“Cannabinoid-based medications possess unique multimodal analgesic mechanisms of action, modulating diverse pain targets.
Cannabinoids are classified based on their origin into three categories: endocannabinoids (present endogenously in human tissues), phytocannabinoids (plant derived) and synthetic cannabinoids (pharmaceutical). Cannabinoids exert an analgesic effect, peculiarly in hyperalgesia, neuropathic pain and inflammatory states.
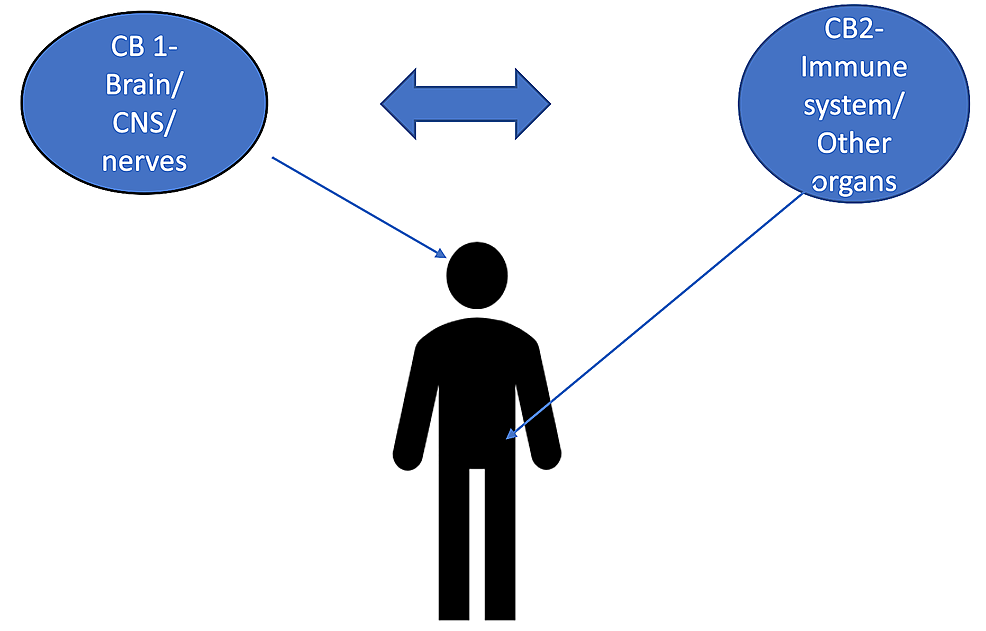
Endocannabinoids are released on demand from postsynaptic terminals and travels retrograde to stimulate cannabinoids receptors on presynaptic terminals, inhibiting the release of excitatory neurotransmitters. Cannabinoids (endogenous and phytocannabinoids) produce analgesia by interacting with cannabinoids receptors type 1 and 2 (CB1 and CB2), as well as putative non-CB1/CB2 receptors; G protein-coupled receptor 55, and transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1. Moreover, they modulate multiple peripheral, spinal and supraspinal nociception pathways.
Cannabinoids-opioids cross-modulation and synergy contribute significantly to tolerance and antinociceptive effects of cannabinoids. This narrative review evaluates cannabinoids’ diverse mechanisms of action as it pertains to nociception modulation relevant to the practice of anesthesiologists and pain medicine physicians.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33239391/
https://rapm.bmj.com/content/early/2020/11/24/rapm-2020-102114

 “The burden of chronic pain has affected many individuals leading to distress and discomfort, alongside numerous side effects with conventional therapeutic approaches.
“The burden of chronic pain has affected many individuals leading to distress and discomfort, alongside numerous side effects with conventional therapeutic approaches. “The behavioural effects elicited by chemical constituents of Cannabis sativa, such as
“The behavioural effects elicited by chemical constituents of Cannabis sativa, such as  “Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) promotes antinociception by activating the descending pain modulation pathway and consequently releasing endogenous analgesic substances.
“Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) promotes antinociception by activating the descending pain modulation pathway and consequently releasing endogenous analgesic substances. “It is thought that endogenous cannabinoids have a role in the analgesia induced by specific forms of stress.
“It is thought that endogenous cannabinoids have a role in the analgesia induced by specific forms of stress. “Muscle pain affects approximately 11-24% of the global population.
“Muscle pain affects approximately 11-24% of the global population.