a positive correlation between peak plasma endogenous cannabinoid anandamide with peak plasma 17β-estradiol, luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone levels at ovulation in healthy premenopausal women. Do cannabinoids have an effect on HR+ BC? In this paper we review known and possible interactions between cannabinoids and specific HR+ BC treatments.
In preclinical studies, CB1 and CB2 agonists (i.e., anandamide, THC) have been shown to inhibit the proliferation of ER positive BC cell lines.
There is less evidence for antitumor cannabinoid action in HR+ BC in animal models and there are no clinical trials exploring the effects of cannabinoids on HR+ BC treatment outcomes. Two studies have shown that tamoxifen and several other selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERM) can act as inverse agonists on CB1 and CB2, an interaction with possible clinical consequences. In addition, cannabinoid action could interact with other commonly used endocrine and targeted therapies used in the treatment of HR+ BC.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32106399
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/12/3/525

 “The 20% prevalence of chronic pain in the general population is a major health concern given the often profound associated impairment of daily activities, employment status, and health-related quality of life in sufferers. Resource utilization associated with chronic pain represents an enormous burden for healthcare systems. Although analgesia based on the World Health Organization’s pain ladder continues to be the mainstay of chronic pain management, aside from chronic cancer pain or end-of-life care, prolonged use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or opioids to manage chronic pain is rarely sustainable.
“The 20% prevalence of chronic pain in the general population is a major health concern given the often profound associated impairment of daily activities, employment status, and health-related quality of life in sufferers. Resource utilization associated with chronic pain represents an enormous burden for healthcare systems. Although analgesia based on the World Health Organization’s pain ladder continues to be the mainstay of chronic pain management, aside from chronic cancer pain or end-of-life care, prolonged use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or opioids to manage chronic pain is rarely sustainable. “A growing body of literature indicates that activation of
“A growing body of literature indicates that activation of  “Neuropathic pain conditions including neuropathic orofacial pain (NOP) are difficult to treat. Contemporary therapeutic agents for neuropathic pain are often ineffective in relieving pain and are associated with various adverse effects. Finding new options for treating neuropathic pain is a major priority in pain-related research.
“Neuropathic pain conditions including neuropathic orofacial pain (NOP) are difficult to treat. Contemporary therapeutic agents for neuropathic pain are often ineffective in relieving pain and are associated with various adverse effects. Finding new options for treating neuropathic pain is a major priority in pain-related research. “Metastatic breast cancer is prevalent worldwide, and one of the most common sites of metastasis are long bones. Of patients with disease, the major symptom is pain, yet current medications fail to adequately result in analgesic efficacy and present major undesirable adverse effects.
“Metastatic breast cancer is prevalent worldwide, and one of the most common sites of metastasis are long bones. Of patients with disease, the major symptom is pain, yet current medications fail to adequately result in analgesic efficacy and present major undesirable adverse effects. “The legalisation of
“The legalisation of 