“Various preclinical and clinical studies exhibited the potential of cannabis against various diseases, including cancer and related pain. Subsequently, many efforts have been made to establish and develop cannabis-related products and make them available as prescription products. Moreover, FDA has already approved some cannabis-related products, and more advancement in this aspect is still going on. However, the approved product of cannabis is in oral dosage form, which exerts various limitations to achieve maximum therapeutic effects. A considerable translation is on a hike to improve bioavailability, and ultimately, the therapeutic efficacy of cannabis by the employment of nanotechnology. Besides the well-known psychotropic effects of cannabis upon the use at high doses, literature has also shown the importance of cannabis and its constituents in minimising the lethality of cancer in the preclinical models. This review discusses the history of cannabis, its legal aspect, safety profile, the mechanism by which cannabis combats with cancer, and the advancement of clinical therapy by exploiting nanotechnology. A brief discussion related to the role of cannabinoid in various cancers has also been incorporated. Lastly, the information regarding completed and ongoing trials have also been elaborated.”
Category Archives: Gastric Cancer
The Endocannabinoid System: A Potential Target for the Treatment of Various Diseases
 “The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis, a balance in internal environment (temperature, mood, and immune system) and energy input and output in living, biological systems.
“The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis, a balance in internal environment (temperature, mood, and immune system) and energy input and output in living, biological systems.
In addition to regulating physiological processes, the ECS directly influences anxiety, feeding behaviour/appetite, emotional behaviour, depression, nervous functions, neurogenesis, neuroprotection, reward, cognition, learning, memory, pain sensation, fertility, pregnancy, and pre-and post-natal development.
The ECS is also involved in several pathophysiological diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases. In recent years, genetic and pharmacological manipulation of the ECS has gained significant interest in medicine, research, and drug discovery and development.
The distribution of the components of the ECS system throughout the body, and the physiological/pathophysiological role of the ECS-signalling pathways in many diseases, all offer promising opportunities for the development of novel cannabinergic, cannabimimetic, and cannabinoid-based therapeutic drugs that genetically or pharmacologically modulate the ECS via inhibition of metabolic pathways and/or agonism or antagonism of the receptors of the ECS. This modulation results in the differential expression/activity of the components of the ECS that may be beneficial in the treatment of a number of diseases.
This manuscript in-depth review will investigate the potential of the ECS in the treatment of various diseases, and to put forth the suggestion that many of these secondary metabolites of Cannabis sativa L. (hereafter referred to as “C. sativa L.” or “medical cannabis”), may also have potential as lead compounds in the development of cannabinoid-based pharmaceuticals for a variety of diseases.”
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/22/17/9472
“Cannabis sativa L. as a Natural Drug Meeting the Criteria of a Multitarget Approach to Treatment”
Education and communication are critical to effectively incorporating cannabis into cancer treatment
 “Providers need to be better equipped to discuss medical cannabis with patients even if they are not willing to prescribe it. The oncology community would be well served to ensure that providers are aware of existing cannabis research and are able to incorporate it into their communications with patients instead of leaving patients to figure out medical cannabis on their own.”
“Providers need to be better equipped to discuss medical cannabis with patients even if they are not willing to prescribe it. The oncology community would be well served to ensure that providers are aware of existing cannabis research and are able to incorporate it into their communications with patients instead of leaving patients to figure out medical cannabis on their own.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32986251/
https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cncr.33204
Cancer patients’ experiences with medicinal cannabis-related care
 “Background: Little is known about medical cannabis (MC)-related care for patients with cancer using MC.
“Background: Little is known about medical cannabis (MC)-related care for patients with cancer using MC.
Methods: Semistructured telephone interviews were conducted in a convenience sample of individuals (n = 24) with physician-confirmed oncologic diagnoses and state/district authorization to use MC (Arizona, California, Florida, Illinois, Massachusetts, Oregon, New York, and Washington, DC) from April 2017 to March 2019. Standard qualitative techniques were used to assess the degree of MC-related health care oversight, MC practices, and key information sources.
Results: Among 24 participants (median age, 57 years; range, 30-71 years; 16 women [67%]), MC certifications were typically issued by a professional new to a patient’s care after a brief, perfunctory consultation. Patients disclosed MCuse to their established medical teams but received little medical advice about whether and how to use MC. Patients with cancer used MC products as multipurpose symptom management and as cancer-directed therapy, sometimes in lieu of standard-of-care treatments. Personal experimentation, including methodical self-monitoring, was an important source of MC know-how. Absent formal advice from medical professionals, patients relied on nonmedical sources for MC information.
Conclusions: Patients with cancer used MC with minimal medical oversight. Most received MC certifications through brief meetings with unfamiliar professionals. Participants desired but were often unable to access high-quality clinical information about MC from their established medical teams. Because many patients are committed to using MC, a product sustained by a growing industry, medical providers should familiarize themselves with the existing data for MM and its limitations to address a poorly met clinical need.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32986266/
“Notably, oncology patients reported using medical cannabis (MC) for symptom management and as cancer‐directed therapy, sometimes instead of traditional treatments.”
https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cncr.33202
Anti-Cancer Potential of Cannabinoids, Terpenes, and Flavonoids Present in Cannabis
 “In recent years, and even more since its legalization in several jurisdictions, cannabis and the endocannabinoid system have received an increasing amount of interest related to their potential exploitation in clinical settings. Cannabinoids have been suggested and shown to be effective in the treatment of various conditions. In cancer, the endocannabinoid system is altered in numerous types of tumours and can relate to cancer prognosis and disease outcome. Additionally, cannabinoids display anticancer effects in several models by suppressing the proliferation, migration and/or invasion of cancer cells, as well as tumour angiogenesis. However, the therapeutic use of cannabinoids is currently limited to the treatment of symptoms and pain associated with chemotherapy, while their potential use as cytotoxic drugs in chemotherapy still requires validation in patients. Along with cannabinoids, cannabis contains several other compounds that have also been shown to exert anti-tumorigenic actions. The potential anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids, present in cannabis, are explored in this literature review.”
“In recent years, and even more since its legalization in several jurisdictions, cannabis and the endocannabinoid system have received an increasing amount of interest related to their potential exploitation in clinical settings. Cannabinoids have been suggested and shown to be effective in the treatment of various conditions. In cancer, the endocannabinoid system is altered in numerous types of tumours and can relate to cancer prognosis and disease outcome. Additionally, cannabinoids display anticancer effects in several models by suppressing the proliferation, migration and/or invasion of cancer cells, as well as tumour angiogenesis. However, the therapeutic use of cannabinoids is currently limited to the treatment of symptoms and pain associated with chemotherapy, while their potential use as cytotoxic drugs in chemotherapy still requires validation in patients. Along with cannabinoids, cannabis contains several other compounds that have also been shown to exert anti-tumorigenic actions. The potential anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids, present in cannabis, are explored in this literature review.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32708138/
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/12/7/1985
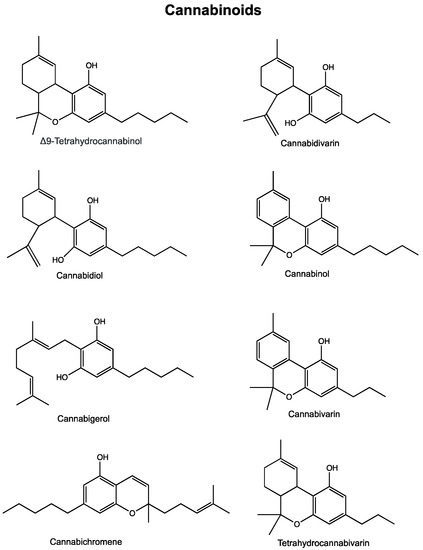
Cannabinoids as anticancer therapeutic agents.
 “The recent announcement of marijuana legalization in Canada spiked many discussions about potential health benefits of Cannabis sativa. Cannabinoids are active chemical compounds produced by cannabis, and their numerous effects on the human body are primarily exerted through interactions with cannabinoid receptor types 1 (CB1) and 2 (CB2). Cannabinoids are broadly classified as endo-, phyto-, and synthetic cannabinoids. In this review, we will describe the activity of cannabinoids on the cellular level, comprehensively summarize the activity of all groups of cannabinoids on various cancers and propose several potential mechanisms of action of cannabinoids on cancer cells.”
“The recent announcement of marijuana legalization in Canada spiked many discussions about potential health benefits of Cannabis sativa. Cannabinoids are active chemical compounds produced by cannabis, and their numerous effects on the human body are primarily exerted through interactions with cannabinoid receptor types 1 (CB1) and 2 (CB2). Cannabinoids are broadly classified as endo-, phyto-, and synthetic cannabinoids. In this review, we will describe the activity of cannabinoids on the cellular level, comprehensively summarize the activity of all groups of cannabinoids on various cancers and propose several potential mechanisms of action of cannabinoids on cancer cells.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32249682
“Endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids can be used for cancer therapy. Cannabis extracts have stronger anti-tumor capacity than single cannabinoids. Combination of several cannabinoids may have more potent effect on cancer.”
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/15384101.2020.1742952?journalCode=kccy20
The Endocannabinoid System: A Target for Cancer Treatment.
 “In recent years, the endocannabinoid system has received great interest as a potential therapeutic target in numerous pathological conditions.
“In recent years, the endocannabinoid system has received great interest as a potential therapeutic target in numerous pathological conditions.
Cannabinoids have shown an anticancer potential by modulating several pathways involved in cell growth, differentiation, migration, and angiogenesis.
However, the therapeutic efficacy of cannabinoids is limited to the treatment of chemotherapy-induced symptoms or cancer pain, but their use as anticancer drugs in chemotherapeutic protocols requires further investigation.
In this paper, we reviewed the role of cannabinoids in the modulation of signaling mechanisms implicated in tumor progression.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31979368
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/3/747
“In addition to the symptomatic therapy of cancer patients, the antitumor effects of cannabinoids (whether in monotherapy or in combination with other cancer therapies) have promising potential in the treatment of cancer patients.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31950844
“In addition to the well-known palliative effects of cannabinoids on some cancer-associated symptoms, a large body of evidence shows that these molecules can decrease tumour growth in animal models of cancer. In addition, cannabinoids inhibit angiogenesis and decrease metastasis in various tumour types in laboratory animals. Thus, numerous studies have provided evidence that thc and other cannabinoids exhibit antitumour effects in a wide array of animal models of cancer.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4791144/
“Antitumour actions of cannabinoids.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30019449
“The endocannabinoid system as a target for the development of new drugs for cancer therapy” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12723496
“Cannabinoids as Anticancer Drugs.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28826542
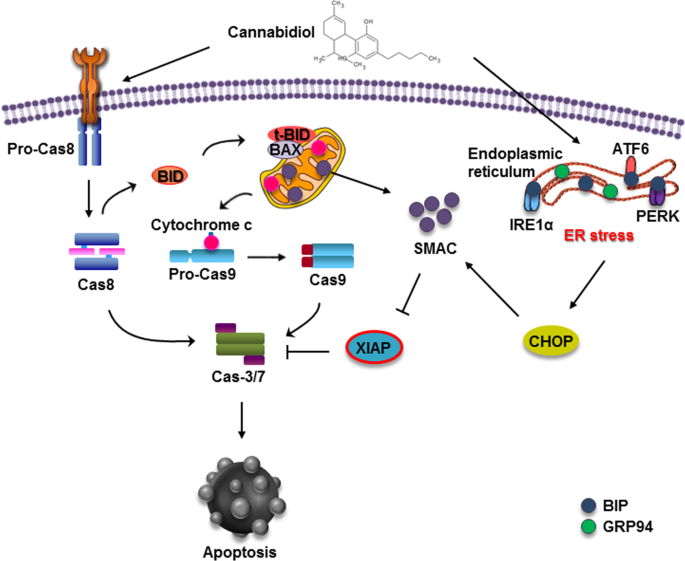
Cannabidiol promotes apoptosis via regulation of XIAP/Smac in gastric cancer.
 “According to recent studies, Cannabidiol (CBD), one of the main components of Cannabis sativa, has anticancer effects in several cancers. However, the exact mechanism of CBD action is not currently understood.
“According to recent studies, Cannabidiol (CBD), one of the main components of Cannabis sativa, has anticancer effects in several cancers. However, the exact mechanism of CBD action is not currently understood.
Here, CBD promoted cell death in gastric cancer.
We suggest that CBD induced apoptosis by suppressing X-linked inhibitor apoptosis (XIAP), a member of the IAP protein family. CBD reduced XIAP protein levels while increasing ubiquitination of XIAP. The expression of Smac, a known inhibitor of XIAP, was found to be elevated during CBD treatment. Moreover, CBD treatment increased the interaction between XIAP and Smac by increasing Smac release from mitochondria to the cytosol. CBD has also been shown to affect mitochondrial dysfunction.
Taken together, these results suggest that CBD may have potential as a new therapeutic target in gastric cancer.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31699976
“In conclusion, our study showed that CBD induces apoptotic cell death in gastric cancer cells, which is triggered by ER stress generation and subsequent XIAP inhibition by Smac. Taken together, our results suggest the potential of CBD in novel treatments against gastric cancer.”
Cannabidiol Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Cell Apoptosis in Human Gastric Cancer SGC-7901 Cells.
 “The main chemical component of cannabis, cannabidiol (CBD), has been shown to have antitumor properties.
“The main chemical component of cannabis, cannabidiol (CBD), has been shown to have antitumor properties.
The present study examined the in vitro effects of CBD on human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells.
We found that CBD significantly inhibited the proliferation and colony formation of SGC-7901 cells.
These results indicated that CBD could induce G0-G1 phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by increasing ROS production, leading to the inhibition of SGC-7901 cell proliferation, thereby suggesting that CBD may have therapeutic effects on gastric cancer.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31349651
“These findings may be utilized in the development of CBD as a potential drug for the treatment of gastric cancer.”
The heterogeneity and complexity of Cannabis extracts as antitumor agents

“The Cannabis plant contains over 100 phytocannabinoids and hundreds of other components. The biological effects and interplay of these Cannabis compounds are not fully understood and yet influence the plant’s therapeutic effects.
Here we assessed the antitumor effects of whole Cannabis extracts, which contained significant amounts of differing phytocannabinoids, on different cancer lines from various tumor origins.
Our results show that specific Cannabis extracts impaired the survival and proliferation of cancer cell lines as well as induced apoptosis.
Our findings showed that pure (-)-Δ9–trans-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) did not produce the same effects on these cell lines as the whole Cannabis extracts. Furthermore, Cannabis extracts with similar amounts of Δ9-THC produced significantly different effects on the survival of specific cancer cells.
In addition, we demonstrated that specific Cannabis extracts may selectively and differentially affect cancer cells and differing cancer cell lines from the same organ origin. We also found that cannabimimetic receptors were differentially expressed among various cancer cell lines and suggest that this receptor diversity may contribute to the heterogeneous effects produced by the differing Cannabis extracts on each cell line.
Our overall findings indicate that the effect of a Cannabis extract on a specific cancer cell line relies on the extract’s composition as well as on certain characteristics of the targeted cells.”
http://www.oncotarget.com/index.php?journal=oncotarget&page=article&op=view&path[]=26983
“Many previous reports highlight and demonstrate the anti-tumor effects of cannabinoids. In the last decade, accumulating evidence has indicated that phytocannabinoids might have antitumor properties. A number of in vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated the effects of phytocannabinoids on tumor progression by interrupting several characteristic features of cancer. These studies suggest that specific cannabinoids such as Δ9-THC and CBD induce apoptosis and inhibit proliferation in various cancer cell lines.”
