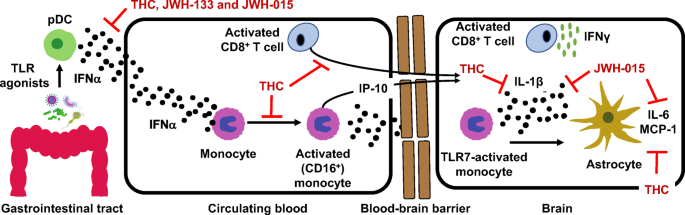
 “HIV infection affects an estimated 38 million people. Approximately 50% of HIV patients exhibit neurocognitive dysfunction termed HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder (HAND). HAND is a consequence of chronic low-level neuroinflammation due to HIV entry into the brain. Initially, monocytes become activated in circulation and traffic to the brain. Monocytes, when activated, become susceptible to infection by HIV and can then carry the virus across the blood brain barrier. Once in the brain, activated monocytes secrete chemokines, which recruit virus-specific CD8+ T cells into the brain to further promote neuroinflammation. HAND is closely linked to systemic inflammation driven, in part, by HIV but is also due to persistent translocation of microorganisms across the GI tract. Persistent anti-viral responses in the GI tract compromise microbial barrier integrity. Indeed, HIV patients can exhibit remarkably high levels of activated (CD16+) monocytes in circulation.
“HIV infection affects an estimated 38 million people. Approximately 50% of HIV patients exhibit neurocognitive dysfunction termed HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder (HAND). HAND is a consequence of chronic low-level neuroinflammation due to HIV entry into the brain. Initially, monocytes become activated in circulation and traffic to the brain. Monocytes, when activated, become susceptible to infection by HIV and can then carry the virus across the blood brain barrier. Once in the brain, activated monocytes secrete chemokines, which recruit virus-specific CD8+ T cells into the brain to further promote neuroinflammation. HAND is closely linked to systemic inflammation driven, in part, by HIV but is also due to persistent translocation of microorganisms across the GI tract. Persistent anti-viral responses in the GI tract compromise microbial barrier integrity. Indeed, HIV patients can exhibit remarkably high levels of activated (CD16+) monocytes in circulation.
Recent studies, including our own, show that HIV patients using medical marijuana exhibit lower levels of circulating CD16+ monocytes than non-cannabis using HIV patients. Cannabis is a known immune modulator, including anti-inflammatory properties, mediated, in part, by ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), as well as less characterized minor cannabinoids, such as cannabidiol (CBD), terpenes and presumably other cannabis constituents. The immune modulating activity of THC is largely mediated through cannabinoid receptors (CB) 1 and 2, with CB1 also responsible for the psychotropic properties of cannabis.
Here we discuss the anti-inflammatory properties of cannabinoids in the context of HIV and propose CB2 as a putative therapeutic target for the treatment of neuroinflammation. Graphical Abstract HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder is a systemic inflammatory disease leading to activation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells, monocytes and T cells. Monocyte and CD8 T cell migration across the BBB and interaction with astrocytes promotes neurotoxic inflammatory mediators release. CB2 ligands are proposed as therapeutics capable of suppressing systemic and localized inflammation.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32409991
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11481-020-09918-7

 “HIV infection leads to blood-brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction that does not resolve despite viral suppression on antiretroviral therapy and is associated with adverse clinical outcomes.
“HIV infection leads to blood-brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction that does not resolve despite viral suppression on antiretroviral therapy and is associated with adverse clinical outcomes. “Neuropathic pain associated with nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), therapeutic agents for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), responds poorly to available drugs.
“Neuropathic pain associated with nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), therapeutic agents for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), responds poorly to available drugs. “Aging and HIV have adverse effects on the central nervous system, including increased inflammation and neural injury and confer risk of neurocognitive impairment (NCI).
“Aging and HIV have adverse effects on the central nervous system, including increased inflammation and neural injury and confer risk of neurocognitive impairment (NCI). “HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder (HAND) affects nearly half of all HIV-infected individuals. Synaptodendritic damage correlates with neurocognitive decline in HAND, and many studies have demonstrated that HIV-induced neuronal injury results from excitotoxic and inflammatory mechanisms.
“HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder (HAND) affects nearly half of all HIV-infected individuals. Synaptodendritic damage correlates with neurocognitive decline in HAND, and many studies have demonstrated that HIV-induced neuronal injury results from excitotoxic and inflammatory mechanisms. “Heavy cannabis users had decreased frequencies of human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR+CD38+CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell frequencies, compared to frequencies of these cells in non-cannabis-using individuals.
“Heavy cannabis users had decreased frequencies of human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR+CD38+CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell frequencies, compared to frequencies of these cells in non-cannabis-using individuals. “Thanks to the success of modern antiretroviral therapy (ART), people living with HIV (PLWH) have life expectancies which approach that of persons in the general population. However, despite the ability of ART to suppress viral replication, PLWH have high levels of chronic systemic inflammation which drives the development of comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes and non-AIDS associated malignancies.
“Thanks to the success of modern antiretroviral therapy (ART), people living with HIV (PLWH) have life expectancies which approach that of persons in the general population. However, despite the ability of ART to suppress viral replication, PLWH have high levels of chronic systemic inflammation which drives the development of comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes and non-AIDS associated malignancies. “Mortality among individuals co-infected with HIV and hepatitis C virus (HCV) is relatively high. We evaluated the association between psychoactive substance use and both HCV and non-HCV mortality in HIV/HCV co-infected patients in France, using Fine and Gray’s competing-risk model adjusted for socio-demographic, clinical predictors and confounding factors, while accounting for competing causes of death. Over a 5-year median follow-up period, 77 deaths occurred among 1028 patients.
“Mortality among individuals co-infected with HIV and hepatitis C virus (HCV) is relatively high. We evaluated the association between psychoactive substance use and both HCV and non-HCV mortality in HIV/HCV co-infected patients in France, using Fine and Gray’s competing-risk model adjusted for socio-demographic, clinical predictors and confounding factors, while accounting for competing causes of death. Over a 5-year median follow-up period, 77 deaths occurred among 1028 patients.
